Brinzolamide
Synonym(s):(5R)-5-Ethylamino-3-(3-methoxypropyl)-2,2-dioxo-2?6,9-dithia-3-azabicyclo[4.3.0]nona-7,10-diene-8-sulfonamide;(R)- 4-(ethylamino)-3,4-dihydro-2-(3-methoxypropyl)-2H-Thieno[3,2-e]-1,2-thiazine-6-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide;AL 4862
- CAS NO.:138890-62-7
- Empirical Formula: C12H21N3O5S3
- Molecular Weight: 383.51
- MDL number: MFCD08067749
- EINECS: 620-511-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 13:58:55
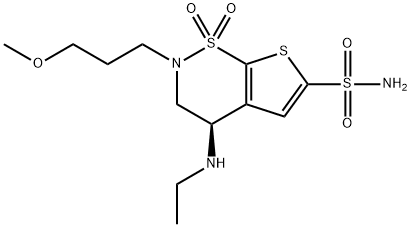
What is Brinzolamide?
Absorption
Brinzolamide is absorbed through the cornea following topical ocular administration. The substance is also absorbed into the systemic circulation where it binds strongly to carbonic anhydrase in red blood cells (RBCs). Plasma concentrations are very low.
Toxicity
Developmental toxicity studies with brinzolamide in rabbits at oral doses of 1, 3, and 6 mg/kg/day (20, 60, and 120 times the recommended human ophthalmic dose) produced maternal toxicity at 6 mg/kg/day and a significant increase in the number of fetal variations, such as accessory skull bones, which was only slightly higher than the historical value at 1 and 6 mg/kg. In rats, statistically, decreased body weights of fetuses from dams receiving oral doses of 18 mg/kg/day (180 times the recommended human ophthalmic dose) during gestation were proportional to the reduced maternal weight gain, with no statistically significant effects on organ or tissue development. Increases in unossified sternebrae reduced ossification of the skull, and unossified hyoid that occurred at 6 and 18 mg/kg were not statistically significant. No treatment-related malformations were seen. Following oral administration of 14C-brinzolamide 14Cbrinzolamide to pregnant rats, radioactivity was found to cross the placenta and was present in the fetal tissues and blood.
Developmental toxicity studies performed in rats with oral doses of 0.66 mg brimonidine base/kg revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus. Dosing at this level resulted in a plasma drug concentration approximately 100 times higher than that seen in humans at the recommended human ophthalmic dose. In animal studies, brimonidine crossed the placenta and entered fetal circulation to a limited extent.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Brinzolamide should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Brinzolamide caused urinary bladder tumours in female mice at oral doses of 10 mg/kg/day and in male rats at oral doses of 8 mg/kg/day in 2-year studies. Brinzolamide was not carcinogenic in male mice or female rats dosed orally for up to 2 years. The carcinogenicity appears secondary to kidney and urinary bladder toxicity. These levels of exposure cannot be achieved with topical ophthalmic dosing in humans.
The following tests for the mutagenic potential of brinzolamide were negative: (1) in vivo mouse micronucleus assay, (2) in vivo sister chromatid exchange assay, and (3) the Ames E. coli test. The in vitro mouse lymphoma forward mutation assay was negative in the absence of activation but positive in the presence of microsomal activation. In this assay, there was no consistent dose-response relationship to the increased mutation frequency, and cytotoxicity likely contributed to the high mutation frequency. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, as a class, are not mutagenic, and the weight of evidence supports the fact that brinzolamide is consistent with the class. In reproduction studies of brinzolamide in rats, there were no adverse effects on the fertility or reproductive capacity of males or females at doses up to 18 mg/kg/day (180 times the recommended human ophthalmic dose).
Description
Brinzolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor developed by Alcon (now Novartis) as a treatment for primary and open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. It was First approval in the United States in 1998 under the trade name Azopt. It is the second of this class after dorzolamide (1995). Brinzolamide was approved as a generic medication in the United States in November 2020.Brinzolamide is a white powder commercially formulated as a 1% ophthalmic suspension to reduce intraocular pressure (IOP). In patients with primary open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension, brinzolamide produced significant reductions in IOP and showed less ocular discomfort than dorzolamide.
Chemical properties
Brinzolamide has a molecular weight of 383.5 and a melting point of about 131°C. It is a white powder or crystalline Solid, which is insoluble in water, very soluble in methanol and soluble in ethanol.
Originator
Alcon (US)
The Uses of Brinzolamide
Brinzolamide is a sulfonamide and carbonic anhydrase inhibitor with specific affinity for carbonic anhydrase II. Following topical ocular administration, brinzolamide inhibits carbonic anhydrase II, an enzyme that is responsible for the movement of sodium and fluid transport in the eye. This inhibition leads to a decrease in aqueous humor secretion, probably by slowing the formation of bicarbonate ions, and results in a reduction in intraocular pressure. Brinzolamide is used to treat increased pressure in the eye caused by open-angle glaucoma.
The Uses of Brinzolamide
Brinzolamide has been used as a melanin binding compound or drug in melanin binding assays. It has also been used as a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor (CAI).
Background
Brinzolamide is a highly specific, non-competitive, reversible carbonic anhydrase II (CA-II) inhibitor indicated to reduce ocular pressure in patients with ocular hypertension or open-angle glaucoma. Although the exact pathophysiology of glaucoma is still unknown, one of the main hallmarks of this disease is vascular dysregulation and abnormalities. The resulting vascular resistance increases intraocular pressure, thus impairing ocular perfusion. Although systemic anti-carbonic anhydrase (CA) therapy has been used for almost 50 years with varying degrees of success, systemic administration results in an increase in incidences of adverse effects.
Brinzolamide was developed as a topical solution to the systemic side effects and dorzolamide, the first-ever approved topical CA inhibitor with contrasting results and evidence. Unlike dorzolamide, brinzolamide has a higher lipophilicity to facilitate diffusion across the blood-retinal barrier. Brinzolamide was approved by the FDA in 1998 as a standalone product and in 2013 as a combination product with brimonidine tartrate. In Europe, it was also approved as a combination product with timolol in 2008.
Indications
Brinzolamide, a heterocyclic sulfonamide, is a topical CAI suspension with a high affinity for the carbonic anhydrase II isoenzyme. Because the ocular hypotensive effect of the drug is equivalent whether dosed twice or three times daily, brinzolamide 1% may be administered twice daily. Brinzolamide, either as a standalone agent or in combination with brimonidine, is approved by the FDA for the treatment of elevated intraocular pressure in patients with ocular hypertension or open-angle glaucoma. Brinzolamide has also been approved in Europe to be combined with timolol to treat the same conditions.
Definition
ChEBI: Brinzolamide is a sulfonamide and a thienothiazine. It has a role as an antiglaucoma drug and an EC 4.2.1.1 (carbonic anhydrase) inhibitor.
Preparation
Brinzolamide synthesis method: using thiophene as raw material, 3-acetyl-2,5-dichlorothiophene (4) is obtained by chlorination and acetylation, and 4 is reacted with sodium benzyl sulfide to obtain 6,6, which is chlorinated and ammoniated. Chemical and oxidation reactions "one-pot" synthesis of 7, Carbon-based α-hydrobromination of 7 with Pyridinium tribromide gives 9,9 is asymmetrically reduced under the action of (+)-Ipc2BCl to obtain 11, which is then subjected to N-alkylation and sulfonamidation to generate (S)-3,4-dihydro-4-hydroxy-2-(3-methoxyl propyl)-2H-thieno[3,2-e]-1,2-thiazine-6-sulfonamide-1,1-dioxide, the sulfonamide group was protected with trimethyl orthoacetate to give 15 , first introduce p-toluenesulfonyl group and then replace it with ethylamino group, and remove the sulfonamide group protecting group to obtain brinzolamide. The synthesis of intermediate 4 in this route is convenient, and each step of the reaction does not require column chromatography, and the total yield is 13.4%.
Graphical Synthetic Routes of Olanzapine
brand name
Azopt (Alcon).
Therapeutic Function
Antiglaucoma
General Description
Brinzolamide is a small molecular weight compound that has an ability to bind melanin. This drug is used in ocular therapy.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Brinzolamide is a carbonic anhydrase II inhibitor used to lower intraocular pressure.
Clinical Use
Brinzolamide is indicated for the treatment of elevated IOP in patients with ocular hypertension or open-angle glaucoma.The drug is commercially available as a sterile 1.0% aqueous suspension with a pH of approximately 7.5. BAC 0.01% is added as a preservative.
The efficacy and safety of brinzolamide 1%, either two or three times daily, were evaluated in 572 patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension against timolol 0.5% twice daily and dorzolamide 2.0% three times daily. Mean IOP changes were -3.8 to -5.7 mm Hg, -4.2 to -5.6 mm Hg, and-4.3 to-5.9 mm Hg for two- and three-times-daily brinzolamide and dorzolamide dosing, respectively. The mean IOP changes for timolol 0.5% ranged from -5.6 to -6.3 mm Hg (Figure 10-15). Brinzolamide was well tolerated, with 1.8% (twice daily) and 3% (three times daily) of patients reporting ocular discomfort versus 16.4% with dorzolamide. Complaints of blurred vision were higher with brinzolamide (5–6%) than dorzolamide (1%) or timolol (0%).
A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials reported peak ocular hypotensive effect on IOP of 17% (19% to 15%) and trough effect of 17% (19% to 15%).
Side Effects
Both brinzolamide and dorzolamide exhibit similar taste abnormalities. A single case report of the development of metabolic acidosis from topical brinzolamide has been described after twice-daily dosing. Other adverse events are negligible for brinzolamide except for some blurring of vision, attributable to its suspension vehicle.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Brinzolamide is chemically similar to dorzolamide and reduces aqueous humor production by altering H+/Na+ active transport mechanisms associated with aqueous humor production in the ciliary epithelial cells. It can be used as a substitute for dorzolamide and some patients that exhibit excessive topical irritation following application of dorzolamide drops, tolerate brinzolamide better or vice versa. Cats seem to be particularly sensitive to irritation from topical dorzolamide and often brinzolamide can be used in these patients. Comparative data is available suggesting that brinzolamide and dorzolamide are equally effective in animal patients.
Research
Inhibition of carbonic anhydrase II (CA-II) in the ciliary process of the eye slows the formation of bicarbonate and, thus, fluid flow, lowering intraocular pressure (IOP).
The IOP-reducing effect of brinzolamide as adjunctive therapy to the prostaglandin analogue travoprost was studied. Following a 4-week run-in with travoprost, patients with an IOP ≥19 mmHg were randomized to receive added treatment with brinzolamide or timolol. An additional decrease in mean diurnal IOP of 3.2 to 3.4 mmHg for the brinzolamide group and 3.2 to 4.2 mmHg for the timolol group was observed. There was a higher incidence of non-serious ocular adverse reactions, mainly related to signs of local irritation, in the brinzolamide/travoprost groups. The events were mild and did not affect the overall discontinuation rates in the studies.
A clinical trial was conducted with brinzolamide in 32 pediatric patients less than 6 years of age diagnosed with glaucoma or ocular hypertension. Some patients were naive to IOP therapy, whilst others were on other IOP-lowering medicinal product(s). Those who had been on previous IOP medicinal products were not required to discontinue their IOP medicinal product(s) until the initiation of monotherapy with brinzolamide.
Among patients who were naive to IOP therapy (10 patients), the efficacy of brinzolamide was similar to that seen previously in adults, with mean IOP reductions from baseline ranging up to 5 mmHg. Among patients on topical IOP-lowering medicinal products (22 patients), mean IOP increased slightly from baseline in the brinzolamide group.
Metabolism
Brinzolamide is metabolized by hepatic cytochrome P450 isozymes, specifically CYP3A4, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8 and CYP2C9. The primary metabolite is N-desethylbrinzolamide followed by the N-desmethoxypropyl and O-desmethyl metabolites as well as an N-propionic acid analog formed by oxidation of the N-propyl side chain of O-desmethyl brinzolamide. Brinzolamide and N-desethylbrinzolamide do not inhibit cytochrome P450 isozymes at concentrations at least 100-fold above maximum systemic levels.
Brimonidine is extensively metabolized by hepatic aldehyde oxidase with the formation of 2-oxobrimonidine, 3-oxobrimonidine, and 2,3-dioxobrimonidine being the major metabolites. Oxidative cleavage of the imidazoline ring to 5-bromo-6-guanidinoquinoxaline is also observed.
Precautions
Brinzolamide has the same contraindications and precautions as dorzolamide.
References
[1] desantis l. preclinical overview of brinzolamide. surv ophthalmol. 2000 jan;44 suppl 2:s119-29.
Properties of Brinzolamide
| Melting point: | 130.0 to 134.0 °C |
| Boiling point: | 586.0±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.50±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO: ≥10mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 9.62±0.40(Predicted) |
| color | white to beige |
| Merck | 14,1376 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 138890-62-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Brinzolamide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Brinzolamide
| InChIKey | HCRKCZRJWPKOAR-JTQLQIEISA-N |
Brinzolamide manufacturer
Century Pharmaceuticals Limited
Jai Radhe Sales
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Brinzolamide 98%View Details
Brinzolamide 98%View Details -
 Brinzolamide 98%View Details
Brinzolamide 98%View Details -
 Brinzolamide 99%View Details
Brinzolamide 99%View Details -
 Brinzolamide 98%View Details
Brinzolamide 98%View Details -
 Brinzolamide 95.00% CAS 138890-62-7View Details
Brinzolamide 95.00% CAS 138890-62-7View Details
138890-62-7 -
 Brinzolamide Api Powder Manufacturer India, Grade Standard: Reagent GradeView Details
Brinzolamide Api Powder Manufacturer India, Grade Standard: Reagent GradeView Details
138890-62-7 -
 Brinzolamide API Powder, Grade Standard: Technical GradeView Details
Brinzolamide API Powder, Grade Standard: Technical GradeView Details
138890-62-7 -
 BRINZOLAMIDEView Details
BRINZOLAMIDEView Details
138890-62-7
