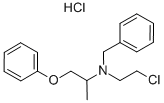
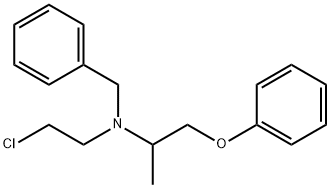
phenoxybenzamine
- CAS NO.:59-96-1
- Empirical Formula: C18H22ClNO
- Molecular Weight: 303.83
- MDL number: MFCD00599580
- EINECS: 2004468
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-09 14:49:17
What is phenoxybenzamine?
Absorption
Twenty to 30 percent of orally administered phenoxybenzamine appears to be absorbed in the active form.
Toxicity
Symptoms of overdose are largely the result of block of the sympathetic nervous system and of the circulating epinephrine. They may include postural hypotension resulting in dizziness or fainting, tachycardia, particularly postural, vomiting; lethargy, and shock.
Originator
Dibenzyline, SKF, US ,1953
The Uses of phenoxybenzamine
Antihypertensive.
Background
An alpha-adrenergic antagonist with long duration of action. It has been used to treat hypertension and as a peripheral vasodilator.
Indications
For the treatment of phaeochromocytoma (malignant), benign prostatic hypertrophy and malignant essential hypertension.
Definition
ChEBI: Phenoxybenzamine is an aromatic amine.
Manufacturing Process
Step 1: In a 500 ml flask equipped with gas inlet tube, dropping funnel and reflux condenser is placed 139 grams of 1-phenoxy-2-propanol. A stream of dry air is bubbled through the alcohol while 55 grams of thionyl chloride is added dropwise with external cooling. The stream of dry air is continued for about six hours or until most of the hydrogen chloride has been expelled and then another 55 grams of thionyl chloride is added. The reaction mixture is allowed to stand twenty-four hours, a few drops of pyridine are added and the mixture heated 4 hours on the steam bath. The cooled reaction mixture is poured into water, the crude product is washed with dilute sodium bicarbonate solution and finally taken up in benzene. The benzene is distilled at ordinary pressure and the residue distilled in vacuo to yield 60-70% of 1-phenoxy-2chloropropane, BP 93°-94°C/5 mm.
Step 2: To 494 grams of ethanolamine, heated to approximately 150°C in a 500 ml flask equipped with stirrer, condenser and dropping funnel, is added 465 grams of 1-phenoxy-2-chloropropane with mechanical stirring. The reaction mixture is then heated to reflux for 3 hours, cooled and poured into a liter of water. The organic layer is extracted into ether and the ether solution is extracted with dilute hydrochloric acid. The aqueous acid solution is then made alkaline with 40% sodium hydroxide solution and the organic base is extracted into ether. Removal of the ether leaves N-(phenoxyisopropyl)ethanolamine which, after recrystallization from hexane, melts at 70.5°-72°C.
Step 3: To 43 grams of N-(phenoxyisopropyl)ethanolamine dissolved in 500 ml of alcohol in a 1,000 ml flask equipped with stirrer and condenser is added 28 grams of benzyl chloride and 18.5 grams of sodium bicarbonate. The mixture is stirred and refluxed for 10 hours and then approximately half the alcohol is removed by distillation. The remaining solution is poured into 500 ml of water and the organic material extracted with 3 100-ml portions of ether. The combined ether extracts are washed with water, dried over anhydrous potassium carbonate and filtered. After removal of the ether, the residue is distilled in vacuo to yield N-(phenoxyisopropyl)-Nbenzylethanolamine, BP 163°-168°C/0.2 mm.
Step 4: A solution of 20 grams of the above amino alcohol is dissolved in 50 ml of dry chloroform and treated with dry hydrogen chloride until acid. Then a solution of 9 grams of thionyl chloride in 50 ml of dry chloroform is added and the reaction mixture is heated on a water bath at 50°-60°C for 2 hours. Most of the chloroform is removed by distillation under reduced pressure. Addition of ether to the residue causes the product to crystallize. After recrystallization from a mixture of alcohol and ether, the N-(phenoxyisopropyl)-N-benzyl-βchloroethylamine hydrochloride melts at 137.5°-140°C.
brand name
Dibenzyline (WellSpring);Dibenzyran.
Therapeutic Function
Adrenergic blocker
World Health Organization (WHO)
Phenoxybenzamine, a long-acting alpha-adrenoreceptor antagonist, was introduced in 1953 and has been used in a variety of peripheral vascular disorders. In 1982 it was shown to have mutagenic activity and in 1985 it was found to be carcinogenic in the rat. Its approved use was subsequently restricted by several regulatory authorities and phenoxybenzamine is currently used to manage hypertensive episodes associated with phaeochromocytoma, as an adjunct to the short-term management of urinary retention due to neurogenic bladder, in the short-term treatment of benign prostatic hypertrophy in patients awaiting surgery, and in inoperable benign prostatic hypertrophy.
Pharmacokinetics
Phenoxybenzamine is indicated for the control of episodes of hypertension and sweating that occur with a disease called pheochromocytoma. If tachycardia is excessive, it may be necessary to use a beta-blocking agent concomitantly. Phenoxybenzamine is a long-acting, adrenergic, alpha-receptor blocking agent which can produce and maintain "chemical sympathectomy" by oral administration. It increases blood flow to the skin, mucosa and abdominal viscera, and lowers both supine and erect blood pressures. It has no effect on the parasympathetic system. Phenoxybenzamine works by blocking alpha receptors in certain parts of the body. Alpha receptors are present in the muscle that lines the walls of blood vessels. When the receptors are blocked by Phenoxybenzamine, the muscle relaxes and the blood vessels widen. This widening of the blood vessels results in a lowering of blood pressure.
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic and neoplastigenic data. Poison by intravenous and intracerebral routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion. Human reproductive effects by ingestion: spermatogenesis. Experimental reproductive effects. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of Cland NOx.
Metabolism
Not Available
Purification Methods
The free base is crystallised from pet ether, and the HCl is crystallised from EtOH/diethyl ether. [Beilstein 12 IV 2204.]
Properties of phenoxybenzamine
| Melting point: | 38-40° |
| Boiling point: | 381.5±27.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.0513 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5600 (estimate) |
| pka | 6.58±0.50(Predicted) |
| color | Crystals from pet ether |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 59-96-1 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | N-(2-Chloroethyl)-N-(1-methyl-2-phenoxyethyl)benzenemethanamine (59-96-1) |
Safety information for phenoxybenzamine
Computed Descriptors for phenoxybenzamine
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 59-96-1 98%View Details
59-96-1 98%View Details
59-96-1 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8