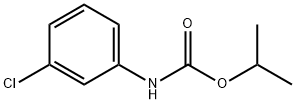
Chlorpropham
Synonym(s):Chloro-ICP;Chloropropham;Isopropyl N-(3-chlorophenyl)carbamate
- CAS NO.:101-21-3
- Empirical Formula: C10H12ClNO2
- Molecular Weight: 213.66
- MDL number: MFCD00037108
- EINECS: 202-925-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-11-18 17:49:23
What is Chlorpropham?
Chemical properties
beige to brown solid
The Uses of Chlorpropham
Chlorpropham is particularly useful in agricultural settings. It is used in pesticide products for treatment of plants and soil.
The Uses of Chlorpropham
Herbicide; plant growth regulator.
The Uses of Chlorpropham
Preemergent and postemergent herbicide used to regulate plant growth and control of weeds in carrot, onion, garlic and other crops
Definition
ChEBI: A carbamate ester that is the isopropyl ester of 3-chlorophenylcarbamic acid.
General Description
Brown chunky solid.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Chlorpropham is a carbamate ester. Carbamates are chemically similar to, but more reactive than amides. Like amides they form polymers such as polyurethane resins. Carbamates are incompatible with strong acids and bases, and especially incompatible with strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is produced by the combination of active metals or nitrides with carbamates. Strongly oxidizing acids, peroxides, and hydroperoxides are incompatible with carbamates.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Chlorpropham are not available, however Chlorpropham is probably combustible.
Agricultural Uses
Herbicide, Plant growth regulator: Chlorpropham is a plant growth regulator that is used primarily in the U.S. to inhibit post-harvest potato sprouting. Other uses include pre-emergence control of grass weeds in alfalfa, beans, blueberries, cane berries, carrots, cranberries, ladino clover, garlic, seed grass, onions, spinach, sugar beets, tomatoes, safflower, soybeans, gladioli and woody nursery stock. It is used to control suckers in tobacco
Trade name
ATLAS® CIPC 40; BEET-KLEEN® (with Fenuron® and isopropyl carbanilate); BUDNIP®; CAMPBELL’S® CIPC 40%; CHLORO IPC®; ELBANIL®; FASCO® WY-HOE; FURLOE®; FURLOE® 4EC; JACK WILSON® CHLORO 51 (OIL); LIRO METOXON®; MIRVALE®; MORCRAN® (with n-1-naphthylphthalamic acid); MSS® CICP; NEXOVAL®; PREVENOL® 56; PREVENTOL®; PREVENTOL® 56; PREWEED®; RESIDUREN®; RESIDUREN® EXTRA; SPROUT NIP®; SPROUT-NIP® EC; SPUDNIC®; SPUD-NIE®; STOPGERME®-S; TATERPEX®; TRIPEC® (with carbamic acid, phenyl-, 1-methylethyl ester); TRIHERBICIDE® CIPC; UNICROP® CIPC; WAREFOG®; Y3®
Environmental Fate
Soil. Hydrolyzes in soil forming 3-chloroaniline (Bartha, 1971; Hartley and Kidd,
1987; Smith, 1988; Rajagopal et al., 1989). In soil, Pseudomonas striata Chester, a
Flavobacterium sp., an Agrobacterium sp. and an Achromobacter sp. readily degraded
chlorpropham to 3-chloroaniline and 2-propanol. Subsequent degradation by enzymatic
hydrolysis yielded carbon dioxide, chloride ions and unidentified compounds (Kaufman,
1967; Rajagopal et al., 1989). Hydrolysis products that may form in soil and in microbial
cultures include N-phenyl-3-chlorocarbamic acid, 3-chloroaniline, 2-amino-4-chlorophenol, monoisopropyl carbonate, 2-propanol, carbon dioxide and condensation products
(Rajagopal et al., 1989). The reported half-lives in soil at 15 and 29°C are 65 and 30 days,
respectively (Hartley and Kidd, 1987)
Plant. Chlorpropham is rapidly metabolized in plants (Ashton and Monaco, 1991).
Metabolites identified in soybean plants include isopropyl-N-4-hydroxy-3-chlorophenylcarbamate, 1-hydroxy-2-propyl-3′-chlorocarbanilate and isopropyl-N-5-chloro-2-hy
Photolytic. The photodegradation rate of chlorpropham in aqueous solution was
enhanced in the presence of a surfactant (TMN-10) (Tanaka et al., 1981). In a later study,
Tanaka et al. (1985) studied the photolysis of chlorpropham (50 mg/L) in aque
Chemical/Physical. Emits toxic phosgene fumes when heated to decomposition (Sax
and Lewis, 1987). In a 0.50 N sodium hydroxide solution at 20°C, chlorpropham was
hydrolyzed to aniline derivatives. The half-life of this reaction was 3.5 days (El-Dib and
Aly, 1976). Simple hydrolysis leads to the formation of 3-chlorophenylcarbamic acid and
2-propanol. The acid is very unstable and is spontaneously converted to 3-chloroaniline
and carbon dioxide (Still and Herrett, 1976)
Properties of Chlorpropham
| Melting point: | 41°C |
| Boiling point: | 247°C |
| Density | 1.18 |
| refractive index | nD20 1.5388 |
| Flash point: | 247°C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | crystalline |
| pka | 13.06±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | light tan |
| Odor | faint char. odor |
| Water Solubility | 0.009 g/100 ml very poor |
| Decomposition | 247 ºC |
| Merck | 14,2187 |
| BRN | 2211397 |
| Exposure limits | An experimental carcinogen and neoplastigen |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong acids, strong bases, strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 101-21-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 12, Sup 7) 1987 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Chlorpropham(101-21-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Chlorpropham (101-21-3) |
Safety information for Chlorpropham
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H351:Carcinogenicity H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Chlorpropham
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Chlorpropham CAS 101-21-3View Details
Chlorpropham CAS 101-21-3View Details
101-21-3 -
 Chlorpropham 98.00% CAS 101-21-3View Details
Chlorpropham 98.00% CAS 101-21-3View Details
101-21-3 -
 Chlorpropham CAS 101-21-3View Details
Chlorpropham CAS 101-21-3View Details
101-21-3 -
 Chlorpropham CAS 101-21-3View Details
Chlorpropham CAS 101-21-3View Details
101-21-3 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4
