Carvedilol
Synonym(s):1-(9H-Carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-[[2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl]amino]-2-propanol;BM-14190;Carvedilol
- CAS NO.:72956-09-3
- Empirical Formula: C24H26N2O4
- Molecular Weight: 406.47
- MDL number: MFCD00864692
- EINECS: 1308068-626-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-08-20 16:56:25
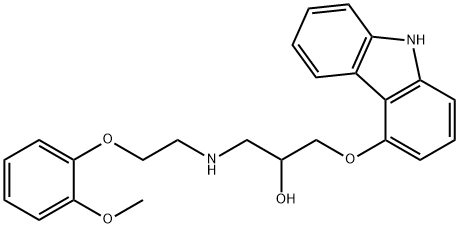
What is Carvedilol?
Absorption
Carvedilol has a bioavailability of 25-35%. Carvedilol has a Tmax of 1 to 2 hours. Taking carvedilol with a meal increases Tmax without increasing AUC. Carvedilol doses of 50mg lead to a Cmax of 122-262μg/L and an AUC of 717-1600μg/L*h. Carvedilol doses of 25mg lead to a Cmax of 24-151μg/L and an AUC of 272-947μg/L*h. Carvedilol doses of 12.5mg lead to a Cmax of 58-69μg/L and an AUC of 208-225μg/L*h.
Toxicity
Patients experiencing an overdose may present with hypotension, bradycardia, cardiac insufficiency, cardiogenic shock, and cardiac arrest. Patients should remain in a supine position and may be given atropine for bradycardia and glucagon followed by sympathomimetics to support cardiovascular function.
Description
Carvedilol is a vasodilating beta-blocker useful in the treatment of hypertension and angina pectoris. In addition to lowering blood pressure, carvedilol decreases total vascular resistance without the reflex tachycardia usually occurring with vasodilators. It is reported to be well tolerated with renal sparing effects.
Description
Carvedilol (Item No. 26286) is an analytical reference standard categorized as a β-adrenergic receptor antagonist and vasodilator. Formulations containing carvedilol have been used to enhance physical performance in athletes. This product is intended for use in analytical forensic applications. This product is also available as a general research tool .
Chemical properties
Colourless Crystalline Solid
Originator
Boehringer Mannheim (Germany)
The Uses of Carvedilol
Carvedilol is a nonselective β-adrenergic blocker with α1-blocking activity. Carvedilol is an antihypertensive used in the treatment of congestive heart failure.
The Uses of Carvedilol
A nonselective -adrenergic blocker with a1-blocking activity. An antihypertensive used in the treatment of congestive heart failure.
The Uses of Carvedilol
antibacterial
The Uses of Carvedilol
veterinary use
The Uses of Carvedilol
For the treatment of mild or moderate (NYHA class II or III) heart failure of ischemic or cardiomyopathic origin.
The Uses of Carvedilol
An α1- and β-adrenergic receptor antagonist.
Indications
Carvedilol is indicated to treat mild to severe heart failure, left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction with ventricular ejection fraction ≤40%, or hypertension.
Background
Carvedilol is a racemic mixture where the S(-) enantiomer is both a beta and alpha-1 adrenoceptor blocker, and the R(+) enantiomer is an alpha-1 adrenoceptor blocker. It is currently used to treat heart failure, left ventricular dysfunction, and hypertension. The dual action of carvedilol is advantageous in combination therapies as moderate doses of 2 drugs have a decreased incidence of adverse effects compared to high dose monotherapy in the treatment of moderate hypertension.
Carvedilol was granted FDA approval on 14 September 1995.
What are the applications of Application
Carvedilol is an α1- and β-adrenergic receptor antagonist
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of carbazoles that is an adrenergic antagonist with non-selective beta- and alpha-1 receptor blocking properties which helps in the management of congestive heart failure.
Manufacturing Process
1-(9H-Carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-((2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl)amino)-2-propanol
may be synthesized by the method of preparation of S-(-)-(1-carbazol-4-
yloxy)-3-[2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)]ethylaminopropan-2-ol (Patent US
4,697,022 and 4,824,963).
27.5 g 4-hydroxycarbazole are dissolved in a mixture of 150 ml 1 N aqueous
sodium hydroxide solution and 70 ml dimethylsulfoxide. To this is added at
ambient temperature 13.9 g epichlorohydrin, followed by stirring for 18 hours
at ambient temperature. 280 ml water are then added thereto, followed by
stirring for 15 min and filtering off with suction. The filter residue is washed
with 0.1 N aqueous sodium hydroxide solution and water and subsequently
dissolved in methylene chloride. The methylene chloride solution is dried over
anhydrous sodium sulfate, treated with active charcoal and floridin and
evaporated. 4-(2,3-Epoxypropoxy)-carbazole is purified by recrystallising twice
from ethyl acetate. From the mother liquors there are isolated a further 4-
(2,3-epoxypropoxy)-carbazole.
10 g 4-(2,3-epoxypropoxy)-carbazole are, together with 13.97 g o-methoxyphenoxyethylamine, heated under reflux in 70 ml isopropanol for 2
hours. The solvent is evaporated off and the residue is stirred for 2 hours with
a mixture of 115 ml toluene, 35 ml cyclohexane and 40 ml ethyl acetate.
After filtering off with suction, the (1-carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-[2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)]-ethylaminopropan-2-ol is recrystallised from 150 ml ethyl
acetate.
brand name
Coreg (GlaxoSmithKline);Dilatrend.
Therapeutic Function
Beta-adrenergic blocker
General Description
Carvedilol (Coreg) is a β-blocker that hasa unique pharmacological profile. Like labetalol, it is aβ-blocker that possesses α1-blocking activity. Only the(S) enantiomer possesses the β-blocking activity, althoughboth enantiomers are blockers of the α1-receptor. Overall,its β-blocking activity is 10- to 100-fold of its α-blocking activity.
Biological Activity
Potent β -adrenoceptor and α 1 -adrenoceptor antagonist (K i values are 0.81, 0.96 and 2.2 nM for β 1 -, β 2 - and α 1 -adrenoceptors respectively) that displays antihypertensive and peripheral vasodilatory activity. Blocks cardiac inward-rectifier K + (K IR ) channels, voltage-dependent Ca 2+ channels and exhibits antioxidant properties at higher concentrations.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Cavedilol is a non-selective β-adrenergic blocker with α1 blocking activity. Carvedilol is used specifically for the treatment of heart failure and high blood pressure. It has been shown to improve left ventricular ejection fraction and may reduce mortality.
Pharmacokinetics
Carvedilol reduces tachycardia through beta adrenergic antagonism and lowers blood pressure through alpha-1 adrenergic antagonism. It has a long duration of action as it is generally taken once daily and has a broad therapeutic index as patients generally take 10-80mg daily. Patients taking carvedilol should not abruptly stop taking this medication as this may exacerbate coronary artery disease.
Clinical Use
Carvedilol is also unique in that it possesses antioxidantactivity and an antiproliferative effect on vascular smoothmuscle cells. It thus has a neuroprotective effect and the abilityto provide major cardiovascular organ protection. It isused in treating hypertension and congestive heart failure.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Carvedilol may be useful as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of heart failure (dilated cardiomyopathy) in dogs. There is a fair amount of controversy at present among veterinary cardiologists as to whether this drug will find a therapeutic niche.
in vitro
carvedilol potently inhibited fe2+-initiated lipid peroxidation in rat brain homogenate with an ic50 of 8.1 μm. in rat brain homogenate, carvedilol protected against fe2+-induced α-tocopherol depletion with an ic50 of 17.6 μm. carvedilol dose-dependently decreased the intensity of the dmpo-oh signal, with an ic50 of 25 μm [1]. carvedilol prevented vascular smooth muscle cell migration, proliferation, and neointimal formation following vascular injury. in human cultured pulmonary artery vascular smooth muscle cells, carvedilol (0.1-10 μm) concentration-dependently inhibited the mitogenesis stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor, epidermal growth factor, thrombin, and serum, with ic50 values ranging from 0.3 to 2.0 μm. carvedilol concentration-dependently inhibited vascular smooth muscle cell migration induced by platelet-derived growth factor with an ic50 value of 3 μm [3].
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anaesthetics: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Analgesics: NSAIDs antagonise hypotensive effect.
Anti-arrhythmics: increased risk of myocardial
depression and bradycardia; increased risk of
bradycardia, myocardial depression and AV block
with amiodarone; increased risk of myocardial
depression and bradycardia with flecainide.
Antibacterials: concentration reduced by rifampicin.
Antidepressants: enhanced hypotensive effect with
MAOIs.
Antihypertensives; enhanced hypotensive effect;
increased risk of withdrawal hypertension with
clonidine; increased risk of first dose hypotensive
effect with post-synaptic alpha-blockers such as
prazosin.
Antimalarials: increased risk of bradycardia with
mefloquine.
Antipsychotics enhanced hypotensive effect with
phenothiazines.
Calcium-channel blockers: increased risk of
bradycardia and AV block with diltiazem;
hypotension and heart failure possible with
nifedipine and nisoldipine; asystole, severe
hypotension and heart failure with verapamil.
Ciclosporin: increased trough concentration, reduce
dose by 20% in affected patients.
Cytotoxics: possible increased risk of bradycardia
with crizotinib.
Diuretics: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Fingolimod: possibly increased risk of bradycardia.
Moxisylyte: possible severe postural hypotension.
Sympathomimetics: severe hypertension with
adrenaline and noradrenaline and possibly with
dobutamine.
Metabolism
Carvedilol can be hydroxlated at the 1 position by CYP2D6, CYP1A2, or CYP1A1 to form 1-hydroxypheylcarvedilol; at the 4 position by CYP2D6, CYP2E1, CYP2C9, or CYP3A4 to form 4'-hydroxyphenylcarvedilol; at the 5 position by CYP2D6, CYP2C9, or CYP3A4 to form 5'-hydroxyphenylcarvedilol; and at the 8 position by CYP1A2, CYP3A4, and CYP1A1 to form 8-hydroxycarbazolylcarvedilol. Carvedilol can also be demethylated by CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP1A2, or CYP2E1 to form O-desmethylcarvedilol. Carvedilol and its metabolites may undergo further sulfate conjugation or glucuronidation before elimination. Carvedilol can be O-glucuronidated by UGT1A1, UGT2B4, and UGT2B7 to form carvedilol glucuronide.
Metabolism
Carvedilol is subject to considerable first-pass metabolism in the liver; the absolute bioavailability is about 25%. It is extensively metabolised in the liver, primarily by the cytochrome P450 isoenzymes CYP2D6 and CYP2C9, and the metabolites are excreted mainly in the bile.
Storage
Store at +4°C
Properties of Carvedilol
| Melting point: | 113-117°C |
| Boiling point: | 655.2±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.250±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: >20mg/mL |
| form | solid |
| pka | 13.90±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | white to off-white |
| Water Solubility | 449.2ug/L(22.5 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,1873 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 72956-09-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Carvedilol
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Carvedilol
Carvedilol manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 72956-09-03 Carvedilol 98%View Details
72956-09-03 Carvedilol 98%View Details
72956-09-03 -
 CARVEDILOL 99%View Details
CARVEDILOL 99%View Details -
 Carvedilol 99%View Details
Carvedilol 99%View Details -
 CARVEDILOL BP/EP/USP 99%View Details
CARVEDILOL BP/EP/USP 99%View Details -
 Carvedilol 98%View Details
Carvedilol 98%View Details -
 72956-09-3 Carvedilol 98%View Details
72956-09-3 Carvedilol 98%View Details
72956-09-3 -
 72956-09-3 98%View Details
72956-09-3 98%View Details
72956-09-3 -
 Carvedilol 98% CAS 72956-09-3View Details
Carvedilol 98% CAS 72956-09-3View Details
72956-09-3
