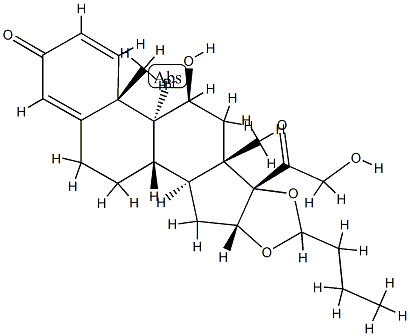
Budesonide
Synonym(s):16,17-Butylidenebis(oxy)-11,21-dihydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
- CAS NO.:51333-22-3
- Empirical Formula: C25H34O6
- Molecular Weight: 430.53
- MDL number: MFCD00083259
- EINECS: 257-139-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-10-29 15:43:00
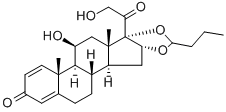
What is Budesonide?
Absorption
Extended release oral capsules are 9-21% bioavailable. A 9mg dose reaches a Cmax of 1.50±0.79ng/mL with a Tmax of 2-8h and an AUC of 7.33ng*hr/mL. A high fat meal increases the Tmax by 2.3h but otherwise does not affect the pharmacokinetics of budesonide.
180-360μg metered inhaled doses of budesonide are 34% deposited in the lungs, 39% bioavailable, and reach a Cmax of 0.6-1.6nmol/L with a Tmax of 10 minutes.
A 1mg nebulized dose is 6% bioavailable, reaching a Cmax of 2.6nmol/L with a Tmax of 20 minutes.
A 9mg oral extended release tablet reaches a Cmax of 1.35±0.96ng/mL with a Tmax of 13.3±5.9h and an AUC of 16.43±10.52ng*hr/mL.
Budesonide rectal foam 2mg twice daily has an AUC of 4.31ng*hr/mL.
Toxicity
Acute overdose of corticosteroids is rare, however prolonged high dosing of corticosteroids can lead to hypercorticism and adrenal axis suppression. In the case of overdose, reduce the dosage of corticosteroids temporarily.
A 200mg oral dose is lethal to female mice while a 400mg oral dose is lethal to male mice.
Description
Budesonide is composed of a 1:1 mixture of epimers of the 16,17-butylacetal, creating a chiral center. The 22R-epimer binds to the GR with higher affinity than does the 22S-epimer (Table 33.5). The butyl acetal chain provided the highest potency for the homologous acetal chains. Its rate of topical uptake into epithelial tissue is more than 100 times faster than that for hydrocortisone and dexamethasone. Approximately 85% of the IV administered dose of budesonide undergoes extensive first-pass hepatic metabolism by CYP3A4 to its primary metabolites, 6β-hydroxybudesonide and 16α-hydroxyprednisolone, which have approximately 1/100 the potency of budesonide. This is an important inactivation step in limiting budesonide's systemic effect on adrenal suppression.
Description
Budesonide is a glucocorticoid and an agonist of glucocorticoid receptors (EC50 = 45.7 pM in a transactivation assay). It is selective for glucocorticoid over mineralocorticoid receptors (EC50 = 7,620 pM). Budesonide inhibits LPS-induced TNF-α release from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs; IC50 = 0.96 nM). It reduces levels of IL-1β and eotaxin in the lungs and the number of eosinophils and neutrophils in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) in a rat model of ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation when administered at a dose of 3 mg/kg. Intracolonic administration of budesonide decreases colon wet weight and colonic myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity in a rat model of oxazolone-induced colitis. Formulations containing budesonide have been used in the treatment of Crohn''s disease, ulcerative colitis, allergic rhinitis, and asthma.
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Budecort,AstraZeneca
The Uses of Budesonide
Budesonide is a glucocorticoid steroid that activates the glucorcorticoid receptor with an EC50 value of 12.4 nM. Like other glucocorticoids, budesonide reduces inflammation and has utility in inflammatory diseases, like asthma and inflammatory bowel disease. Also like other glucocorticoids, budesonide may be abused by athletes.[Cayman Chemical]
The Uses of Budesonide
A non-halogenated glucocorticoid related to triamcinolone hexacetonide. Used as an antiinflammatory agent
The Uses of Budesonide
laxative, antineoplastic
The Uses of Budesonide
The oral capsule is used for the treatment of mild to moderate active Crohn's disease. The oral tablet is used for induction of remission in patients with active, mild to moderate ulcerative colitis. The oral inhalation formulation is used for the treatme
Background
Budesonide is a glucocorticoid that is a mix of the 22R and 22S epimer used to treat inflammatory conditions of the lungs and intestines such as asthma, COPD, Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis.
Budesonide was granted FDA approval on 14 February 1994. It is also available in a combination product with formoterol.
What are the applications of Application
Budesonide is a synthetic anti-inflammatory glucocorticoid
Indications
Budesonide extended release capsules are indicated for the treatment and maintenance of mild to moderate Crohn’s disease. Various inhaled budesonide products are indicated for prophylactic therapy in asthma and to reduce exacerbations of COPD. A budesonide nasal spray is available over the counter for symptoms of hay fever and upper respiratory allergies. Extended-release capsules are indicated to induce remission of mild to moderate ulcerative colitis and a rectal foam is used for mild to moderate distal ulcerative colitis. In addition, a delayed-release capsule formulation of budesonide is indicated to reduce proteinuria in adults with IgA nephropathy at risk of rapid disease progression. In Europe, budesonide is indicated to treat eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) in adults.
Definition
ChEBI: A glucocorticoid steroid having a highly oxygenated pregna-1,4-diene structure. It is used mainly in the treatment of asthma and non-infectious rhinitis and for treatment and prevention of nasal polyposis.
Indications
Budesonide is a synthetic corticosteroid having a potent glucocorticoid and weak mineralocorticoid activity. In standard in vitro and animal models, budesonide has an approximately 200-fold higher affinity for the glucocorticoid receptor and a 1000-fold higher topical antiinflammatory potency than cortisol.
Manufacturing Process
50 grams of desonide (16α-hydroxyprednisolone-16,17-acetonide) and immediately thereafter 12.5 ml of butyraldehyde were added to 500 ml of 70% hydrofluoric acid solution at -5°C, and the mixture was stirred at 0°C one hour and then poured into 5 liters of demineralized water at 0°C. The precipitate was filtered, washed to neutrality with water and dried under vacuum to give 51 g of pure budesonide with an A/B epimer ratio of 9/91.
brand name
Entocort (AstraZeneca); Pulmicort (AstraZeneca); Rhinocort (AstraZeneca).
Therapeutic Function
Corticosteroid
General Description
Budesonide (Pulmicort Turbohaler,Rhinocort) is extensively metabolized in the liver, with 85%to 95% of the orally absorbed drug metabolized by the firstpasseffect. The major metabolites are 6β-hydroxybudesonideand 16α-hydroxyprednisolone, both with less than1% of the activity of the parent compound. Metabolism involvesthe CYP3A4 enzyme, so coadministration of budesonidewith a known CYP3A4 inhibitor should be monitoredcarefully.
General Description
Budesonide, 16α,17-[butylidenebis-(oxy)]-11β,21-dihydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3, 20-dione (Entocort), in oral capsules is used to treat Crohn disease. Theaffinity for the GC is approximately 200-fold greater than thatof hydrocortisone and 15-fold greater than that of prednisolone.Budesonide is a mixture of epimers, with the 22Rform having twice the affinity for the GR of the S epimer.This GC is metabolized by CYP3A4, and its levels can be increasedin the presence of potent CYP3A4 inhibitors.Budesonide is also used in an inhaled formulation for thetreatment of asthma.
Biological Activity
Synthetic anti-inflammatory glucocorticoid that displays chemopreventive activity. Prevents formation of lung adenomas and adenocarcinomas in mice following inhalation or oral administration. Reverses DNA hypomethylation and modulates expression of cancer related genes.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Budesonide is a second generation glucocorticoid with low systemic absorption. It is used as an anti-inflammatory agent in the treatment of asthma, rhinitis, and inflammatory bowel disease. It inhibits the expression of chemokine mRNA and production of eotaxin and RANTES protein in primary human bronchial epithelial cells. Budesonide is currently in clinical trials for the prevention of lung cancer. It shows inhibitory effects on benzo[a]pyrene-induced carcinogenesis of the lung in mice.
Mechanism of action
Budesonide is an acetal formed between the 16α,17α-dihydroxyl groups and butanal. It is a nonhalogenated glucocorticoid with a 16,17-acetal that decreases the mineralocorticoid activity. In receptor affinity studies, the R-epimer was twofold more active than the S-epimer. Because the C-21 hydroxy is free, budesonide is not a prodrug and is active as administered. Only 34% of the metered dose of inhaled budesonide reaches the lung.
Pharmacokinetics
Budesonide is a glucocorticoid used to treat respiratory and digestive conditions by reducing inflammation. It has a wide therapeutic index, as dosing varies highly from patient to patient. Patients should be counselled regarding the risk of hypercorticism and adrenal axis suppression.
Pharmacology
While budesonide is well absorbed from the GI tract, its oral bioavailability is low (about 10%), primarily because of extensive first-pass metabolism in the liver. Two major metabolites (16α-hydroxyprednisolone and 6β- hydroxybudesonide) are formed via the cytochrome P450 3A enzyme. In vitro studies on the binding of the two primary metabolites to the corticosteroid receptor indicate that their affinity for the receptor is less than 1% of that of the parent compound. It is hoped that use of this drug will avoid the long-term adverse reactions seen with systemically active corticosteroids.
Clinical Use
Recently, budesonide (Entecort EC) has been approved for the treatment of mildly to moderately active Crohn’s disease involving the ileum and/or ascending colon.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
While there are inhalational forms of the medication for treating asthma or allergic rhinitis, most veterinary interest involves its potential oral use to treat inflammatory intestinal diseases in small animals that are either refractory to, or intolerant of, systemic steroids. In humans, oral budesonide is indicated for Crohn’s disease.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Aldesleukin: avoid concomitant use.
Antibacterials: metabolism accelerated by rifamycins.
Anticoagulants: efficacy of coumarins and
phenindione may be altered.
Antiepileptics: metabolism accelerated by
carbamazepine, fosphenytoin, phenobarbital,
phenytoin and primidone.
Antifungals: concentration of inhaled and oral
budesonide increased by itraconazole and ketoconazole.
Antivirals: concentration of inhaled, intranasal and
rectal budesonide increased by ritonavir.
Cobicistat: concentration possibly increased by
cobicistat - increased risk of adrenal suppression.
Grapefruit juice: concentration of oral budesonide
increased - avoid.
Vaccines: high dose corticosteroids can impair
immune response to vaccines - avoid with live
vaccines.
Metabolism
Budesonide is 80-90% metabolized at first pass. Budesonide is metabolized by CYP3A to its 2 major metabolites, 6beta-hydroxybudesonide and 16alpha-hydroxyprednisolone. The glucocorticoid activity of these metabolites is negligible (<1/100) in relation to that of the parent compound. CYP3A4 is the strongest metabolizer of budesonide, followed by CYP3A5, and CYP3A7.
Metabolism
Budesonide was metabolized three- to sixfold more rapidly than triamcinolone acetonide. The pharmacokinetics of budesonide after inhalation, oral, and IV administration displayed a mean plasma half-life of 2.8 hours and a systemic bioavailability of approximately 10% after oral administration (Table 33.5) (101). Pulmonary bioavailability is less than 40% after inhalation (70–75% after correction for the amounts of budesonide deposited in the inhalation device and oral cavity). No oxidative metabolism was observed in the lung. When given by inhalation, 32% of the dose is excreted in the urine as metabolites, 15% in the feces, and 41% of the dose remained in the mouthpiece of the inhaler. Following intranasal administration, very little of intranasal budesonide is absorbed from the nasal mucosa. Much of the intranasal dose (~60%) was swallowed, however, and remained in the GI tract to be excreted unchanged in the feces, whereas that fraction of the intranasal dose that was absorbed was extensively metabolized.
Storage
Store at RT
References
[1] ricardo zollner1*, eduardo abib junior1,2*, luciana fernandes duarte2, maurício wesley perroud2andantonioricardo amarante2. bioequivalency study for inhaled drugs: a pharmacodynamic approac. bioequivalence & bioavailability
Properties of Budesonide
| Melting point: | 221-232°C (dec.) |
| Boiling point: | 464.79°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D25 +98.9° (c = 0.28 in methylene chloride) |
| Density | 1.1046 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4593 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Store at RT |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in methylene chloride, sparingly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent). |
| form | powder |
| pka | 12.87±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | 21.53mg/L(temperature not stated) |
| Merck | 14,1468 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 51333-22-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Budesonide
Computed Descriptors for Budesonide
| InChIKey | VOVIALXJUBGFJZ-KWVAZRHASA-N |
Budesonide manufacturer
Kavya Pharma
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
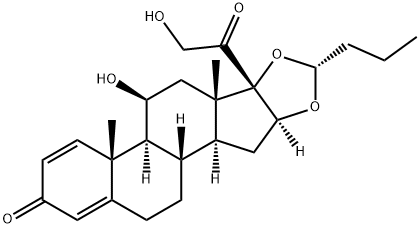
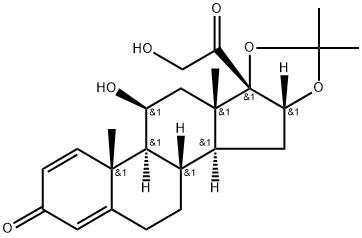
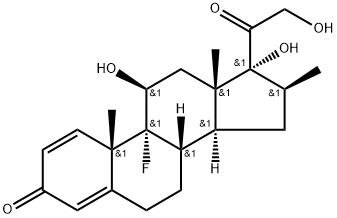
![16α,17-[(1RS)-Butylidenebis(oxy)]-11β-hydroxy-17-(hydroxyMethyl)-D-hoMoandrosta-1,4-diene-3,17a-dione
(Mixture of DiastereoMers)](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/1040085-99-1.gif)

You may like
-
 Budesonide 98%View Details
Budesonide 98%View Details -
 Budesonide 98%View Details
Budesonide 98%View Details -
 Budesonide 99%View Details
Budesonide 99%View Details -
 Budesonide 99%View Details
Budesonide 99%View Details -
 Budesonide Cas 51333 22 3, IPView Details
Budesonide Cas 51333 22 3, IPView Details
51333-22-3 -
 Budesonide Api PowderView Details
Budesonide Api PowderView Details
51333-22-3 -
 Budesonide API PowderView Details
Budesonide API PowderView Details
51333-22-3 -
 Budesonide Powder API MANUFACTURER INDIAView Details
Budesonide Powder API MANUFACTURER INDIAView Details
51333-22-3
