2-Ethoxyethanol
Synonym(s):2-Ethoxyethanol;2-Ethoxyethanol in dimethyl sulfoxide;Ethyl glycol;Ethylene glycol monoethyl ether;Ethylene Glycol Monoethyl Ether, "Cellosolve"
- CAS NO.:110-80-5
- Empirical Formula: C4H10O2
- Molecular Weight: 90.12
- MDL number: MFCD00002869
- EINECS: 203-804-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:59
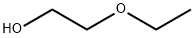
What is 2-Ethoxyethanol?
Description
2-Ethoxyethanol is a stable, colorless, flammable liquid, synthetically produced throughout the world. It belongs to a larger group of glycol ether solvents. 2-Ethoxyethanol is commercially referred to as Ethyl Cellosolve or Cellosolve, a trademark registered by Union Carbide in 1924. It was first synthesized to have the same chemical properties of both alcohols and ethers (hydrophilic and lipophilic) but less volatile, which improves production characteristics. The glycol ethers are made by reacting anhydrous alcohols with ethylene oxide.
Chemical properties
2-Ethoxyethanol is a colorless, viscous liquid with a sweetish odor
Chemical properties
Ethylene glycol monoethyl ether is a colorless liquid with a sweet, mild odor and slightly bitter taste. It is miscible in all proportions of acetone, benzene, carbon tetrachloride, ethyl ether, methanol, and water. It dissolves many oils, resins, and waxes.
Physical properties
Clear, colorless liquid with a sweetish odor. Experimentally determined detection and recognition odor threshold concentrations were 1.1 mg/m3 (300 ppbv) and 2.0 mg/m3 (540 ppbv), respectively (Hellman and Small, 1974).
The Uses of 2-Ethoxyethanol
2-Ethoxyethanol is widely used as an industrial solvent and production intermediate. It is produced by the reaction of ethylene oxide with ethanol. The glycol ethers are miscible in polar and nonpolar solutions, which make them useful solvents in paints and surface coatings, stains, lacquers, inks, and dyes. Additional uses include industrial deicing, hydraulic fluids, and cleaning agents. 2-Ethoxyethanol was once used in cosmetic products but is no longer used due to toxicity associated with dermal absorption. Global production has been on the decline in recent years based on demonstrated toxicity through oral, dermal, and inhalation routes of exposure. The use of ethylene glycol ethers has largely been replaced by relatively safer substitutes, primarily propylene glycol ethers; however, their use as a solvent and chemical process intermediate poses potential for release into the environment.
The Uses of 2-Ethoxyethanol
antiobesity agent pancreatic lipase inhibitor
The Uses of 2-Ethoxyethanol
Ethylene glycol monoethyl ether is used in varnish removers, lacquers, and as a solvent for printing inks, duplicating fluids, and epoxy. Ethylene glycol monobutyl ether is used in hydraulic fluids, as a coupling agent for water-based coatings, in vinyl and acrylic paints and varnishes, and as a solvent for varnishes, enamels, spray lacquers, dry cleaning compounds, textiles, and cosmetics.
Definition
ChEBI: A hydroxyether that is the ethyl ether derivative of ethylene glycol.
General Description
A clear colorless liquid. Flash point of 120°F. Less dense than water. Its vapors are heavier than air.
Air & Water Reactions
Flammable. Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
ETHYLENE GLYCOL MONOMETHYL ETHER may react with oxidizing materials, i.e. hydrogen peroxide, to form peroxides. 2-Ethoxyethanol dissolves many oils, resins and waxes.
Hazard
Toxic by skin absorption. Moderate fire risk.
Health Hazard
Some eye irritation. Inhalation of vapors causes irritation of nose.
Health Hazard
EGEE is a teratogen and at high concentration a toxic substance. The target organs arethe lungs, kidney, liver, and spleen. Animalexperiments indicated that inhalation of itsvapors at 2000 ppm for several hours couldproduce toxic effect. Death resulted from kid ney injury when the test species were sub jected to a 24-hour exposure. It producedkidney injury, hematuria, and microscopiclesions of both the liver and kidney. EGEEmay be absorbed through the skin. Wheninserted into the eyes, it produced corneal irritation. The recovery occurred within 24 hours
Investigating the subchronic inhalationtoxicology of EGEE in the rat and rabbit,Barbee et al. (1984) reported no biologicalsignificant effect of this compound in theseanimals at an exposure level of 400 and100 ppm, respectively. Chronic treatment ofrats with EGEE at 0.5–1.0 g/kg in an oraldose caused enlargement of adrenal gland inmale rats and affected the development ofspontaneous lesions of the spleen (males andfemales), pituitary (males and females), andLD50 value(rats):3000 mg/kg(NIOSH1986)testis (males) (Melnick 1984).
LC50 value (mice): 1820 ppm/7 hr (NIOSH 1986)
In humans there is no report of any severe poisoning case. The toxic effect from inhaling its vapors at 1000 ppm may be less than noticeable. EGEE is less toxic than EGME. Whenadministeredorallyto youngmale rats, EGEE produced testicular atrophy similar to that of EGME (Nagano et al. 1984). However, a fivefold dose, 250–1000 mg/kg/day, was required to elicit equivalent severity (Foster et al. 1984)
Reproductive toxicity of EGEE has been investigated extensively (Lamb et al. 1984; Hardin et al. 1984; Oudiz et al. 1984). Testicular atrophy, decline in sperm count, and increased abnormal sperm were observed in treated male rats, but no specific anomalies were noted in the females. Wier et al. (1987) investigated postnatal growth and survival. EGEE produced embryo lethality and malformations and decreased fetal weight. Prenatal exposure to EGEE produced kinked tails in pups. Ethanol caused potentiation of reproductive toxicity of EGEE (Nelson et al. 1984).
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic gases, such as carbon monoxide, may be produced in fire.
Chemical Reactivity
Reactivity with Water No reaction; Reactivity with Common Materials: No reaction; Stability During Transport: Stable; Neutralizing Agents for Acids and Caustics: Not pertinent; Polymerization: Not pertinent; Inhibitor of Polymerization: Not pertinent.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion, skin contact, intravenous, and intraperitoneal routes. Mildly toxic by inhalation and subcutaneous routes. An experimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductive effects. A mild eye and skin irritant. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame; can react with oxidzing materials. Moderate explosion hazard in the form of vapor when exposed to heat or flame. Mxture with hydrogen peroxide + polyacrylamide gel + toluene is explosive when dry. To fight fire, use alcohol foam, dry chemical. See also GLYCOL ETHERS.
Potential Exposure
This material is used as a solvent for nitrocellulose and alkyd resins in lacquers; as a solvent for printing inks; in dyeing leathers and textiles; in the formulation of cleaners and varnish removers; as an anti-icing additive in brake fluids and auto and aviation fuels.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit. Keepvictim under medical observation
Environmental Fate
Biological. Bridié et al. (1979) reported BOD and COD values of 1.03 and 1.92 g/g using
filtered effluent from a biological sanitary waste treatment plant. These values were determined
using a standard dilution method at 20 °C for a period of 5 d. When a sewage seed was used in a
separate screening test, a BOD value of 1.27 g/g was obtained. Similarly, Heukelekian and Rand
(1955) reported a 5-d BOD value of 1.42 g/g which is 72.4% of the ThOD value of 1.96 g/g.
Photolytic. Grosjean (1997) reported a rate constant of 1.87 x 10-11 cm3/molecule?sec at 298 K
for the reaction of 2-ethoxyethanol and OH radicals in the atmosphere. Based on an atmospheric
OH radical concentration of 1.0 x 106 molecule/cm3, the reported half-life of methanol is 0.35 d
(Grosjean, 1997). Stemmler et al. (1996) reported a rate constant of 1.66 x 10-11 cm3/molecule?sec
for the OH radical-initiated oxidation of 2-ethoxyethanol in synthetic air at 297 K and 750 mmHg.
Major reaction products identified by GC/MS (with their yields) were ethyl formate, 34%;
ethylene glycol monoformate, 36%; ethylene glycol monoacetate, 7.8%; and ethoxyacetaldehyde,
24%.
Chemical/Physical. 2-Ethoxyethanol will not hydrolyze (Kollig, 1993).
At an influent concentration of 1,024 mg/L, treatment with GAC resulted in an effluent
concentration of 886 mg/L. The adsorbability of the carbon used was 28 mg/g carbon (Guisti et
al., 1974).
Storage
Color Code—Red: Flammability Hazard: Store ina flammable liquid storage area or approved cabinet awayfrom ignition sources and corrosive and reactive materials.Prior to working with this chemical you should be trainedon its proper handling and storage. Before entering confinedspace where this chemical may be present, check to makesure that an explosive concentration does not exist. 2-Ethoxyethanol must be stored to avoid contact with strongoxidizers, such as nitrates, permanganates, chlorine, bromine, or chlorine dioxide, since violent reactions occur.Store in tightly closed containers in a dark, cool, well-ventilated area away from heat. Sources of ignition, such assmoking and open flames, are prohibited where 2-ethoxyethanol is used, handled, or stored in a manner that couldcreate a potential fire or explosion hazard. Keep in darkbecause of possible formation of explosive peroxides.
Shipping
UN1171 Ethylene glycol monoethyl ether, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid.
Purification Methods
Dry it with CaSO4 or K2CO3, filter and fractionally distil it. Peroxides can be removed by refluxing with anhydrous SnCl2 or by filtration under slight pressure through a column of activated alumina. [Beilstein 1 IV 2377.]
Toxicity evaluation
The toxicity associated with 2-ethoxyethanol is likely caused more by the primary metabolite, ethoxyacetic acid, than by the parent compound. The metabolites have a longer half-life implying a higher accumulation following repeated exposures. Both in vitro and in vivo studies have shown toxic effects from administration of the metabolites that were not seen at higher doses of the parent. Developmental and male reproductive toxicity has been widely documented for several compounds in the glycol ether family, and potency is associated with the length of the hydrocarbon chain: the shorter the chain, the more potent the developmental and reproductive effects. Despite the vast collection of toxicity studies conducted internationally, the exact mechanism of developmental and reproductive toxicity is not well understood. A potential mechanism for the male reproductive toxicity is direct action on Sertoli and/or germ cells by ethoxyacetic acid. The testes have relatively high levels of cytochrome P450 and are an active site of metabolism. Investigators have found that ethoxyacetic acid can cause degeneration of spermatocytes in vitro, and damage to spermatocytes seen in vivo can be suppressed when metabolism of 2-ethoxyethanol is inhibited.
Incompatibilities
May form explosive mixture with air. Strong oxidizers may cause fire and explosions. Attacks some plastics, rubber and coatings. Able to form peroxides. Incompatible with strong acids; aluminum and its alloys
Waste Disposal
Dissolve or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≧100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal
Properties of 2-Ethoxyethanol
| Melting point: | -100 °C |
| Boiling point: | 135 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.93 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 3.1 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 3.8 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 107.6 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | water: miscible |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | 14.44±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | Clear, colorless |
| Odor | Sweetish; mild, pleasant, ethereal. |
| Odor Threshold | 0.58ppm |
| explosive limit | 1.8-15.7%(V) |
| Water Solubility | miscible |
| FreezingPoint | -70℃ |
| λmax | λ: 215 nm Amax: 1.00 λ: 225 nm Amax: 0.50 λ: 250 nm Amax: 0.20 λ: 305 nm Amax: 0.01 |
| Merck | 14,3750 |
| BRN | 1098271 |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA skin 5 ppm (18.5 mg/m3) (ACGIH).
. |
| Dielectric constant | 29.6(24℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Readily forms explosive mixtures with air - note the wide explosion range. Vapour may travel considerable distance to a source of ignition. Flammable. Incompatible with strong acids, strong bases, strong oxidizing agents, aluminium, alkalies. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 110-80-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Ethanol, 2-ethoxy-(110-80-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2-Ethoxyethanol (110-80-5) |
Safety information for 2-Ethoxyethanol
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H226:Flammable liquids H302:Acute toxicity,oral H331:Acute toxicity,inhalation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for 2-Ethoxyethanol
2-Ethoxyethanol manufacturer
Oswal Udhyog
R J Organics
Jaiswal S Cyber Shop
C.H. Chemicals
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Ethyl Cellosolve 98%View Details
Ethyl Cellosolve 98%View Details -
 Ethyl Cellosolve 99%View Details
Ethyl Cellosolve 99%View Details -
 2-Ethoxy Ethanol (SQ) CAS 110-80-5View Details
2-Ethoxy Ethanol (SQ) CAS 110-80-5View Details
110-80-5 -
 Ethyl Cellosolve CASView Details
Ethyl Cellosolve CASView Details -
 ETHYLENEGLYCOL MONOETHYLETHER (109-86-4)View Details
ETHYLENEGLYCOL MONOETHYLETHER (109-86-4)View Details
109-86-4 -
 Liquid Industrial Grade Ethyl Glycol CAS Number: 107-21-1, 98%View Details
Liquid Industrial Grade Ethyl Glycol CAS Number: 107-21-1, 98%View Details
107-21-1 -
 Ethyl CellosolveView Details
Ethyl CellosolveView Details
110-80-5 -
 Ethyl Cello SolveView Details
Ethyl Cello SolveView Details
110-80-5
