Chidamide
- CAS NO.:743420-02-2
- Empirical Formula: C22H19FN4O2
- Molecular Weight: 390.41
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
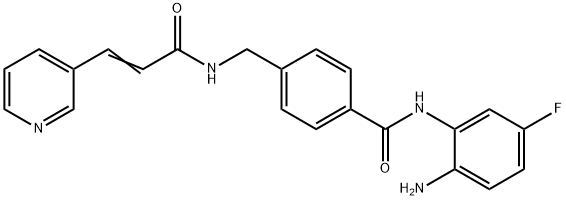
What is Chidamide?
Description
Chidamide (Epidaza®), a class I HDAC inhibitor, was discovered and developed by ChipScreen and approved by the CFDA in December 2014 for the treatment of recurrent of refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Chidamide, also known as CS055 and HBI- 8000, is an orally bioavailable benzamide type inhibitor of HDAC isoenzymes class I 1–3, as well as class IIb 10, with potential antineoplastic activity. It selectively binds to and inhibits HDAC, leading to an increase in acetylation levels of histone protein H3.74 This agent also inhibits the expression of signaling kinases in the PI3K/ Akt and MAPK/Ras pathways and may result in cell cycle arrest and the induction of tumor cell apoptosis. Currently, phases I and II clinical trials are underway for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer and for the treatment of breast cancer, respectively.
The Uses of Chidamide
De-5-fluoro 4-Fluorochidamide is an analogue of Chidamide (CAS 743420-02-0), a hitsone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACI) that enhances gemcitabine (G305000) cytotoxicity in pancreatic cancer cells.
What are the applications of Application
Chidamide is an HDAC inhibitor
Synthesis
The scalable synthetic approach to chidamide very closely follows the discovery route. The sequence began with the condensation of commercial nicotinaldehyde (52) and malonic acid (53) in a mixture of pyridine and piperidine. Next, activation of acid 54 with N,N0-carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) and subsequent reaction with 4-aminomethyl benzoic acid (55) under basic conditions afforded amide 56 in 82% yield. Finally, activation of 56 with CDI prior to treatment with 4-fluorobenzene- 1,2-diamine (57) and subsequent treatment with TFA and THF yielded chidamide (VIII) in 38% overall yield from 52. However, no publication reported that mono-N-Boc-protected bis-aniline was used to approach Chidamide.

References
[1] gong k, xie j, yi h, li w. cs055 (chidamide/hbi-8000), a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor, induces g1 arrest, ros-dependent apoptosisand differentiation in human leukaemia cells. biochem j. 2012 may 1;443(3):735-46.
[2] wang h1, guo y, fu m, liang x, etal. , antitumor activity of chidamide in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. mol med rep. 2012 jun;5(6):1503-8.
Properties of Chidamide
| Melting point: | >145°C (dec.) |
| Boiling point: | 600.2±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.336±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C(protect from light) |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly, Sonicated) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 12.30±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | Off-White to Pale Beige |
Safety information for Chidamide
Computed Descriptors for Chidamide
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Chidamide 95% CAS 743420-02-2View Details
Chidamide 95% CAS 743420-02-2View Details
743420-02-2 -
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4