Azilsartan Medoxomil
- CAS NO.:863031-21-4
- Empirical Formula: C30H24N4O8
- Molecular Weight: 568.53
- MDL number: MFCD19443688
- EINECS: 1308068-626-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 13:58:55
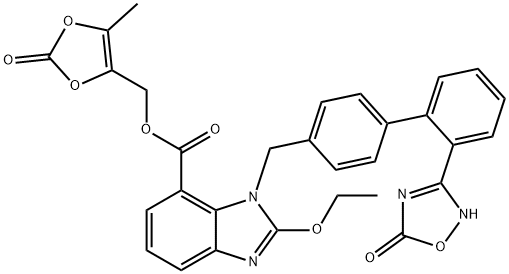
What is Azilsartan Medoxomil?
Absorption
During absorption, azilsartan medoxomil is hydrolyzed to azilsartan. The parent drug is not detectable in plasma after oral administration. The absolute bioavailability of azilsartan is estimated to be 60%. Tmax ranges from 1.5 to three hours. Steady-state levels of azilsartan are achieved within five days, and no accumulation in plasma occurs with repeated once-daily dosing.
Toxicity
No maximum toxic doses have been established yet for azilsartan. There is limited human data available related to azilsartan medoxomil overdosage. In clinical trials, healthy subjects tolerated once-daily doses up to 320 mg of azilsartan medoxomil well. In the event of drug overdose, supportive measures should be initiated as azilsartan is not dialyzable.
Azilsartan is a teratogenic agent with a risk of congenital abnormalities. Azilsartan and other ARB drugs are considered fetotoxic during the second and third trimesters.
Description
Azilsartan medoxomil (Edarbi), an angiotensin II receptor antagonist, was approved by the U.S. FDA in February 2011 for the treatment of hypertension in adults. The discovery of azilsartan was the result of a medicinal chemistry effort to identify an ARB with a different carboxylic acid isostere than the ones found in the marketed ARBs. Several of the marketed ARBs use a tetrazole group as a carboxylic acid isostere. The medicinal chemistry approach that led to azilsartan involved the replacement of this commonly used tetrazole with a 5-oxo-1,2,4-oxadiazole group. Azilsartan can be synthesized by Suzuki coupling of p-tolyl boronic acid to 2-bromobenzonitrile, followed by bromination of the methyl group. The bromide is displaced to introduce a protected 2-ethoxy-1H-benzo[d] imidazole-7-carboxylate. The cyano group is converted to a hydroxylamidine, followed by reaction with an alkyl-chloroformate and intramolecular cyclization to form the 5-oxo-1,2,4-oxadiazole ring. The acid is then deprotected and converted to a prodrug. The parent, azilsartan has been extensively characterized in vitro and compared with other marketed AT1 antagonists olmesartan, valsartan, telmisartan, irbesartan, and candesartan. Azilsartan was found to be a potent (IC50=2.6 nM), selective, inverse agonist of the AT1 receptor. From washout experiments, azilsartan was found have slow dissociation from the receptor and thus is characterized as an insurmountable antagonist.
Description
Azilsartan medoxomil is a prodrug form of azilsartan , a potent and selective angiotensin II receptor 1 (AT1) antagonist. Azilsartan medoxomil (0.1-10 mg/kg) reduces blood pressure and decreases plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1) levels in the plasma, left ventricle, and aortic wall in mice in a dose-dependent manner. It also inhibits the pressor response induced by angiotensin II in normotensive rats (ID50 = 0.12 mg/kg) and reduces blood pressure and improves glucose infusion, a marker of insulin sensitivity, in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Azilsartan medoxomil also has more potent antiproteinuric effects in Wistar fatty rats than olmesartan medoxomil . Formulations containing azilsartan medoxomil have been used in the treatment of hypertension.
Originator
Takeda (United States)
The Uses of Azilsartan Medoxomil
Azilsartan medoxomil is a long-acting angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) that is used to lower hypertension. When Azilsartan medoxomil enters the gastrointestinal tract, it is rapidly converted to its active form, Azilsartan (A926900).
Background
Azilsartan medoxomil is a prodrug that is broken down to azilsartan, which belongs in the angiotensin-receptor blocking (ARB) drug class. It is a selective AT1 subtype angiotensin II receptor antagonist. Azilsartan medoxomil is a relatively recently-developed antihypertensive drug that was first approved by the FDA in February 2011. Many guidelines recommend the use of ARBs as first-line therapy when initiating antihypertensive therapy and indicate that the clinical efficacy of ARBs is comparable to angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors that are also used as first-line treatment for hypertension.
Azilsartan medoxomil is marketed under the brand name Edarbi. It is used to treat hypertension as monotherapy or in combination with other antihypertensive drugs. It is also available in a combination product with chlorthalidone. As hypertension is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, early management of hypertension has several implications on patients' survival rate and quality of life in the future. Lowering blood pressure is associated with a reduced risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. Azilsartan medoxomil is thus speculated to lower mortality rates and the onset of cardiovascular disease. Although there is no clinical significance yet determined, azilsartan medoxomil may have potential off-label uses in patients with a history of myocardial infarction or heart failure.
Indications
Azilsartan medoxomil is indicated for the treatment of hypertension to lower blood pressure in patients over 18 years of age. It may be used either alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents. Some antihypertensive drugs have lesser effects on blood pressure in black patients.
Azilsartan medoxomil is available as a fixed-dose combination product with chlorthalidone, which is indicated for the treatment of hypertension in patients whose hose blood pressure is not adequately controlled on monotherapy. It may be used as initial therapy if a patient is likely to need multiple drugs to achieve blood pressure goals.
Azilsartan medoxomil belongs to the angiotensin-receptor blocking (ARB) class of drugs, which are used to decrease the progression of moderate-to-severe albuminuria and prevent the recurrence of atrial fibrillation as off-label uses in patients with diabetes mellitus and hypertension.
Definition
ChEBI: A carboxylic ester obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of azilsartan with the hydroxy group of 4-(hydroxymethyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one. A prodrug for azilsartan, it is used for treatment of hypertension.
brand name
Edarbi
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacodynamic effects of azilsartan medoxomil are mediated by its active metabolite, azilsartan. Azilsartan inhibits the pressor effects of an angiotensin II infusion in a dose-related manner. At a single 32 mg dose, azilsartan inhibited the maximal pressor effect by approximately 90% at peak plasma concentrations and by 60% at 24 hours after administration. In healthy subjects receiving single and repeated doses of azilsartan medoxomil, plasma angiotensin I and II concentrations and plasma renin activity increased, while plasma aldosterone concentrations decreased. Like other ARBs, azilsartan causes dose-dependent decrease in peripheral resistance and decreases smooth muscle vascular tone. As azilsartan blocks the angiotensin II receptor, the negative regulatory feedback of angiotensin II on renin secretion is inhibited; however, the resulting increased plasma renin activity and angiotensin II circulating levels do not overcome the blood pressure-lowering effect of azilsartan. Blood pressure-lowering effects of antihypertensive agents can be reduced in patients of African descent. However, there are no recommended dosage adjustment of azilsartan on the basis of a patient’s sex, race, or degree of renal or hepatic impairment.
Azilsartan medoxomil has negligible effects on serum potassium or sodium levels. Azilsartan does not affect the biosynthesis of angiotensin II nor bradykinin levels. It also does not bind to any ion channels that are involved in cardiovascular regulation.
Metabolism
After azilsartan medoxomil is hydrolyzed into its active metabolite, azilsartan is metabolized to two primary metabolites, which are pharmacologically inactive. The major metabolite in plasma is metabolite M-II, which is formed via O-dealkylation mediated by CYP2C9. The minor metabolite is metabolite M-I, which is formed via decarboxylation mediated by CYP2C8 and CYP2B6. MII has approximately 50% systemic exposure of azilsartan, and MI has less than 1% systemic exposure of azilsartan.
Properties of Azilsartan Medoxomil
| Melting point: | 160-161oC |
| Density | 1.45 |
| storage temp. | Refrigerator |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly, Heated, Sonicated) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 6.99±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | White to Light Beige |
Safety information for Azilsartan Medoxomil
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Azilsartan Medoxomil
Azilsartan Medoxomil manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![(Z)-Methyl 2-ethoxy-3-((2'-(N'-hydroxycarbaMiMidoyl)biphenyl-4-yl)Methyl)-3H-benzo[d] iMidazole-4-carboxylate](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/147403-65-4.gif)
You may like
-
 863031-21-4 Azilsartan Medoxomil 98%View Details
863031-21-4 Azilsartan Medoxomil 98%View Details
863031-21-4 -
 863031-21-4 98%View Details
863031-21-4 98%View Details
863031-21-4 -
 Azilsartan Medoxomil 98%View Details
Azilsartan Medoxomil 98%View Details
863031-21-4 -
 Azilsartan Medoxomil 863031-21-4 98%View Details
Azilsartan Medoxomil 863031-21-4 98%View Details
863031-21-4 -
 863031-21-4 Azilsartan Medoxomil 98%View Details
863031-21-4 Azilsartan Medoxomil 98%View Details
863031-21-4 -
 863031-21-4 Azilsartan Medoxomil 99%View Details
863031-21-4 Azilsartan Medoxomil 99%View Details
863031-21-4 -
 Azilsartan medoxomil CAS 863031-21-4View Details
Azilsartan medoxomil CAS 863031-21-4View Details
863031-21-4 -
 Azilsartan medoxomil 95% CAS 863031-21-4View Details
Azilsartan medoxomil 95% CAS 863031-21-4View Details
863031-21-4
