beryllium chloride
- CAS NO.:7787-47-5
- Empirical Formula: BeCl2
- Molecular Weight: 79.92
- MDL number: MFCD00042674
- EINECS: 232-116-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
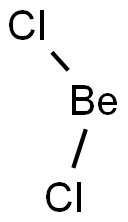
What is beryllium chloride?
Chemical properties
Beryllium chloride is available as colorless to yellow crystals. It decomposes rapidly on contact with water producing hydrogen chloride, and attacks many metals in the presence of water. Beryllium chloride emits irritating or toxic fumes (or gases) in a fi re.
Physical properties
Beryllium chloride has the formula BeCl2 with a molecular weight of 79.9176 g/mol. Beryllium chloride, BeCl2, melts at 405°C and boils at 520°C. That compares with 714°C and 1412°C for magnesium chloride. The solid is a one-dimensional polymer consisting of edge-shared tetrahedra. In contrast, BeF2 is a threedimensional polymer, with a structure akin to that of quartz. In the gas phase, BeCl2 exists both as a linear monomer and a bridged dimer with two bridging chlorine atoms where the beryllium atom is 3-coordinate. This linear shape contrasts with the monomeric forms of some of the dihalides of the heavier members of group 2, e.g. CaF2, SrF2, BaF2, SrCl2, BaCl2 and Ba that are all nonlinear.

beryllium chloride lewis structure
The pure chloride is a glassy, transparent mass having a specific gravity of 2.01 at 15°C. It becomes fluid toward 440°C, passing through a viscous condition, but above 800° C it begins to volatilize, yielding white and very deliquescent crystals. It dissolves readily in water, but is only slightly soluble in absolute alcohol. By cooling an alcoholic solution to 23°C, one can obtain a white crystalline mass which, however, melts easily as the temperature rises.
Beryllium chloride, an electron-deficient compound similar to aluminum chloride, is a Lewis acid. The anhydrous salt is used as a catalyst in organic reactions.
History
Although early workers (1798) obtained the chloride in solution, the pure salt was not made until about 1827 when one worker of the time prepared it in the sublimed anhydrous state by passing chlorine gas over a heated mixture of carbon and beryllium oxide. Finally (1885), it was prepared as the pure chloride in very pure form for the purpose of determining its vapor density by the action of dry hydrochloric acid gas on the metal, but the pure salt was not produced until 1898 when one worker made it by heating the double fluoride of ammonium and beryllium, which had previously been dried over phosphoric anhydride, in a current of dry carbon dioxide and cooled in an atmosphere of the same gas. He also prepared it by the action of hydrofluoric acid gas on the carbide. No matter what method is used, it was determined that the materials must be absolutely dry if a pure chloride is to be obtained.
The Uses of beryllium chloride
Beryllium chloride (BeCl2) is used as a catalyst to accelerate many organic reactions, and beryllium chloride is the electrolyte used along with NaCl in the electrolytic process to produce beryllium metal.
The Uses of beryllium chloride
In dry form, as catalyst for organic reactions.
The Uses of beryllium chloride
Beryllium chloride is used as a component of molten salt baths for electrowinning or electrorefining of the metal. The compound hydrolyzes readily with atmospheric moisture, evolving HCl, so protective atmospheres are required during processing.
Definition
ChEBI: A compound of beryllium (+2 oxidation state) and chloride in the ratio 1:2.
Preparation
Beryllium chloride is prepared by passing chlorine over beryllium oxide and carbon:
BeO + C + Cl2 → BeCl2 + CO
It also is made by combination of beryllium with chlorine.
General Description
White to green solid with a sharp odor.
Air & Water Reactions
Reacts with water with evolution of heat. Forms beryllium oxide and hydrochloric acid solution. Corrodes most metals in presence of moisture. Flammable and explosive hydrogen gas may collect in enclosed spaces [USCG, 1999].
Reactivity Profile
Acidic salts, such as BERYLLIUM CHLORIDE, are generally soluble in water. The resulting solutions contain moderate concentrations of hydrogen ions and have pH's of less than 7.0. They react as acids to neutralize bases. These neutralizations generate heat, but less or far less than is generated by neutralization of inorganic acids, inorganic oxoacids, and carboxylic acid. They usually do not react as either oxidizing agents or reducing agents but such behavior is not impossible. Many of these compounds catalyze organic reactions. BERYLLIUM CHLORIDE reacts with vigor with sulfur nitrides. Some explode upon intimate mixing, i.e. tetrasulfur tetranitride.
Hazard
Very toxic.
Health Hazard
Inhalation causes pneumonitis, nasopharyngitis, tracheobronchitis, dyspnea, chronic cough. Ingestion causes irritation of mouth and stomach. Contact with dust causes conjunctival inflammation of eyes and irritation of skin. Any dramatic, unexplained weight loss should be considered as a possible first indication of beryllium disease.
Health Hazard
Exposures to beryllium chloride cause redness, pain and blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Inhalation of beryllium chloride causes cough, sore throat, shortness of breath
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic and irritating beryllium oxide fumes and hydrogen chloride may form in fires.
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen withexperimental tumorigenic data. Poison by ingestion andintraperitoneal routes. An experimental teratogen. Otherexperimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported.When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumesof
Synthesis
Beryllium chloride can be prepared directly from beryl by chloride or by chlorination of beryllium oxide under reducing conditions. Beryllium chloride is especially well suited for purification by distillation in a stream of hydrogen and fractional condensation. The significantly lower-boiling chlorides of aluminum, silicon, and iron(III) can be separated by careful temperature control. Iron(II) chloride, which is reduced by hydrogen, stays in the residue.
Properties of beryllium chloride
| Melting point: | 399 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 520°C |
| Density | 1.899 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 1 mm at 291°C (subl) |
| solubility | soluble in ethanol, ethyl ether, pyridine; insoluble in
benzene, toluene |
| form | white-yellow orthorhombic crystals |
| color | Colorless, deliquescent needles, or orthorhombiccrystals |
| Water Solubility | very soluble H2O with evolution of heat [MER06]: g/100g solution H2O: 40.35 (0°C), 41.72 (25°C); solid phase, BeCl2 · 4H2O [KRU93]; soluble alcohol, benzene, ether [HAW93] |
| Merck | 13,1170 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7787-47-5 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Beryllium chloride (7787-47-5) |
Safety information for beryllium chloride
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P332+P313:IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for beryllium chloride
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
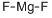
You may like
-
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
2058-74-4 -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
