Dexmedetomidine
- CAS NO.:113775-47-6
- Empirical Formula: C13H16N2
- Molecular Weight: 200.28
- MDL number: MFCD00880557
- EINECS: 601-281-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 15:53:33
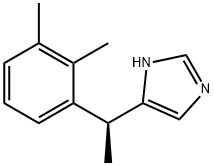
What is Dexmedetomidine?
Chemical properties
White Solid
The Uses of Dexmedetomidine
Dexmedetomidine is a sedative drug that has many benefits when given to children under anesthesia, such as improved pain relief and reduced agitation following their surgery. The FDA-approved indications for dexmedetomidine are sedation of intubated and mechanically ventilated patients in the intensive care unit (ICU) and peri-procedural (or peri-operative) sedation of non-intubated patients.
Background
An agonist of receptors, adrenergic alpha-2 that is used in veterinary medicine for its analgesic and sedative properties. It is the racemate of dexmedetomidine.
Indications
Administered intravenously, dexmedetomidine is indicated for the sedation of initially intubated and mechanically ventilated patients during treatment in intensive care settings, and for the sedation of non-intubated patients prior to and/or during surgery and other procedures. It is also available as a buccally- or sublingually-administered dissolvable film for the acute treatment of agitation associated with schizophrenia or bipolar I or II disorder.
Definition
ChEBI: Dexmedetomidine is a medetomidine. It has a role as an alpha-adrenergic agonist, a non-narcotic analgesic, an analgesic and a sedative. It is an enantiomer of a levomedetomidine.
brand name
Precedex (Hospira).
Pharmacokinetics
Dexmedetomidine activates 2-adrenoceptors, and causes the decrease of sympathetic tone, with attenuation of the neuroendocrine and hemodynamic responses to anesthesia and surgery; it reduces anesthetic and opioid requirements; and causes sedation and analgesia.
Side Effects
This drug is most commonly given to cause sedation, so extreme sedation/lethargy for a short period of time is an expected side effect. Pale gums and lowered heart and respiratory rates can occur. Rarely, vomiting, diarrhea, and collapse may occur. When injected into the muscle, this medication can cause temporary pain at the injection site.
Metabolism
Hepatic
Mode of action
The mechanism of action of dexmedetomidine is as an Adrenergic alpha2-Agonist. Dexmedetomidine selectively binds to presynaptic alpha-2 adrenoceptors located in the brain, thereby inhibiting the release of norepinephrine from synaptic vesicles. This leads to an inhibition of postsynaptic activation of adrenoceptors, which inhibit sympathetic activity, thereby leading to sedation and anxiolysis. The analgesic effect of this agent is mediated by binding to alpha-2 adrenoceptors in the spinal cord.
References
https://www.statpearls.com/articlelibrary/viewarticle/20424/
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/dexmedetomidine
https://www.drugs.com/mtm/dexmedetomidine.html
Dexmedetomidine: A Review of Its Use for Sedation in the Intensive Care Setting DOI: 10.1007/s40265-015-0419-5
Properties of Dexmedetomidine
| Melting point: | 146-149°C |
| Boiling point: | 381.9±11.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.053±0.06 g/cm3 (20 ºC 760 Torr) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO > 10 mM |
| form | Powder |
| pka | 13.89±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White to off-white |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C13H16N2/c1-9-5-4-6-12(10(9)2)11(3)13-7-14-8-15-13/h4-8,11H,1-3H3,(H,14,15)/t11-/m0/s1 |
Safety information for Dexmedetomidine
Computed Descriptors for Dexmedetomidine
| InChIKey | CUHVIMMYOGQXCV-NSHDSACASA-N |
| SMILES | C1NC([C@H](C2=CC=CC(C)=C2C)C)=CN=1 |
Dexmedetomidine manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 113775-47-6 Dexmedetomidine 98%View Details
113775-47-6 Dexmedetomidine 98%View Details
113775-47-6 -
 113775-47-6 98%View Details
113775-47-6 98%View Details
113775-47-6 -
 113775-47-6 98%View Details
113775-47-6 98%View Details
113775-47-6 -
 Dexmedetomidine 95% CAS 113775-47-6View Details
Dexmedetomidine 95% CAS 113775-47-6View Details
113775-47-6 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1