Candesartan cilexetil
Synonym(s):2-ethoxy-1-[[2′-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]-1H-Benzimidazole-7-carboxylic acid 1-[[(cyclohexyloxy)carbonyl]oxy]ethyl ester;Candesartan cilexetil;TCV 116;TCY 116
- CAS NO.:145040-37-5
- Empirical Formula: C33H34N6O6
- Molecular Weight: 610.66
- MDL number: MFCD00871371
- EINECS: 627-030-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 13:58:55
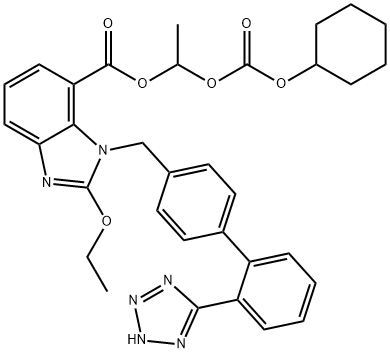
What is Candesartan cilexetil ?
Absorption
Following administration of the candesartan cilexetil prodrug, the absolute bioavailability of candesartan was estimated to be 15%. Food with a high fat content has no effect on the bioavailability of candesartan from candesartan cilexetil.
Toxicity
No lethality was observed in acute toxicity studies in mice, rats and dogs given single oral doses of up to 2000 mg/kg of candesartan cilexetil or in rats given single oral doses of up to 2000 mg/kg of candesartan cilexetil in combination with 1000 mg/kg of hydrochlorothiazide. In mice given single oral doses of the primary metabolite, candesartan, the minimum lethal dose was greater than 1000 mg/kg but less than 2000 mg/kg.
Description
Candesartan cilexetil is a prodrug form of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1) antagonist candesartan . Atacand was launched in Australia, Belgium, Canada, Denmark, Finland, the Netherlands, Norway, Sweden, S. Africa and the US as an antihypertensive agent. Pharmacological studies have indicated Atacand is about 10-fold more potent than Losartan and has a long elimination half-life. Like losartan, Atacand is converted to its active form during GI absorption (via ester hydrolysis). It is a potent antagonist of angiotensin II type 1 receptors. This occurs through tight binding and slow dissociation, and is more potent than ACE inhibitors. It is well tolerated (can be taken by elderly and those with type II diabetes) and has no gender effects.
Chemical properties
It appears as a white or off-white powder.It is soluble in methanol but insoluble in water.
Originator
Takeda (Japan)
The Uses of Candesartan cilexetil
N,N-Desmethoxyethyl Candesartan Cilexetil is an impurity of Candesartan Cilexetil(C175580); An antihypertensive used in the treatment of congestive heart failures.
Indications
May be used as a first line agent to treat uncomplicated hypertension, isolated systolic hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy. May be used as a first line agent to delay progression of diabetic nephropathy. Candesartan may be also used as a second line agent in the treatment of congestive heart failure, systolic dysfunction, myocardial infarction and coronary artery disease in those intolerant of ACE inhibitors.
What are the applications of Application
Candesartan Celexetil Ester is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist
Background
Candesartan is an angiotensin-receptor blocker (ARB) that may be used alone or with other agents to treat hypertension. It is administered orally as the prodrug, candesartan cilexetil, which is rapidly converted to its active metabolite, candesartan, during absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. Candesartan lowers blood pressure by antagonizing the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS); it competes with angiotensin II for binding to the type-1 angiotensin II receptor (AT1) subtype and prevents the blood pressure increasing effects of angiotensin II. Unlike angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, ARBs do not have the adverse effect of dry cough. Candesartan may be used to treat hypertension, isolated systolic hypertension, left ventricular hypertrophy and diabetic nephropathy. It may also be used as an alternative agent for the treatment of heart failure, systolic dysfunction, myocardial infarction and coronary artery disease.
Definition
ChEBI: Candesartan cilexetil is a member of biphenyls.
Manufacturing Process
3-Nitrophthalic acid (35 g) in 300 ml ethanol and 20 ml concentrated sulfuric
acid was heated under reflux for 24 hours. The solvent was evaporated in
vacuo and the residue was poured into 700 ml cold water. The mixture was
extracted with ethyl acetate. The aqueous layer was made acidic with
hydrochloric acid and the mixture was extracted with methylene chloride.
After evaporation of methylene chloride was obtained 29 g (74%) ethyl 2-
carboxy-3-nitrobenzoate.
A mixture of 23.9 g ethyl 2-carboxy-3-nitrobenzoate and 12 ml thionyl
chloride in 150 ml benzene were heated under reflux for 3 hours. The reaction
mixture was concentrated to dryness. The resultant acid chloride (26 g) was
dissolved in 20 ml. The solution was added to a mixture of sodium azide (9.75
g) in 20 ml DMF with stirring. The reaction mixture was poured into 200 ml a
mixture of ether-hexane (3:1). The organic layer was washed with water and
evaporated. The residue was dissolved in 200 ml tert-butanol and the solution
was heated gradually with stirring, followed by heating under reflux for 2
hours. The reaction mixture was concentrated to give an oily ethyl 2-
butoxycarbonylamino-3-nitrobenzoate (30 g).
To a solution of ethyl 2-butoxycarbonylamino-3-nitrobenzoate (29 g) in 50 ml
THF was added, while stirring under ice-cooling, sodium hydride (60%
dispersion in mineral oil, 2.8 g). After 20 min to the mixture were added 18 g
4-(2-cyanophenyl)benzyl bromide and 0.36 g potassium iodide. After heating
for 10 hours under reflux the solvent was evaporated and the residue was
partitioned between 250 ml water and 200 ml ether. The organic layer was
washed with water, dried and concentrated to give yellow syrup. The syrup
was dissolved in a mixture of 60 ml trifluoroacetic acid and 40 ml methylene
chloride and the solution was stirred for 2 hour at room temperature. The
reaction mixture was concentrated to dryness and to residue was added 200
ml ethyl ether to give crystals of ethyl 2-[(2'-cyanobiphenyl-4-
yl)methylamino]nitrobenzoate (22.1 g, 85%), M.P. 118-119°C.
To a solution of 10.4 g ethyl 2-[(2'-cyanobiphenyl-4-yl)methylamino]
nitrobenzoate in 50 ml ethanol was added 28.1 g stannous dichloride
dihydrate and the mixture was stirred for 2 hours at 80°C. The solvent was evaporated. To the ice-cooling mixture of the residue in 300 ml ethyl acetate
was added dropwise 2 N NaOH (500 ml). The aqueous layer was extracted
with ethyl acetate (200 ml x 2). The organic layers were combined and
evaporated to dryness. Product was purified by column chromatography on
silica gel. Recrystallization from ethyl acetate-hexane gave colorless crystals
ethyl-3-amino-2-[[(2'-cyanobiphenyl-4-yl)methyl]amino]benzoate (7.3 g,
79%), M.P. 104-105°C.
Acetic acid (0.2 g) was added to a solution of ethyl-3-amino-2-[[(2'-
cyanobiphenyl-4-yl)methyl]amino]benzoate (1 g) in ethylorthocarbonate (5
ml). The mixture was stirred at 80°C for 1 hours. The reaction mixture was
concentrated. The solution was washed with an aqueous solution of NaHCO3
and water. The solvent was evaporeted to give crystals. Recrystallization from
ethyl acetate-benzene afforded colorless crystals 1-[(2'-cyanobiphenyl-4-
yl)methyl]-2-ethoxybenzimidazole-7-carboxylate (0.79 g, 69%), M.P. 131-
132°C.
A mixture of 1-[(2'-cyanobiphenyl-4-yl)methyl]-2-ethoxybenzimidazole-7-
carboxylate (0.7 g) and trimethyltin azide (0.7 g) in toluene (15 ml) was
heated under reflux for 4 days. The reaction mixture was concentrated, and to
the residue were added methanol (20 ml) and 1 N HCl (10 ml). The solution
was stirred at room temperature for 30 minutes and adjusted to pH 3-4 with
1 N NaOH. After removal of the solvent, the residue was partitioned between
chloroform and water. The organic layer was evaporated to dryness to dive a
syrup. The syrup was purified by column chromatography on silica gel to give
crystals. Recrystallization from ethyl acetate-benzene afforded colorless
crystals ethyl 2-ethoxy-1-[[2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]-
methyl]benzimidazole-7-carboxylate (0.35 g, 45%), M.P. 158-159°C.
Ethyl 2-ethoxy-1-[[2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]-methyl]benzimidazole-
7-carboxylate (0.24 g) was stirred with 1 N NaOH (1.5 ml) in ethanol (4 ml)
for 1 hours at 80°C. The reaction mixture was concentrated, and the
concentrate was exrtacted with water and ethyl acetate. The aqueous layer
was adjusted to pH 3-4 with 1 N HCl to give crystals. Recrystallization from
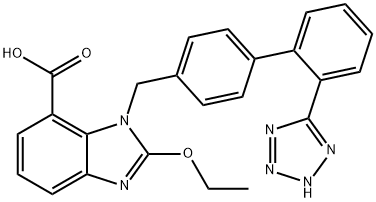
ethyl acetate-benzene afforded colorless crystals of 2-ethoxy-1-[[2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]-methyl]benzimidazole-7-carboxylic acid (0.15 g,
67%), M.P. 183-185°C.
To a solution of 2-ethoxy-1-[[2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]-
methyl]benzimidazole-7-carboxylic acid (2.07 g) in methylene chloride (10 ml)
were added trityl chloride (1.59 g) and triethylamine (0.8 ml). The mixture
was stirred at room temperature for 1 hour. The mixture was washed with
water and concentrated to dryness. The residue was purified by column
chromatography on silica gel to give crystals. Recrystallization from ethyl
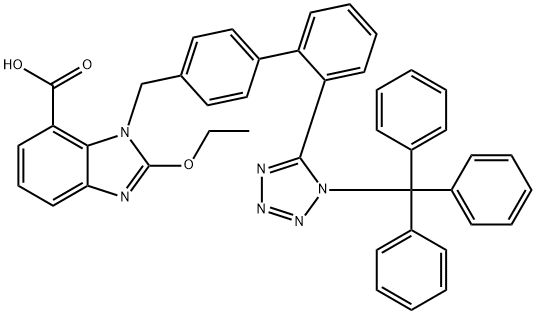
acetate-benzene afforded colorless crystals 2-ethoxy-1-[[2'-(N-triphenylmethyltetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]-methyl]benzimidazole-7-carboxylic
acid (2.12 g, 66%), M.P. 168-170°C.
To a solution 2-ethoxy-1-[[2'-(N-triphenylmethyltetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]-
methyl]benzimidazole-7-carboxylic acid (0.5 g) in DMF (5 ml) were added
potassium carbonate (0.12 g) and cyclohexyl 1-iodoethyl carbonate (0.26 g).
The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 1 hour. To the mixture was
added water and the mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic
layer was washed with water and dried. After removal of the solvent, the residue was dissolved in methanol (10 ml) and to solution was added 1 N HCl
(2 ml). The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 1 hour. After removal
of the solvent, the residue was purified by column chromatography on silica
gel to give colorless powder (0.21 g), M.P. 103-106°C. The mixture was
stirred for 3 hours at room temperature. To the powder (1 g) obtained as
above was added ethanol (6 ml). The mixture was stirred for 3 hours at room
temperature and allowed to stand under ice-cooling. The mixture was then
stirred for 1 hour at temperature not higher than 10°C. Resultant crystals
were collected and washed with cold ethanol. The crystals were dried at 25°C
for 9 hours under reduced pressure, then at 35°C for further 18 hours to
obtain white powdery crystal 1-(cyclohexyloxycarbonyloxy)ethyl 2-ethoxy-1-
[[2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]methyl]-benzimidazole-7-carboxylate
(0.94 g, M.P. 158-166°C).
brand name
Atacand (AstraZeneca).
Therapeutic Function
Antihypertensive
General Description
Pharmaceutical secondary standards for application in quality control provide pharma laboratories and manufacturers with a convenient and cost-effective alternative to the preparation of in-house working standards
Biochem/physiol Actions
Candesartan cilexetil is the prodrug form of the potent angiotensin II receptor antagonist, candesartan. The prodrug is cleaved by esterases within the intestine to liberate the active molecule.
Pharmacokinetics
Candesartan cilexetil is an ARB prodrug that is rapidly converted to candesartan, its active metabolite, during absorption from the gastrointestinal tract. Candesartan confers blood pressure lowering effects by antagonizing the hypertensive effects of angiotensin II via the RAAS. RAAS is a homeostatic mechanism for regulating hemodynamics, water and electrolyte balance. During sympathetic stimulation or when renal blood pressure or blood flow is reduced, renin is released from granular cells of the juxtaglomerular apparatus in the kidneys. Renin cleaves circulating angiotensinogen to angiotensin I, which is cleaved by angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) to angiotensin II. Angiotensin II increases blood pressure by increasing total peripheral resistance, increasing sodium and water reabsorption in the kidneys via aldosterone secretion, and altering cardiovascular structure. Angiotensin II binds to two receptors: type-1 angiotensin II receptor (AT1) and type-2 angiotensin II receptor (AT2). AT1 is a G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) that mediates the vasoconstrictive and aldosterone-secreting effects of angiotensin II. Studies performed in recent years suggest that AT2 antagonizes AT1-mediated effects and directly affects long-term blood pressure control by inducing vasorelaxation and increasing urinary sodium excretion. Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) are non-peptide competitive inhibitors of AT1. ARBs block the ability of angiotensin II to stimulate pressor and cell proliferative effects. Unlike ACE inhibitors, ARBs do not affect bradykinin-induced vasodilation. The overall effect of ARBs is a decrease in blood pressure.
Clinical Use
Angiotensin-II antagonist:
Hypertension
Heart failure
Side Effects
Candesartan cilexetil may lead to various kinds of adverse reactions including headache, back pain, dizziness, upper respiratory tract infection, pharyngitis, rhinitis, bronchitis, coughing, sinusitis, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, arthralgia and albuminuria. It should be warned that candesartan cilexetil might have remarkable fetal toxicity. Therefore, upon pregnancy, candesartan cilexetil should be discontinued. It could also cause hypotension for heart-failure patients.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anaesthetics: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Analgesics: antagonism of hypotensive effect and
increased risk of renal impairment with NSAIDs;
hyperkalaemia with ketorolac and other NSAIDs.
Antihypertensives: increased risk of hyperkalaemia
hypotension and renal impairment with ACE-Is and
aliskiren.
Ciclosporin: increased risk of hyperkalaemia and
nephrotoxicity.
Diuretics: enhanced hypotensive effect;
hyperkalaemia with potassium-sparing diuretics.
ESAs: increased risk of hyperkalaemia; antagonism
of hypotensive effect.
Lithium: reduced excretion, possibility of enhanced
lithium toxicity.
Potassium salts: increased risk of hyperkalaemia.
Tacrolimus: increased risk of hyperkalaemia and
nephrotoxicity
Metabolism
The prodrug candesartan cilexetil undergoes rapid and complete ester hydrolysis in the intestinal wall to form the active drug, candesartan. Elimination of candesartan is primarily as unchanged drug in the urine and, by the biliary route, in the feces. Minor hepatic metabolism of candesartan (<20%) occurs by O-deethylation via cytochrome P450 2C9 to form an inactive metabolite. Candesartan undergoes N-glucuronidation in the tetrazole ring by uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A3 (UGT1A3). O-glucuronidation may also occur. 75% of candesartan is excreted as unchanged drug in urine and feces.
Metabolism
Candesartan is mainly eliminated unchanged via urine and bile and only to a minor extent eliminated by hepatic metabolism (CYP2C9). The renal elimination of candesartan is both by glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion. Following an oral dose of 14C-labelled candesartan cilexetil, approximately 26% of the dose is excreted in the urine as candesartan and 7% as an inactive metabolite while approximately 56% of the dose is recovered in the faeces as candesartan and 10% as the inactive metabolite.
Properties of Candesartan cilexetil
| Melting point: | 168-170?C |
| Boiling point: | 843.3±75.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.37±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: ≥15mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | pKa 3.55 (H2O t=25.0 I=0.025) (Uncertain);5.91(H2O t=25.0 I=0.025) (Uncertain) |
| color | white to beige |
| λmax | 304nm(EtOH)(lit.) |
| Merck | 14,1739 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 145040-37-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Candesartan cilexetil
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H361:Reproductive toxicity H400:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Candesartan cilexetil
| InChIKey | GHOSNRCGJFBJIB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C1(OCC)N(CC2=CC=C(C3=CC=CC=C3C3=NNN=N3)C=C2)C2=C(C(OC(OC(OC3CCCCC3)=O)C)=O)C=CC=C2N=1 |
Candesartan cilexetil manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![Methyl 1-[(2'-cyanobiphenyl-4-yl)methyl]-2-ethoxy-1H-benzimidazole-7-carboxylate](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/139481-44-0.gif)
![Ethyl -2-ethoxy-1-[[(2-(1Htetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl-) methyl]](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/139481-58-6.gif)
![Ethyl-2-Ethoxy-1-[[(2'-Cyanobiphenyl-4-yl) Methyl] Benzimidazole]-7-Carboxylate](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/139481-41-7.gif)

You may like
-
 145040-37-5 98%View Details
145040-37-5 98%View Details
145040-37-5 -
 CANDESARTAN CILEXETIL 4.0% DC GRANULES 98%View Details
CANDESARTAN CILEXETIL 4.0% DC GRANULES 98%View Details
145040-37-5 -
 Candesartan cilexetil 98%View Details
Candesartan cilexetil 98%View Details -
 145040-37-5 98%View Details
145040-37-5 98%View Details
145040-37-5 -
 145040-37-5 95-99 %View Details
145040-37-5 95-99 %View Details
145040-37-5 -
 Candesartan Cilexetil CAS 145040-37-5View Details
Candesartan Cilexetil CAS 145040-37-5View Details
145040-37-5 -
 Candesartan cilexetil >98% (HPLC) CAS 145040-37-5View Details
Candesartan cilexetil >98% (HPLC) CAS 145040-37-5View Details
145040-37-5 -
 Candesartan cilexetil 95.00% CAS 145040-37-5View Details
Candesartan cilexetil 95.00% CAS 145040-37-5View Details
145040-37-5
