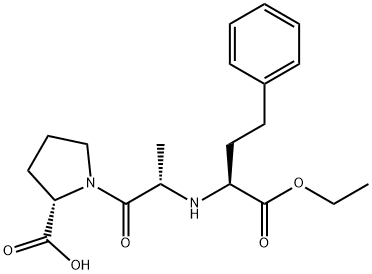
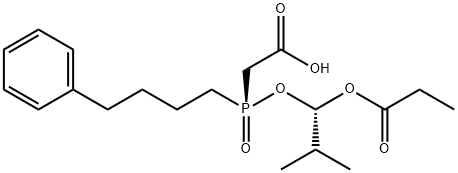
Fosinopril sodium
Synonym(s):Fosinopril;Monopril;Secorvas;Staril;(2S,4S)-4-Cyclohexyl-1-(2-{[2-methyl-1-(propanoyloxy)propoxy](4-phenylbutyl)phosphoryl}acetyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid
- CAS NO.:88889-14-9
- Empirical Formula: C30H46NNaO7P
- Molecular Weight: 586.65
- MDL number: MFCD00897699
- EINECS: 1312995-182-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
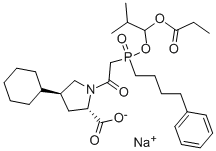
What is Fosinopril sodium?
Description
Fosinopril sodium, an ester prodrug of fosinoprilat, is the first of a new generation of phosphinic acid ACE inhibitors indicated for the once-daily treatment of hypertension. Unlike captopril and lisinopril, it is reportedly effective in increasing the left ventricular peak filling rates and peak ejection rates in hypertensive patients at rest. Another advantage is that fosinopril sodium is metabolized equally by renal and hepatic routes, thereby avoiding the requirement to modify dosage in patients with renal insufficiency.
Chemical properties
White to Off-White Crystalline Solid
Originator
Bristol-Myers Squibb (U.S.A.)
The Uses of Fosinopril sodium
Fosinopril sodium is the ester prodrug of an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, used for the treatment of hypertension and some types of chronic heart failure.
The Uses of Fosinopril sodium
A phosphinic acid containing angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. Antihypertensive.
The Uses of Fosinopril sodium
A labelled phosphinic acid containing angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor.
What are the applications of Application
Fosinopril sodium is an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: The sodium salt of fosinopril. It is used for the treatment of hypertension and heart failure. A pro-drug, its phosphinate ester group is hydrolysed in vivo to give the corresponding phosphininc acid, fosinoprilat, which is the active metaboli e.
Manufacturing Process
To a solution of 4-phenylbutyl phosphinic acid (2.0 g, 0.01 mole) in
chloroform (40 ml) was added triethylamine (3.2 ml, 0.022 mole) and the
mixture was cooled in an ice bath to 0°C. Trimethylsilyl chloride (2.8 ml,
0.022 mole) was added to the above solution dropwise, followed by benzyl
bromoacetate (1.6 ml, 0.011 mole). The ice bath was removed and the
mixture stirred at room temperature for 5 hours and poured into 10%
aqueous HCl (30 ml) and crushed ice (20 g). After shaking the mixture in a
separatory funnel, the chloroform layer was separated and the aqueous layer
was extracted with dichloromethane. The combined organic phase was washed
with brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and the solvents removed in
vacuum. The resulting crude thick oil (3.5 g) was dissolved in 30 ml ether,
hexane was added dropwise to get a turbid solution and the mixture was left
at room temperature overnight to complete the crystallization. It was cooled
in the freezer for 2 hours, filtered and the solid was washed very thoroughly
with hexane (50 ml), ether (50 ml) and again hexane (50 ml), ether (50 ml)
in that order. The solid was vacuum dried to get 2.48 g (71%) of [hydroxy-(4-phenylbutyl)-phosphinyl]acetic acid, phenylmethyl ester, m.p. 68-70°C. TLC
(Silica gel, CH2Cl2:MeOH:HOAc (20:1:1)) shows a single spot.
A solution of 50 g (0.14 mole) of [hydroxy-(4-phenylbutyl)-phosphinyl]acetic
acid, phenylmethyl ester in 300 ml of dry CHCl3 was treated with 28.6 g (0.28
mole) of Et3N, 35.6 g (0.21 mole) of 1-chloroisobutyl propionate, 12.0 g
(0.035 mole) of (n-Bu)4NHSO4 and 5.3 g (0.035 mole) of NaI. The above
mixture was stirred and heated to mild reflux for 20 hours, then cooled and
the solvent evaporated in vacuo. The oil residue was dissolved in 150 ml of
ether and washed with 150 ml of water. The aqueous wash was extracted with
150 ml of ether. The combined ether solutions were washed with 5% NaHCO3,
10% NaHSO3 and brine. After drying (MgSO4) the ether was evaporated in
vacuo to give 57.0 g (83%) of crude [[2-methyl-1-(1-oxopropoxy)propoxy](4-
phenylbutyl)phosphinyl]acetic acid, phenyl methyl ester as an oil product.
A solution of 57.0 g (0.12 mole) of [[2-methyl-1-(1-oxopropoxy)propoxy](4-
phenylbutyl)phosphinyl]acetic acid, phenyl methyl ester in 300 ml of ethyl
acetate was treated with 3.0 g of 10% Pd/C and hydrogenated on the Parr
apparatus (45 psi) for 4 hours. The mixture was filtered through Hyflo and the
solution was extracted with 5% NaHCO3. The aqueous extracts were washed
with ether, cooled to 5°C and treated with 36 ml of HOAc. The product was
extracted into ethyl acetate, dried (MgSO4) and the solvent was evaporated in
vacuo. The residue was dissolved in 300 ml of toluene and the solvent was
evaporated in vacuo to remove last traces of acetic acid. The oil residue
became semi-solid on standing at room temperature. The yield of the product
of debenzoylation - 2-[carboxymethyl)-(4-phenylbutyl)-phosphinoyloxy]-2-
methylpropionic acid ethyl ester (racemic mixtures) was 39.8 g (72%).
A suspension of 10.0 g (0.026 mole) of [[2-methyl-1-(1-oxopropoxy)propoxy]
(4-phenylbutyl)phosphinyl]acetic acid in 50 ml of isopropyl ether was stirred
vigorously for 15 min, then kept at 5°C for 20 hours. The colorless product
was filtered, washed with a small amount of cold isopropyl ether to give 5.0 g
of [[2-methyl-1-(1-oxopropoxy)propoxy](4-phenylbutyl)phosphinyl]acetic acid
(A/B isomer, racemic mixture) , m.p. 87-89°C. The filtrate was evaporated in
vacuo and retained for isolation of isomer C/D. A solution of the above
material in 110 ml of hot isopropyl ether was filtered through a hot glass
funnel (glass wool). The cooled solution gave 4.6 g (92%) of desired product,
m.p. 90-92°C.
To a vigorously stirred suspension of 980 g (3.33 mol) of l-cinchonidine in 6 L
of ethyl acetate maintained at 45°C was gradually added 1275.5 g (3.33 mol)
of A/B isomer mixture and stirring then continued for an additional 2.5 hours
while the resulting suspension of salt was gradually heated to 70°C when
complete solution was obtained. After filtration (Hyflo) from a small amount of
insoluble material, the solution was seeded and cooled. The crystalline product
which separated was then filtered, washed with 1200 ml of 1:1 ethyl
acetate/isopropyl ether, and dried in vacuo to give 1897.2 g of cinchonidine
salt enriched in the B-isomer, m.p. 106-109°C, [α]D = -59.3° (c = 1,
methanol). This material was combined with 136.8 g of similarly prepared
material (from 0.412 mol of A/B isomer) and the total quantity (2014 g)
recrystallized from 10.18 L of boiling ethyl acetate to afford after filtration,
washing with 1500 ml of the same solvent mixture used before, and drying in
vacuo 1162 g (92%) of [[2-methyl-1-(1-oxopropoxy)propoxy](4-phenylbutyl) phosphinyl]acetic acid (Resolution; isomer B), cinchonidine salt (1:1), m.p.
120-122°C (dec.), [α]D= -45° (c = 1, methanol), [α]365 = -185.5° (c = 1,
methanol). A sample (10 g) was recrystallized twice from acetonitirle and
three times from ethyl acetate additionally to give salt of m.p. 125-126°C
(dec.), [α]D= -42.2°.
A slurry of methyl-1-(1-oxopropoxy)propoxy](4-phenylbutyl)phosphinyl]acetic
acid (B-isomer), dried in vacuo at room temperature for 72 hours, (230.4 g,
0.6 moles) and hydroxybenzotriazole hydrate, dried, in vacuo at 80°C for 24
hours, (101.1 g, 0.66 mole) dichloromethane (sieved dried) (6 L) was chilled
in an ice/acetone bath and treated with N,N-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (136 g,
0.66 mole). The mixture was warmed to room temperature and stirred for 3
hours. The mixture was then chilled in ice/acetone and treated with (trans)-4-
cyclohexyl-L-proline, hydrochloride (154.2 g, 0.66 mole) followed by
diisopropylethylamine (170.7 g, 1.32 mole). The reaction mixture was stirred
at room temperature for 18 hours. The mixture was then chilled, treated with
water (1 L) and concentrated in vacuo to remove dichloromethane. The
residue was diluted with ether (3600 ml) and water (3600 ml) and filtered.
The filtrate was brought to pH = 1.8 with 10% hydrochloric acid. The ether
layer was separated and the aqueous layer washed with ethyl acetate (3 x 2
L). The combined organic layers were washed with 5% KHSO4 (3 x 1 L), water
(3 x 1 L) and brine (1 L), dried over magnesium sulfate and concentrated in
vacuo to yield 398.9 g of crude [R,1S,4S]-4-Cyclohexyl-1-[[[2-methyl-1-(1-
oxopropoxy)propoxy](4-phenylbutyl)phosphinyl]acetyl]-L-proline, monosodium
salt (isomer B). The crude product was dissolved in acetone (4393 ml),
treated with a solution of 2-ethyl hexanoic acid, sodium salt (117.3 g) in
acetone (1468 ml), then stirred at room temperature overnight. The resultant
precipitate was collected by filtration, washed with acetone (3 x 400 ml) and
hexane (1 L) then dried in vacuo. Yield 277 g, m.p. 195-196°C, [α]D= -5.1°
(MeOH, c = 2), HI = 99.8%. Isomer "A" was not detectable.
brand name
Monopril (Bristol-Myers Squibb);Staril.
Therapeutic Function
Antihypertensive
General Description
Fosinopril sodium, (4S)-4-cyclohexyl-1-[[[(RS)-1-hydroxy-2-methylpropoxy](4-phenylbutyl)phosphinyl]acetyl]-L-proline sodium salt (Monopril),is a phosphorus-containing ACE inhibitor. It is inactive butserves as a prodrug, being completely hydrolyzed by intestinaland liver enzymes to the active diacid fosinoprilat.
Clinical Use
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor:
Hypertension
Heart failure
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anaesthetics: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Analgesics: antagonism of hypotensive effect and
increased risk of renal impairment with NSAIDs;
hyperkalaemia with ketorolac and other NSAIDs.
Antihypertensives: increased risk of hyperkalaemia,
hypotension and renal failure with ARBs and
aliskiren.
Bee venom extract: possible severe anaphylactoid
reactions when used together.
Ciclosporin: increased risk of hyperkalaemia and
nephrotoxicity.
Cytotoxics: increased risk of angioedema with
everolimus.
Diuretics: enhanced hypotensive effect;
hyperkalaemia with potassium-sparing diuretics.
ESAs: increased risk of hyperkalaemia; antagonism
of hypotensive effect.
Gold: flushing and hypotension with sodium
aurothiomalate.
Lithium: reduced excretion, possibility of enhanced
lithium toxicity.
Potassium salts: increased risk of hyperkalaemia.
Tacrolimus: increased risk of hyperkalaemia and
nephrotoxicity.
Metabolism
Fosinopril acts as a prodrug of the diacid fosinoprilat, its
active metabolite. Fosinopril is rapidly and completely
hydrolysed to fosinoprilat in both gastrointestinal mucosa
and liver.
Fosinoprilat is excreted both in urine and in the faeces via
the bile.
References
[1] shionoiri h, naruse m, minamisawa k, ueda s, himeno h, hiroto s, takasaki i. fosinopril. clinical pharmacokinetics and clinical potential. clin pharmacokinet. 1997 jun;32(6):460-80.
Properties of Fosinopril sodium
| Melting point: | 196-198°C |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | H2O: >20mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| color | white to off-white |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 88889-14-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Fosinopril sodium
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Fosinopril sodium
Fosinopril sodium manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![sodium:(2S,4S)-4-cyclohexyl-1-[2-[(2-methyl-1-propanoyloxypropoxy)-[4-(2,3,4,5,6-pentadeuteriophenyl)butyl]phosphoryl]acetyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylate](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20180527/GIF/1217513-43-3.gif)
You may like
-
 88889-14-9 Fosinopril sodium 98%View Details
88889-14-9 Fosinopril sodium 98%View Details
88889-14-9 -
 88889-14-9 98%View Details
88889-14-9 98%View Details
88889-14-9 -
 Fosinopril sodium CAS 88889-14-9View Details
Fosinopril sodium CAS 88889-14-9View Details
88889-14-9 -
 Fosinopril sodium 98.00% CAS 88889-14-9View Details
Fosinopril sodium 98.00% CAS 88889-14-9View Details
88889-14-9 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1