Cadmium sulfate
Synonym(s):Cadmium monosulfate;Cadmium sulfate (Cd(SO4 ))
- CAS NO.:10124-36-4
- Empirical Formula: Cd.H2O4S
- Molecular Weight: 210.49
- MDL number: MFCD00010923
- EINECS: 233-331-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02

What is Cadmium sulfate?
Description
Cadmium sulfate is a white to colorless, odorless, crystalline substance. Molecular weight=208.48;Freezing/Melting point=1000℃. Hazard Identification(based on NFPA-704 M Rating System): Health 3,Flammability 0, Reactivity 0. Soluble in water;solubility=76 g/100 mL at 0℃.
Chemical properties
Cadmiumsulfate, CdS04, is an effiorescent crystalline solid that is soluble in water. It is used as an antiseptic,in the treatment of venereal diseases and rheumatism, and to detect the presence of hydrogen sulfide.
Chemical properties
Cadmium sulfate is a white to colorless, odorless, crystalline substance.
Physical properties
Colorless orthogonal crystal; the hydrates have monoclinic crystal system; density 4.69 g/cm3 (density of mono-, and octahydrates is 3.79 and 3.08 g/cm3, respectively); melts at 1,000°C (octahydrate decomposes at 40°C); soluble in water, insoluble in ethanol.
The Uses of Cadmium sulfate
Cadmium sulfate (CdS), also called “orange cadmium,” is used to produce phosphors and fluorescent screens. It is also used as a pigment in inks and paints, to color ceramics glazes, in the manufacture of transistors in electronics, photovoltaic cells, and solar cells, and in fireworks.
The Uses of Cadmium sulfate
Applied in the formation of novel two-dimensional Cd-SCN coordination solids with unusual and tailorable, checkerboard- or herringbone-patterned structures these structures are important steps toward technologically useful materials.1
The Uses of Cadmium sulfate
It is a catalyst in Marsh test fir arsenic; determination of hydrogen sulfide.
What are the applications of Application
Cadmium sulfate is a chemical used in the formation of two-dimensional Cd-SCN coordination solids
Preparation
Cadmium sulfate is prepared by the reaction of cadmium metal or its oxide or hydroxide with dilute sulfuric acid:
CdO + H2SO4 → CdSO4+ H2
CdO + H2SO4 → CdSO4 + H2O
Cd(OH)2 + H2SO4 → CdSO4+ 2H2O.
Definition
ChEBI: Cadmium sulfate is a cadmium salt.
General Description
Odorless white solid. Sinks and mixes slowly with water.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Cadmium sulfate acts as a weakly acidic inorganic salt, which is soluble in water. The resulting solutions contain moderate concentrations of hydrogen ions and have pH's of less than 7.0. They react as acids to neutralize bases. These neutralizations generate heat, but less or far less than is generated by neutralization of inorganic acids, inorganic oxoacids, and carboxylic acid. They usually do not react as either oxidizing agents or reducing agents but such behavior is not impossible. Many of these compounds catalyze organic reactions.
Hazard
A confirmed carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Inhalation may cause dryness of throat, coughing, constriction in chest, and headache. Ingestion may cause salivation, vomiting, abdominal pains, or diarrhea. Contact with eyes causes irritation.
Health Hazard
Exposures to cadmium salts by absorption are most effi cient via the respiratory tract. The symptoms of health effects include, but are not limited to, irritation, headache, metallic taste, and/or cough. Severe exposures cause shortness of breath, chest pain, and fl u-like symptoms with weakness, fever, headache, chills, sweating, nausea and muscular pain, pulmonary edema, liver and kidney damage, and death. Prolonged exposures, even at relatively low concentrations, may result in kidney damage, anemia, pulmonary fi brosis, emphysema, perforation of the nasal septum, loss of smell, male reproductive effects, and an increased risk of cancer of the lung and of the prostate. Decrease in bone density, renal stones, and other evidence of disturbed calcium metabolism have been reported.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic cadmium oxide fume may form in fires.
Safety Profile
Confirmed human carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic data. Poison by ingestion, subcutaneous, and intraperitoneal routes. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. See also CADMIUM COMPOUNDS and SULFATES. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of Cd and SOx.
Potential Exposure
It is used in pigments, electroplating; as a fungicide; and in synthetic and analytical chemistry. Also used in fluorescent screens; as an electrolyte. Incompatibilities: Acts as a weak inorganic acid; neutralizes bases. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides, sulfur, selenium, tellurium, zinc
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for atleast 15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seekmedical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, includ?ing resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medi?cal attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.Medical observation is recommended for 24 48 h afterbreathing overexposure, as pulmonary edema may bedelayed. As first aid for pulmonary edema, a doctor orCadmium sulfate 515authorized paramedic may consider administering a corticosteroid spray.Note to physician: In case of fume inhalation, treat for pulmonary edema. Give prednisone or other corticosteroidorally to reduce tissue response to fume. Positive-pressureventilation may be necessary. Treat metal fume fever withbed rest, analgesics, and antipyretics. The symptoms ofmetal fume fever may be delayed for 4-12 h followingexposure: it may last less than 36 h.Note to physician: For severe poisoning do not use BAL[British Anti-Lewisite, dimercaprol, dithiopropanol(C3H8OS2)] as it is contraindicated or ineffective inpoisoning from cadmium.
Storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard: Store in asecure poison location. Prior to working with Cadmium sulfate, you should be trained on its proper handling and storage. A regulated, marked area should be established wherethis chemical is handled, used, or stored in compliance withOSHA Standard 1910.1045. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area away from oxidizers andmetals.
Shipping
UN2570 Cadmium compounds, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with strong oxidizers,sulfur, selenium, tellurium, zinc. Acts as a weak inorganicacid; neutralizes bases. May ignite combustible materials.
Precautions
Cadmium compounds cause more health disorders to occupational workers and persons with pre-existing skin disorders, eye problems, blood disorders, prostate problems, or impaired liver, kidney, or respiratory function. These workers are more susceptible to the effects of cadmium salts. On contact with cadmium, exposed workers should wash the skin and eyes immediately with plenty of water
Properties of Cadmium sulfate
| Melting point: | 41 °C |
| Density | 4.691 |
| vapor pressure | 26.8hPa at 25℃ |
| solubility | water: soluble |
| form | Powder |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | 1130 G/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,1627 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.01 mg/m3; TWA 0.002 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 9 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10124-36-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cadmium sulfate (10124-36-4) |
Safety information for Cadmium sulfate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H330:Acute toxicity,inhalation H340:Germ cell mutagenicity H350:Carcinogenicity H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. |
Computed Descriptors for Cadmium sulfate
Cadmium sulfate manufacturer
Jaiswal S Cyber Shop
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

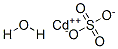

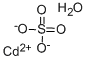
You may like
-
 Cadmium sulfate 98%View Details
Cadmium sulfate 98%View Details -
 Cadmium sulfate, For analysis ACS CAS 10124-36-4View Details
Cadmium sulfate, For analysis ACS CAS 10124-36-4View Details
10124-36-4 -
 Cadmium sulfate, For analysis ACS CAS 10124-36-4View Details
Cadmium sulfate, For analysis ACS CAS 10124-36-4View Details
10124-36-4 -
 Cadmium sulfate CAS 10124-36-4View Details
Cadmium sulfate CAS 10124-36-4View Details
10124-36-4 -
 Cadmium sulfate CAS 10124-36-4View Details
Cadmium sulfate CAS 10124-36-4View Details
10124-36-4 -
 CADMIUM SULPHATEView Details
CADMIUM SULPHATEView Details
10124-36-4 -
 Electroplating Circuit Jcssuper 7790-84-3 Cadmium Sulphate Extrapure 100 Gm., Grade Standard: Chemical GradeView Details
Electroplating Circuit Jcssuper 7790-84-3 Cadmium Sulphate Extrapure 100 Gm., Grade Standard: Chemical GradeView Details
10124-36-4 -
 Solid Cadmium sulfate (10124-36-4), Grade Standard: Industrial Grade, Packaging Type: BagView Details
Solid Cadmium sulfate (10124-36-4), Grade Standard: Industrial Grade, Packaging Type: BagView Details
10124-36-4
