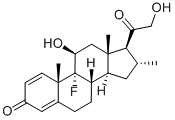
Betamethasone
Synonym(s):9α-Fluoro-11β,17α,21-trihydroxy-16β-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione;9α-Fluoro-16β-methyl-11β,17α,21-trihydroxy-1,4-pregnadiene-3,20-dione;9α-Fluoro-16β-methylprednisolone;Betamethasone;Betamethasone valerate impurity A (PhEur)
- CAS NO.:378-44-9
- Empirical Formula: C22H29FO5
- Molecular Weight: 392.47
- MDL number: MFCD00062969
- EINECS: 206-825-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-10-29 15:43:00
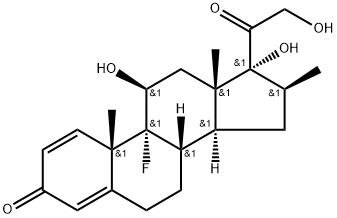
What is Betamethasone?
Absorption
The absorption and potency of any topical corticosteroid including betamethasone depends on the vehicle in which the steroid is delivered. For example, betamethasone dipropionate 0.05% ointment is classified as a highly potent topical steroid, while betamethasone dipropionate 0.05% cream or lotion is considered to be moderately potent.
There are several structural modifications that can determine the potency of a topical corticosteroid. For example, corticosteroids containing a halogen at specific carbons, or that contain esters are more potent due to enhanced lipophilicity. As such, there is a marked difference between topical products containing betamethasone dipropionate vs. betamethasone valerate. Betamethasone dipropionate contains 2 esters which enhances its potency, while betamethasone valerate has only one ester and is less potent.
It should be noted that the use of occlusive dressings with topical steroids significantly increases the absorption, increasing the risk for adverse effects.
Toxicity
Chronic high doses of glucocorticoids can lead to the development of cataracts, glaucoma, hypertension, water retention, hyperlipidemia, peptic ulcer, pancreatitis, myopathy, osteoporosis, mood changes, psychosis, dermal atrophy, allergy, acne, hypertrichosis, immune suppression, decreased resistance to infection, moon face, hyperglycemia, hypocalcemia, hypophosphatemia, metabolic acidosis, growth suppression, and secondary adrenal insufficiency. Overdose may be treated by adjusting the dose or stopping the corticosteroid as well as initiating symptomatic and supportive treatment.
Description
Shortly after the introduction of dexamethasone, betamethasone, which differs from dexamethasone only in configuration of the 16-methyl group, was made available for the treatment of rheumatic diseases and dermatologic disorders. This analogue, which contains a 16β-methyl group, has received sufficient clinical trial examination to indicate that it is as effective as dexamethasone or, perhaps, even slightly more active. Although this drug has been reported to be less toxic than other steroids, some clinical investigators suggest that it is best used for short-term therapy.
Description
Betamethasone is a synthetic corticosteroid. Like other corticosteroids, betamethasone has anti-inflammatory actions. Betamethasone also accelerates fetal lung maturation and has been used to decrease neonatal mortality and morbidity in infants born before 34 weeks of gestation.
Chemical properties
White to Off-White Solid
Originator
Celestone,Schering,US,1961
The Uses of Betamethasone
Betamethasone is a glucocorticoid used as an anti-inflammatory agent.
The Uses of Betamethasone
glucocorticoid, antiinflammatory
The Uses of Betamethasone
anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive
Background
Betamethasone is a long-acting corticosteroid with immunosuppressive and antiinflammatory properties. It can be used topically to manage inflammatory skin conditions such as eczema, and parenterally to manage several disease states including autoimmune disorders. Betamethasone has potent glucocorticoid activity and negligible mineralocorticoid activity.
Indications
As a member of the corticosteroid family, betamethasone is indicated for the treatment of several inflammatory conditions. As topical monotherapy, betamethasone is indicated to relieve pruritic and inflammatory symptoms of corticosteroid-responsive-dermatoses. Betamethasone can be used topically in combination with a vitamin D analog such as calcipotriene to treat plaque psoriasis. The corticosteroid is also available as an injectable suspension and can be used to manage a range of inflammatory conditions including endocrine disorders, gastrointestinal disorders, and rheumatic disorders among other conditions.
What are the applications of Application
Betamethasone is a glucocorticoid that induces gene expression and apoptosis
Definition
ChEBI: Betamethasone is a glucocorticoid, a 20-oxo steroid, a 21-hydroxy steroid, a 17alpha-hydroxy steroid, a fluorinated steroid, an 11beta-hydroxy steroid, a 3-oxo-Delta(1),Delta(4)-steroid, a primary alpha-hydroxy ketone and a tertiary alpha-hydroxy ketone. It has a role as an anti-inflammatory drug, an anti-asthmatic agent and an immunosuppressive agent. It derives from a hydride of a pregnane.
Manufacturing Process
Betamethasone acetate is converted to betamethasone by means of hydrochloric acid in a methanol-chloroform-water mixture as described in US Patent 3,164,618.
brand name
Celestone Syrup and Tablets (Schering).
Therapeutic Function
Glucocorticoid
General Description
Betamethasone, 9-fluoro-11β,17,21-trihydroxy-16β-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione,is available as a variety of ester derivatives.
Betamethasone valerate, USP (17-valerate)
Betamethasone acetate, USP (21-acetate)
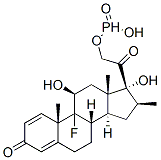
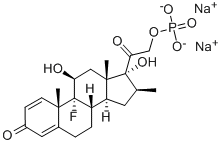
Betamethasone sodium phosphate, USP (21-sodiumphosphate)
Betamethasone dipropionate, USP (17-propionate,21-propionate).
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Biochem/physiol Actions
Betamethasone, an?isomer?of dexamethasone is also termed as 9α-fluoro-16β-methyl-11 β,17,21-trihydroxypregna-1,4-dien-3,20-dione or 9α-fluoro-16β-methylprednisolone (27.1.52). It can be used as an anti-itch agent and treating dermatitis?and?eczema.
Pharmacokinetics
Corticosteroids bind to the glucocorticoid receptor inhibiting pro-inflammatory signals, while promoting anti-inflammatory signals. Corticosteroids have a wide therapeutic window as patients may require doses that are multiples of what the body naturally produces. Patients who require long-term treatment with a corticosteroid should be counselled regarding the risk of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis suppression and increased susceptibility to infections.
Clinical Use
Corticosteroid:
Suppression of inflammatory and allergic disorders
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Side Effects
Toxic side effects, such as increased appetite, weight gain, and facial mooning, occur with prolonged use.
Safety Profile
Low toxicity by ingestion. Anexperimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductiveeffects. When heated to decomposition it emits toxicfumes of F-.
Synthesis
Betamethasone is 9α-fluoro-16β-methyl-11 β,17,21-trihydroxypregna- 1,4-dien-3,20-dione, or simply 9α-fluoro-16β-methylprednisolone (27.1.52). As seen from the chemical name of the drug, betamethasone only differs from dexamethasone in the orientation of the methyl group at C16. The proposed method of synthesis differs from the other method in a number of details and successive reactions besides the first stage, in particular concerning the addition of the methyl group at C16 of the steroid ring. Betamethasone, like dexamethasone, is synthesized from 3α-acetoxy-16-pregnen-11,20-dione; however, the methyl group at C16 of the steroid ring is not reacted with methylbromide, but rather is reacted with diazomethane followed by hydrogenation of the double bond between carbon atoms C16–C17 of the steroid ring using a palladium on carbon catalyst, which results in the corresponding β-orientation of the introduced methyl group.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Aldesleukin: avoid concomitant use.
Antibacterials: metabolism accelerated by rifampicin;
metabolism possibly inhibited by erythromycin;
concentration of isoniazid possibly reduced.
Anticoagulants: efficacy of coumarins and
phenindione may be altered.
Antiepileptics: metabolism accelerated by
carbamazepine, fosphenytoin, phenobarbital,
phenytoin and primidone.
Antifungals: increased risk of hypokalaemia with
amphotericin - avoid; metabolism possibly inhibited
by itraconazole and ketoconazole.
Antivirals: concentration possibly increased by
ritonavir.
Ciclosporin: rare reports of convulsions in patients
on ciclosporin and high-dose corticosteroids.
Cobicistat: concentration of betamethasone possibly
increased.
Diuretics: enhanced hypokalaemic effects of
acetazolamide, loop diuretics and thiazide diuretics.
Vaccines: high dose corticosteroids can impair
immune response to vaccines; avoid with live
vaccines.
Metabolism
The metabolism of betamethasone yields 6 metabolites. The metabolic processes include 6β hydroxylation, 11β-hydroxyl oxidation, and reduction of the C-20 carbonyl group followed by removal of the side chain.
Metabolism
Corticosteroids are metabolised mainly in the liver but also in other tissues, and are excreted in the urine. The slower metabolism of the synthetic corticosteroids with their lower protein-binding affinity may account for their increased potency compared with the natural corticosteroids.
Purification Methods
Betamethasone crystallises from ethyl acetate, and has max at 238nm (log 4.18) in MeOH. The 21-acetate [287-24-6] crystallises from Me2CO/Et2O (charcoal) m 196-201o (205-208o) and has [] D 20 +140o (CHCl3). [Taub et al. J Am Chem Soc 82 4012 1960, Olivetto et al. J Am Chem Soc 80 6688 1958, Beilstein 8 IV 3501.]
References
[1] pharmacology review(s)-fda.
Properties of Betamethasone
| Melting point: | 235-237°C |
| Boiling point: | 568.2±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D +108° (acetone) |
| Density | 1.1283 (estimate) |
| refractive index | 118 ° (C=1, Dioxane) |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, sparingly soluble in anhydrous ethanol, very slightly soluble in methylene chloride. |
| form | neat |
| pka | 12.13±0.70(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | 58mg/L(25 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,1180 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 378-44-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, 9alpha-fluoro-11beta,17alpha,21-trihydroxy-16beta-methyl-(378-44-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, 9-fluoro-11,17,21-trihydroxy-16-methyl-, (11.beta.,16.beta.)- (378-44-9) |
Safety information for Betamethasone
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Betamethasone
Betamethasone manufacturer
Clickchem Research LLP
Akhil Healthcare Private Limited
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
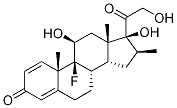
You may like
-
 378-44-9 98%View Details
378-44-9 98%View Details
378-44-9 -
 Betamethasone Valerate EP Impurity A 98%View Details
Betamethasone Valerate EP Impurity A 98%View Details
378-44-9 -
 Betamethasone 99%View Details
Betamethasone 99%View Details -
 Betamethasone 99%View Details
Betamethasone 99%View Details -
 Betamethasone CAS 378-44-9View Details
Betamethasone CAS 378-44-9View Details
378-44-9 -
 Betamethasone 95.00% CAS 378-44-9View Details
Betamethasone 95.00% CAS 378-44-9View Details
378-44-9 -
 Betamethasone 99% (HPLC) CAS 378-44-9View Details
Betamethasone 99% (HPLC) CAS 378-44-9View Details
378-44-9 -
 Technical Grade Powder Betamethasone, Prescription, Packaging Type: PacketsView Details
Technical Grade Powder Betamethasone, Prescription, Packaging Type: PacketsView Details
378-44-9
