Azilsartan
Synonym(s):1-[[2′-(2,5-Dihydro-5-oxo-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl) [1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]-2-ethoxy-1H-benzimidazole-7-carboxylic acid;2-Ethoxy-1-{[2′-(5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]methyl}-1H-benzimidazole-7-carboxylic acid;TAK-536
- CAS NO.:147403-03-0
- Empirical Formula: C25H20N4O5
- Molecular Weight: 456.45
- MDL number: MFCD20278186
- EINECS: 808-058-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-12 15:32:36
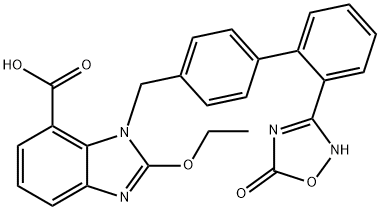
What is Azilsartan?
Description
Azilsartan is an effective medication that serves as an antagonist of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor, known as AT1. It is the active metabolite of the prodrug azilsartan medoxomil, which is converted to azilsartan through a hydrolysis process that occurs in the gastrointestinal tract and liver.
The antagonistic activity of azilsartan is demonstrated by its ability to inhibit angiotensin II-induced responses. Specifically, it reduces the angiotensin II-induced accumulation of inositol-1-phosphate in COS-7 cells that express recombinant human AT1 receptors, with an IC50 value of 2.6 nM. This indicates that azilsartan not only blocks the receptor but also prevents the signaling pathways initiated by angiotensin II.
Chemical properties
White to Off-White Solid
The Uses of Azilsartan
Azilsartan is an analgesic and antiinflammatory drugs containing angiotensin II antagonists.
The Uses of Azilsartan
Azilsartan is an angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptor antagonist with IC50 of 2.6 nM
Definition
ChEBI: A benzimidazolecarboxylic acid that is benzimidazole-7-carboxylic acid substituted at position 2 by a methoxy group and at position 1 by a 2'-[(5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]methyl group. Used (as the prodrug, azilsartan medoxomil) f r treatment of hypertension.
Clinical Use
Azilsartan is an orally active medication that functions as a potent angiotensin II blocker, specifically targeting the type 1 angiotensin II receptors. This higher potency and slower off-rate kinetics of azilsartan contribute to its enhanced effectiveness in lowering blood pressure compared to other drugs in its class.
The drug was first approved and launched in Japan for the treatment of arterial hypertension in May 2012. It is marketed under the trade name Azilva?. Notably, azilsartan was discovered and developed by Takeda, a pharmaceutical company with a history of innovation in this field. Takeda is also responsible for the development and launch of a prodrug form of azilsartan, known as azilsartan kamedoxomil or Edarbi?, which was introduced to the market in 2010.
The development of azilsartan and its prodrug represents a significant advancement in the treatment of hypertension, offering patients a more effective option for managing their blood pressure.
Synthesis
The most likely process-scale synthetic route likely mimics that which is disclosed in Takeda?ˉs
patents, and this is described in the scheme below. Commercial available benzoic acid 21 was activated as
the correspndong acyl azide and underwent a Curtius rearrangement to give carbamate 22 in 57% yield
(three steps from compound 21). The resulting aniline 22 was then alkylated with commercial 4-
(bromomethyl)-2'-cyanobiphenyl 23 to give benzylamine 24 in 85% yield. Nitroamine 24 was then
exposed to mildly acidic conditions to affect Boc-removal prior to reduction via ferric chloride hydrate
in the presence of hydrazine hydrate. The resulting diamine 25 arose in 64% yield across the two-step
sequence. Interestingly, tt was found that metal catalysts under conventional hydrogenation conditions
caused partial debenzylation, which led the authors to arrive at the hydrazine/ferric chloride conditions.
Next, benzimidazole formation was achieved upon treatment of diamine 25 with ethyl orthocarbonate in
acetic acid. The resulting ethoxylbenzimidazole 26 was procured in 86% yield, and this benzonitrile was
further reacted with hydroxylamine hydrochloride and sodium methoxide to provide amidoxime 27 in
90% as white powder. Next, activation with ethyl chlorocarbonate gave 28 followed by heating in
refluxing xylene to give oxadiazolone 29 in 23% yield from hydroxyamidine 27. Finally ester 29 was
saponified with 2N LiOH in methanol to give azilsartan (V) in 84% yield.


An improved scalable route (Scheme below) to azilsartan was reported and features reproducibly better
yields.43 Hydroxyamidine 30 was treated with dimethyl carbonate and sodium methoxide, which
triggered they key cyclization along with concomitant transesterification to deliver 29. Milder aqueous
sodium hydroxide hydrolysis converted this methyl ester 29 to azilsartan (V) in 88-90% yield.
Properties of Azilsartan
| Melting point: | 188 °C(dec.) |
| Density | 1.42 |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: soluble15mg/mL (clear solution) |
| pka | 2.05±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | powder |
| color | white to beige |
Safety information for Azilsartan
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H361:Reproductive toxicity H413:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for Azilsartan
| InChIKey | KGSXMPPBFPAXLY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Azilsartan manufacturer
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran
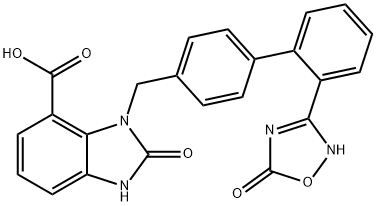
![1H-BenziMidazole-7-carboxylic acid, 1-[[2'-(2,5-dihydro-5-oxo-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl]Methyl] -2-ethoxy-, ethyl ester](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/1403474-70-3.gif)
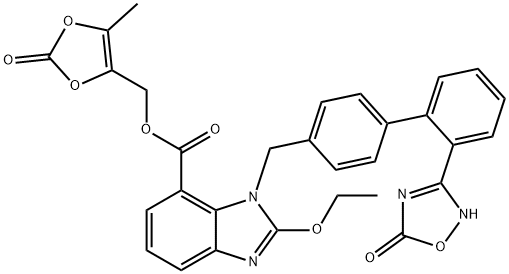
![ethyl2-oxo-3-((2'-(5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)biphenyl-4-yl)Methyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo[d]iMidazole-4-carboxylate](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20150408/GIF/1403474-76-9.gif)
You may like
-
 147403-03-0 98%View Details
147403-03-0 98%View Details
147403-03-0 -
 Azilsartan 98%View Details
Azilsartan 98%View Details -
 Azilsartan 98% CAS 147403-03-0View Details
Azilsartan 98% CAS 147403-03-0View Details
147403-03-0 -
 Azilsartan 147403-03-0 98%View Details
Azilsartan 147403-03-0 98%View Details
147403-03-0 -
 Azilsartan 147403-03-0 98%View Details
Azilsartan 147403-03-0 98%View Details
147403-03-0 -
 Azilsartan 98%View Details
Azilsartan 98%View Details -
 Azilsartan CAS 147403-03-0View Details
Azilsartan CAS 147403-03-0View Details
147403-03-0 -
 Azilsartan CAS 147403-03-0View Details
Azilsartan CAS 147403-03-0View Details
147403-03-0
