Beryllium fluoride
- CAS NO.:7787-49-7
- Empirical Formula: BeF2
- Molecular Weight: 47.01
- MDL number: MFCD00014194
- EINECS: 232-118-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
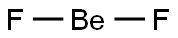
What is Beryllium fluoride?
Description
Beryllium fluoride has the formula, BeF2, and is a hygroscopic, amorphous solid with a melting point of 800°C. It is soluble in water and is used in beryllium metallurgy in which the metal, Be, is employed as an alloy. Solid crystalline BeF2 has a silica-like structure with beryllium in a four-coordinate position.
Chemical properties
Beryllium fluoride is readily soluble in water, dissolving in its own water of hydration as BeF2·2H2O. The compound cannot be crystallized from solution and is prepared by thermal decomposition of ammonium fluoberyllate, (NH4)2BeF4.
Physical properties
Glassy solid; tetragonal crystal system; hygroscopic; density 2.1 g/cm3; melts BERYLLIUM FLUORIDE 101 at 552°C; vaporizes at 1,169°C; very soluble in water; sparingly soluble in alcohol.
The Uses of Beryllium fluoride
Beryllium fluoride is used in biochemistry, particularly protein crystallography, since it binds in some of the same ways as phosphate does in human tissues. ADP and beryllium fluoride together tend to bind to ATP sites and inhibit protein action, making it possible to crystallize proteins in the bound state. Beryllium fluoride forms a basic constituent of the preferred fluoride salt mixture used in liquid-fluoride nuclear reactors. Typically, beryllium fluoride is mixed with LiF to form a base solvent, into which fluorides of uranium and thorium are introduced. Beryllium fluoride is exceptionally chemically stable and LiF/BeF2 mixtures have low melting points and the best neutronic properties of any of the fluoride salt combinations appropriate for reactor use.
The Uses of Beryllium fluoride
manufacture of Be and Be alloys; manufacture of glass; in nuclear reactors.
The Uses of Beryllium fluoride
Beryllium fluoride (BeF2) is an example of beryllium that has an oxidation state of +2, combining with a negative anion element with an oxidation state of –1. Beryllium fluoride is also used along with magnesium metal in the chemical reduction process to produce beryllium metal.
What are the applications of Application
Beryllium fluoride is a chemical used in protein crystallography as a mimic of phosphate. ADP and beryllium fluoride together tend to bind to ATP sites and inhibit protein action, making it possible to crystallise proteins in the bound state. Principal precursor for the manufacture of beryllium metal.
Definition
ChEBI: The fluoride salt of beryllium (+2 oxidation state). In the solid state it exists as a glass, with four-coordinate Be2+ tetrahedral centres and two-coordinate fluoride centres. As a gas it adopts a linear triatomic structure and in the liquid state a fluctuating tetrahedral structure. In protein crystallography it is used as a mimic of phosphate.
Preparation
Beryllium fluoride is made by thermal decomposition of ammonium beryllium fluoride at 900 to 950°C.
Manufacturing Process
First, beryllium hydroxide is dissolved in an ammonium hydrogen fluoride solution. The resulting ammonium tetrafluoroberyllate is dissociated to a small extent in the solution that the pH can be varied over a wide range without precipitating beryllium hydroxide. Impurities can thus be precipitated relatively easily as hydroxides. Aluminum is precipitated as hydroxide by increasing the pH to 8.3. Chromium and manganese are precipitated by oxidation with lead dioxide, and manganese is precipitated by oxidation with lead dioxide and manganese dioxide. Copper, nickel, and lead are precipitated as sulfides. Ammonium tetrafluoroberyllate is freely soluble in water. When concentrated by evaporation, it crystallizes without water or hydration. Above 130 ?C, it dissociates into ammonium fluoride and beryllium fluoride. Between 900 and 1100 ?C, ammonium tetrafluoroberyllate dissociates into gaseous beryllium fluoride and gaseous ammonium fluoride. The latter can be recycled into the process as ammonium hydrogen fluoride by dissolving it in aqueous hydrogen fluoride. Cooling produces beryllium fluoride as vitreous grains.
General Description
Odorless white solid. Denser than water.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Beryllium fluoride is incompatible with the following: Acids, caustics, chlorinated hydrocarbons, oxidizers, magnesium, molten lithium .
Hazard
A known carcinogen. Toxic by inhalation and ingestion.
Health Hazard
Any dramatic weight loss should be considered as possible first indication of beryllium disease. Inhalation causes irritation of nose, throat, and lungs, severe pneumonitis, and/or pulmonary edema. Ingestion causes fatigue, weakness, loss of appetite. Contact with eyes causes severe irritation and burns. Contact with skin causes dermatitis and non-healing ulcers.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic and irritating vapor of unburned material may form in fire.
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen withexperimental carcinogenic and tumorigenic data byinhalation. Poison by ingestion, subcutaneous,intravenous, and intraperitoneal routes. Incompatible with Mg. When heated to decomposition, itemits very toxic fumes of BeO and F
Properties of Beryllium fluoride
| Melting point: | 545 °C |
| Boiling point: | 1169°C (estimate) |
| Density | 1,986 g/cm3 |
| solubility | very soluble in H2O; slightly soluble in ethanol |
| form | Powder |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | very soluble H2O [MER06]; slightly soluble alcohol [HAW93] |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Beryllium difluoride (7787-49-7) |
Safety information for Beryllium fluoride
Computed Descriptors for Beryllium fluoride
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
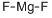
You may like
-
 873-83-6 6-Aminouracil (or) 4-Amino-2,6- dihydroxypyrimidine, (or) 6-Amino2,4-pyrimidinediol 99%View Details
873-83-6 6-Aminouracil (or) 4-Amino-2,6- dihydroxypyrimidine, (or) 6-Amino2,4-pyrimidinediol 99%View Details
873-83-6 -
 55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 -
 N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
13162-05-5 -
 Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 207557-35-5 99%View Details
207557-35-5 99%View Details
207557-35-5 -
 2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0 -
 181228-33-1 (S)-Methyl 3-amino-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)propanote Hydrochloride (DAP-OMe. HCl) 99%View Details
181228-33-1 (S)-Methyl 3-amino-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)propanote Hydrochloride (DAP-OMe. HCl) 99%View Details
181228-33-1