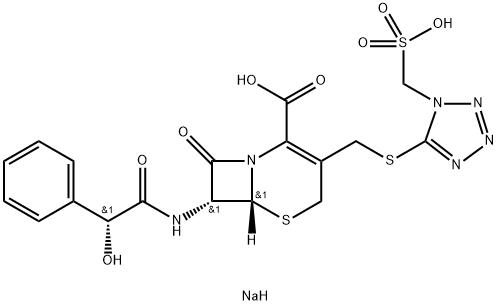
Cefonicid
- CAS NO.:61270-58-4
- Empirical Formula: C18H18N6O8S3
- Molecular Weight: 542.57
- MDL number: MFCD00865008
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-28 16:48:35

What is Cefonicid?
Description
Cefonicid has an unesterified D-mandelic acid moiety at C-7 and a methylsulfothiotetrazole group at C-3. The latter is related to the MTT moiety mentioned above under cefamandole nafate; however, the clotting problems and Antabuse-like side effects associated with MTT have not been reported with cefonicid. The extra acid group in the C-3 side chain leads to this molecule being sold as an injectable disodium salt. Pain and discomfort at IM sites is experienced by some patients, as is a burning sensation and phlebitis. Cefonicid has a longer half-life than the other members of its group but achieves this at the price of somewhat lower potency against Gram-positive bacteria and aerobes. The drug is somewhat unstable, needs to be protected from light and heat, and may yellow or darken. If modest, however, this does not necessarily mean that the potency has decreased significantly, but overt precipitation does. Kirby-Bauer disk testing may overestimate the sensitivity of β-lactamase–producing bacteria to this agent, so some extra caution in interpretation of laboratory results is required.
The Uses of Cefonicid
A semi-synthetic cephalosporin antibiotic related to Cefamandole. Antibacterial
Background
A second-generation cephalosporin administered intravenously or intramuscularly. Its bactericidal action results from inhibition of cell wall synthesis. It is used for urinary tract infections, lower respiratory tract infections, and soft tissue and bone infections.
Indications
For the treatment of bacterial infections caused by susceptible microorganisms.
Definition
ChEBI: A cephalosporin bearing {[1-(sulfomethyl)-1H-tetrazol-5-yl]sulfanyl}methyl and (R)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetamido groups at positions 3 and 7, respectively, of the cephem skeleton.
Antimicrobial activity
Activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms
in vitro is depressed by the presence of 50% serum. It is highly
bound to plasma protein (98%) and has an extended plasma
half-life of 4.5–5 h. A 1 g intramuscular dose achieves a mean
peak plasma concentration of around 83 mg/L. Following a
1 g intravenous bolus dose, mean peak plasma concentrations
of 130–300 mg/L have been reported. In patients treated for
community-acquired pneumonia, concentrations of 2–4 mg/L
have been found in sputum.
It is predominantly excreted by renal secretion, 83–89%
being recovered unchanged in the urine over 24 h. Plasma
half-life is linearly related to creatinine clearance. As a
result of its high protein binding it is not removed by
hemodialysis.
It is generally well tolerated; pain on injection, rash and
positive Coombs’ test are reported in some patients. It has
been used to treat respiratory, soft tissue and urinary infections.
Available in Italy.
Pharmacokinetics
Cefonicid is a second-generation cephalosporin administered intravenously or intramuscularly. Its bactericidal action results from inhibition of cell wall synthesis. It is used for urinary tract infections, lower respiratory tract infections, and soft tissue and bone infections.
Synthesis
Cefonicid, 7-D-mandelamido-3-[[(1-sulfomethyl]-1H-tetrazol-5-yl]thio] methyl]- 8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-en-2-carboxylic acid (32.1.2.26), is structurally similar to cefamandole and differs in the presence of a sulfonic acid group in the methyl substituent of the tetrazol ring. It is synthesized by a method analogous to that of the synthesis of cefamandole.
Metabolism
Not metabolized.
Properties of Cefonicid
| Density | 1.92±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| pka | -1.23±0.50(Predicted) |
Safety information for Cefonicid
Computed Descriptors for Cefonicid
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1