Calcium cyanamide
Synonym(s):Calcium carbimide;Cyanamide calcium derivative;Cyanamide calcium salt
- CAS NO.:156-62-7
- Empirical Formula: CCaN2
- Molecular Weight: 80.1
- MDL number: MFCD00064894
- EINECS: 205-861-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-06-13 14:48:16
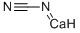
What is Calcium cyanamide?
Absorption
It presents a very rapid absorption which has caused the presence of side effects as nausea, headache and vomiting. The oral bioavailability of calcium carbimide depends on the administered dose which can vary from 50-81% on a dose of 0.3-1.5 mg/kg respectively. In preclinical trials, peak plasma concentration occurred at 60 minutes after administration. The values of Cmax, AUC and T max of calcium carbimide of a dose of 1.5 mg/kg were 1.65 mcg/ml, 77.86 mcg/mg min and 12 minutes respectively.
Toxicity
Calcium carbimide presents antithyroid activity which can be of clinical relevance in patients with preexisting hypothyroid disease. It can also present some other minor side effects as fatigue, skin rash, ear ringing, mild depression, increased urination and impotence.
Description
Calcium cyanamide is a blackish-gray, shinycrystalline material or powder. Molecular weight=80.11;Specific gravity (H2O:1)=2.29; Freezing/Melting point 51340℃ (sublimes .1500℃). Hazard Identification (basedon NFPA-704 M Rating System): Health 3, Flammability 1,Reactivity 1. Insoluble in water; reaction.
Chemical properties
Calcium cyanamide is a blackish-gray, shiny crystalline material or powder.
Physical properties
Pure product is a colorless, hexagonal crystal or white powder. Commercial grade material may be grayish-black powder or lump (the color is due to presence of calcium carbide and other impurities); density 2.29 g/cm3; melts around 1,340°C; sublimes around 1,150 to 1,200°C on rapid heating; reacts with water.
The Uses of Calcium cyanamide
Calcium Cyanamide is used as a fertilizer, herbicide, insecticide, a steel-making additive and an ore processing material. It can also be used to make thiourea, guanidine and ferrocyanides. manufacture of calcium cyanide, melamine, dicyandiamide.
The Uses of Calcium cyanamide
Calcium cyanamide has its major use as a fertilizer. However, it has a number of other uses, such as a herbicide and a defoliant for cotton plants. It is finding increasing use as a chemical intermediate. For example, it is being used to produce dicyandiamide, which in turn can be polymerized to form the widely used monomer, melamine. The conversion to calcium cyanide and hence into a variety of other uses is also important commercially.
The Uses of Calcium cyanamide
Manufacture of calcium cyanide and dicyandiamide; formerly used as a defoliant and herbicide
Background
Calcium carbimide, sold as the citrate salt, is an alcohol-sensitizing agent. Its effects are similar to the drug disulfiram (Antabuse) in that it interferes with the normal metabolism of alcohol by preventing the breakdown of the metabolic product acetaldehyde. Calcium carbimide was conceived as an alternative for the treatment of alcoholism with a reduced side effect profile either when it is consumed accompanied by alcohol or without it. This drug was developed by Lederle Cyanamid Canada Inc and approved for marketing in Canada in 1959. The current status of calcium carbimide is cancelled post marketing.
Indications
Calcium carbimide has not been approved by the FDA but the intended indication is for the treatment of alcoholism. This medication was marketed in Canada, United Kingdom and Europe under the trade name of Temposil for the sole use of alcoholism treatment.
Definition
ChEBI: The calcium salt of cyanamide, formed when calcium carbide reacts with nitrogen
Definition
calcium cyanamide: A colourlesssolid, CaCN2, which sublimes at1300°C. It is prepared by heating calciumdicarbide at 800°C in a streamof nitrogen:
CaC2(s) + N2(g) → CaCN2(s) + C(s)
The reaction has been used as amethod of fixing nitrogen in countriesin which cheap electricity isavailable to make the calcium dicarbide(the cyanamide process). Calciumcyanamide can be used as afertilizer because it reacts with waterto give ammonia and calcium carbonate:
CaCN2(s) + 3H2O(l) → CaCO3(s) +2NH3(g)
It is also used in the production ofmelamine, urea, and certain cyanidesalts.
Production Methods
Calcium cyanamide was first produced commercially around 1900 as a fertilizer. The process of making calcium cyanamide involves three raw materials—coke, coal, and limestone— plus nitrogen. The limestone (calcium carbonate) is burned with coal to produce calcium oxide. The calcium oxide is then allowed to react with amorphous carbon in the furnace at 2000°C with the formation of calcium carbide (CaC2). Finely powdered calcium carbide is heated to 1000°C in an electric furnace into which pure nitrogen is passed. It is then removed and uncombined calcium carbide removed by leaching.
Preparation
Calcium cyanamide is prepared from calcium carbide. The carbide powder is heated at about 1,000°C in an electric furnace into which nitrogen is passed for several hours. The product is cooled to ambient temperatures and any unreacted carbide is leached out cautiously with water.
CaC2 + N2 → CaCN2 + C (ΔHƒ°= –69.0 kcal/mol at 25°C)
General Description
A colorless to gray, odorless solid. May cause illness from ingestion. May irritate the skin. If exposed to water or high temperatures, calcium cyanamide may generate toxic and flammable fumes. Used to make pesticides and in fertilizers.
Air & Water Reactions
Depending on the calcium carbide content, the cyanamide reacts with water (moisture from air or soil) to produce acetylene and hydrated calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide. Absorption of water during handling or storage of technical calcium cyanamide may cause explosion [Pieri, M. Chem. Abs. 46, 8335 1952].
Reactivity Profile
When hydrated CALCIUM CARBIDE generates salts of calcium that are basic and are generally soluble in water. The resulting solutions contain moderate concentrations of hydroxide ions and have pH's greater than 7.0. They react as bases to neutralize acids. These neutralizations generate heat, but less or far less than is generated by neutralization of the bases in reactivity group 10 (Bases) and the neutralization of amines. They usually do not react as either oxidizing agents or reducing agents but such behavior is not impossible.
Hazard
Fire risk with moisture or combined with calcium carbide. Skin, eye, and upper respiratory tract irritant. Questionable carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Inhalation or contact with vapors, substance or decomposition products may cause severe injury or death. May produce corrosive solutions on contact with water. Fire will produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control may cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Produce flammable gases on contact with water. May ignite on contact with water or moist air. Some react vigorously or explosively on contact with water. May be ignited by heat, sparks or flames. May re-ignite after fire is extinguished. Some are transported in highly flammable liquids. Runoff may create fire or explosion hazard.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Agricultural Uses
Calcium cyanamide (CaCN2) is a dark colored,
granulated material containing around 21 % nitrogen. Its
dark color is due to the presence of calcium carbide.
Calcium cyanamide is produced by heating a mixture
of limestone with coal in a nitrogen atmosphere.
Generally, the process is carried out in three steps. In the
first step, calcium carbonate (limestone) is decomposed
at about 1100°C.
In the second step, calcium oxide (CaO) and coke (or
coal) are heated in an electric furnace to produce calcium
carbide.
The final step involves heating the powdered calcium
carbide at about 1100°C with pure nitrogen (produced by
liquefaction of air and fractional distillation) to produce
calcium cyanamide.
The fertilizer-grade calcium cyanamide contains 21 %
nitrogen, 11 % calcium, 11 % free carbon, 5% oil, 2 to
4% water and oxides of aluminum, iron and silicon. In
the presence of moisture and air, calcium
dicyandiamide (a poisonous compound) is formed. It
distinctly leaves alkalinity in the soil equivalent to 1.3 kg
calcium carbonate (CaCO3) per 0.45 kg of nitrogen
applied. At pH 7 or below, calcium dicyandiamide is
converted into urea and lime within one week of its being
in the soil.
When dry, calcium cyanamide is dusty but it is
generally used as granules. It is poisonous, irritating to
the skin and used as a pesticide, fertilizer and defoliant in
cotton. It is as good a fertilizer as sodium nitrate or
ammonium sulphate, but not as fast acting.
Calcium cyanamide is an excellent weed killer,
especially for tobacco plants, when applied 2 to 3 weeks
before sowing. It is also used for producing melamine,
urea and certain cyanide salts.
Pharmacokinetics
Administration of calcium carbimide causes a syndrome characterized by intense flushing, rapid pulse, panting respiration and perception of acetaldehyde in the exhaled breath. This syndrome remains for a few hours after alcohol consumption and it stops completeley after 24 hours. This syndrome is caused by the accumulation of acetaldehyde and altered vascular reaction. Therefore, the more the alcohol consumption the more the adverse effects caused by acetaldehyde accumulation.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, inhalation, sh contact, intravenous, and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic to humans by ingestion. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. Mutation data reported. The fatal dose, by ingestion, is probably around 20 to 30 g for an adult. It does not have a cyanide effect. Calcium cyanamide is not believed to have a cumulative action. Flammable. Reaction with water forms the explosive acetylene gas. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx and CN-. See also CALCIUM COMPOUNDS, AMIDES, and CYANIDE
Potential Exposure
Calcium cyanamide is used in agriculture as a fertilizer, herbicide; defoliant for cotton plants; and pesticide. It is also used in the manufacture of dicyandiamide and calcium cyanide as a desulfurizer in the iron and steel industry; and in steel hardening.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Carcinogenicity
Calcium cyanamide was weakly mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium strain TA1535 and nonmutagenic in strain TA100.
Metabolism
The activity of calcium carbimide requires an initial metabolic transformation to the bioactive form. The transformation requires the activity of catalase and the presence of H2O2 for the formation of N-hydroxycyanamide. This bioactive compound will later spontaneosly decompose into cyanide and nitroxyl. The nitroxyl component will be the direct inhibitor of the aldehyde dehydrogenase.
Storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with calciumcyanamide you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, wellventilated area away from moisture. A regulated, markedarea should be established where this chemical is handled,used, or stored in compliance with OSHA Standard1910.1045.
Shipping
UN1403 Calcium cyanamide with .1% calcium carbide, Hazard Class: 4.3; Labels: 4.3-Dangerous when wet material
Incompatibilities
Commercial grades of calcium cyanamide may contain calcium carbide; contact with any form of moisture solutions may cause decomposition, liberating explosive acetylene gas and ammonia. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. May polymerize in water or alkaline solutions to dicyanamide. Contact with all solvents tested also causes decomposition
Properties of Calcium cyanamide
| Melting point: | >300 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 2.29 |
| vapor pressure | 0.51Pa at 20℃ |
| solubility | reacts with H2O |
| form | Powder |
| color | Gray to dark gray |
| Specific Gravity | 2.29 |
| Water Solubility | insoluble H2O, but undergoes hydrolysis releasing acetylene and ammonia [HAW93] [MER06] |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,1662 |
| BRN | 4124391 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 156-62-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Calcium cyanamide (156-62-7) |
Safety information for Calcium cyanamide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H261:Substances And Mixtures Which, In Contact With Water,Emit Flammable Gases H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P231+P232:Handle under inert gas. Protect from moisture. P333+P313:IF SKIN irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Calcium cyanamide
| InChIKey | QFSRQFUIHVTIDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Calcium cyanamide manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 156-62-7 Calcium Cyanamide 99%View Details
156-62-7 Calcium Cyanamide 99%View Details
156-62-7 -
 Calcium cyanamide CAS 156-62-7View Details
Calcium cyanamide CAS 156-62-7View Details
156-62-7 -
 Calcium cyanamide 97.00% CAS 156-62-7View Details
Calcium cyanamide 97.00% CAS 156-62-7View Details
156-62-7 -
 Calcium Cyanamide CAS 156-62-7View Details
Calcium Cyanamide CAS 156-62-7View Details
156-62-7 -
 Calcium cyanamide CAS 156-62-7View Details
Calcium cyanamide CAS 156-62-7View Details
156-62-7 -
 CALCIUM CYANAMIDEView Details
CALCIUM CYANAMIDEView Details
156-62-7 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
