Chlorsulfuron
Synonym(s):1-(2-Chlorophenylsulfonyl)-3-(4-methoxy-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-urea;Chlorsulfuron
- CAS NO.:64902-72-3
- Empirical Formula: C12H12ClN5O4S
- Molecular Weight: 357.77
- MDL number: MFCD00128059
- EINECS: 265-268-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-07-02 08:55:17
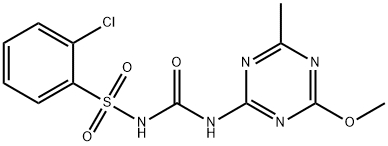
What is Chlorsulfuron?
Description
Chlorsulfuron is one of the first sulfonylurea herbicides
developed and commercialized by DuPont. Dr George Levitt
and his team at DuPont first synthesized chlorsulfuron in 1976,
and it was commercialized for use as a herbicide in 1981. It is
currently registered by DuPont in the United States, Canada,
the European Union, Russia, the Ukraine, Australia, New
Zealand, South Africa, Saudi Arabia, and in several countries of
South America.
Compared with many other herbicides that are applied at
levels of pounds per acre (or kilograms per acre), sulfonylureas
are highly effective at use rates of less than an ounce per acre
(approximately 6 g per acre for chlorsulfuron).
Chemical properties
Colorless, odorless crystals
The Uses of Chlorsulfuron
Chlorsulfuron is used as a postemergence herbicide for the control of dicotyledonous weeds, with excellent safety for wheat and other cereals crops. While chlorsulfuron is primarily used to control weeds in cereals, it can also be used in range and pasture applications. It is currently only used to a minor extent for nonfood industrial applications and right-of-way purposes.
The Uses of Chlorsulfuron
Triazine urea herbicide used to control broad-leaved weeds and some annual grass weeds.
Definition
ChEBI: Chlorsulfuron is an N-sulfonylurea that is N-carbamoyl-2-chlorobenzenesulfonamide in which one of the hydrogens attached to the non-sulfonylated nitrogen has been replaced by a 4-methoxy-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl group. A herbicide used for the control of broadleaf weeds in wheat, barley and oats. It has a role as an agrochemical, a herbicide and an EC 2.2.1.6 (acetolactate synthase) inhibitor. It is a N-sulfonylurea, a member of monochlorobenzenes and a methoxy-1,3,5-triazine.
General Description
Colorless crystals. Non corrosive. Insoluble in water. Used as an herbicide.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water. Reacts slowly with water. The reaction is promoted by acid such that the pH is less than 5.0 (1/2 life of 24-48 hrs.). Reaction is also promoted by polar organic solvents such as methanol and acetone.
Agricultural Uses
Herbicide: A selective systemic herbicide used to control most broadleaf weeds and some annual grasses in wheat, barley, oats, duram, rye, triticale and flax. Applied to non-crop sites such as rights-of-way, fence rows and roadsides.
Trade name
DPX 4189®; FINESSE®; GLEAN®; GLEAN 20DF®; LANDMARK® MP; LASHER®; RIVERDALE CORSAIR®; TELAR® DF
Potential Exposure
A selective systemic sulfonylurea herbicide used to control most broadleaf weeds and some annual grasses in wheat, barley, oats, duram, rye, triticale, and flax. Applied to noncrop sites such as rights-of-way, fence rows, and roadsides.
Environmental Fate
Soil. Degrades in soil via hydrolysis followed by microbial degradation forming low
molecular weight, inactive compounds. The estimated half-life was reported to range from
4 to 6 weeks (Hartley and Kidd, 1987; Cremlyn, 1991). Microorganisms capable of
degrading chlorsulfuron are Aspergillis niger, Streptomyces griseolus and Penicillium sp.
(Humburg et al., 1989). One transformation product reported in field soils is 2-chlorobenzenesulfonamide (Smith, 1988)
The reported dissipation rate of chlorsulfuron in surface soil is 0.024/day (Walker and
Brown, 1983). The persistence of chlorsulfuron decreased when soil temperature and
moisture were increased (Walker and Brown, 1983; Thirunarayanan et al., 1985)
Plant. Chlorsulfuron is metabolized by plants to hydroxylated, nonphytotoxic compounds including 2-chloro-N-(((4-methoxy-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-amino)carbonyl)benzenesulfonamide (Duke et al., 1991). Devine and Born (1985) and Peterson and
Photolytic. The reported photolysis half-lives of chlorsulfuron in distilled water, methanol and natural creek water at λ >290 nm were 18, 92 and 18 hours, respectively. In all
cases, 2-chlorobenzene sulfonamide, 2-methoxy-4-methyl-6-amino-1,3,5-triazine and
trace amounts of the tentatively identified compound nitroso-2-chlorophenylsulfone
formed as photoproducts (Herrmann et al., 1985).
Metabolic pathway
Chlorsulfuron is metabolized in wheat and in tolerant broadleaves via different pathways where hydroxylation occurs on the methyl group of the triazine ring and at the phenyl ring of the chlorsulfuron in respective plants. With chemical degradation of chlorsulfuron on dry minerals (Syst.), two pathways of degradation are observed, one of which is direct
Shipping
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required.
Toxicity evaluation
Chlorsulfuron has a moderate to short-lived fate in the environment. It does not bioaccumulate and is not volatile. In the environment, chlorsulfuron degrades via a combination of biotic and abiotic processes. Chlorsulfuron degrades in acidic solutions and soil by cleavage of the sulfonylurea bridge, Odemethylation, and hydroxylation. Chlorsulfuron is metabolized by soil microbes to numerous minor degradation products, is mineralized to CO2, and sequestered as nonextractable residues. Photodegradation is not a significant pathway of dissipation for chlorsulfuron in the environment. Hydrolytic processes are not expected to be a major contributing factor in the environmental degradation of chlorsulfuron, and would only be significant at acidic pH.
Incompatibilities
Slowly hydrolyzes in water, releasing ammonia and forming acetate salts. May bencompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides.
Waste Disposal
It is the responsibility of chemical waste generators to determine the toxicity and physical properties and of a discarded chemical and to properly identify its classification and certification as a hazardous waste and to determine the disposal method. United States Environmental Protection Agency guidelines for the classification determination are listed in 40 CFR Parts 261.3. In addition, waste generators must consult and follow all regional, national, state, and local hazardous waste laws to ensure complete and accurate classification and disposal methods. Recycle any unused portion of the material for its approved use or return it to the manufacturer or supplier. Ultimate disposal of the chemical must consider: the material’s impact on air quality; potential migration in soil or water; effects on animal, aquatic, and plant life; and conformance with environmental and public health regulations
Properties of Chlorsulfuron
| Melting point: | 174-178°C |
| Density | 1.6111 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5630 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| pka | 4.21±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| form | neat |
| color | White to off-white |
| Merck | 13,2210 |
| BRN | 577255 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 64902-72-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Chlorsulfuron(64902-72-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Chlorsulfuron (64902-72-3) |
Safety information for Chlorsulfuron
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Chlorsulfuron
New Products
4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium SODIUM AAS SOLUTION ZINC AAS SOLUTION BUFFER SOLUTION PH 10.0(BORATE) GOOCH CRUCIBLE SINTERED AQUANIL 5 BERYLLIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Chlorosulfuron CAS 64902-72-3View Details
Chlorosulfuron CAS 64902-72-3View Details
64902-72-3 -
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4