Avasimibe
Synonym(s):CI-1011; PD 148515; [[2,4,6-tris(1-methylethyl)phenyl]acetyl]-, 2,6-bis(1-methylethyl)phenyl ester] sulfamic acid
- CAS NO.:166518-60-1
- Empirical Formula: C29H43NO4S
- Molecular Weight: 501.72
- MDL number: MFCD00934956
- EINECS: 1592732-453-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 15:53:33
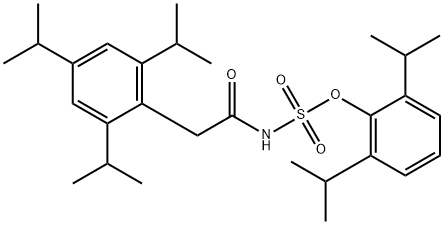
What is Avasimibe?
The Uses of Avasimibe
Avasimibe is a selective inhibitor of Cholesterol Acyltransferase 1 and CYP2C9. Avasimibe is known to induce apoptosis of glioma cell lines as a model of glioblastoma.
The Uses of Avasimibe
Avasimibe has been used as an inhibitor of acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) in Huh7.5.1 cells for testing its combination with direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) and to test its effect on lipid droplet accumulation in acidosis-adapted cancer cells. It may be used as an inhibitor of ACAT to assess cholesterol esterification in Trypanosoma cruzi.
What are the applications of Application
Avasimibe is a cholesterol reducing compound that also inhibits CYP
Definition
ChEBI: Avasimibe is a monoterpenoid.
Biological Activity
avasimibe is an orally bioavailable inhibitor of the acyl coenzyme a: cholesterol acyltransferase (acat) with ic50 value of 60nm [1].avasimibe is developed from a strategy to design acat inhibitors with improved bioavailability. it also has solution stability at acidic ph. in the in vitro assay, the ic50 value is dependent on the concentration of microsomes, the amount of membrane available for adsorption as well as the presence of bsa. the treatment of avasimibe during the process of lipid loading causes a concentration-dependent reduction in cellular cholesteryl ester content. this reduction is not accompanied by the accumulation of intracellular free cholesterol, indicating a better safety profile for avasimibe than other acat inhibitors. avasimibe can also reduce the synthesis and secretion of apo b 100 (a component of vldl) in hepg2 cells. in addition, avasimibe can increase the total bile acid synthesis in rat hepatocytes at the concentration of 3μm [1].apart from the antiatherosclerotic efficacy, avasimibe is also found to take participate in the modulation of app trafficking. it can delay and reduce the maturation of app, limiting the availability of app holoprotein for aβ-generatiion [2].
Biochem/physiol Actions
Avasimibe (CI-1011) is an orally bioavailable Acyl-CoA:Cholesterol O-Acyltransferase (ACAT) inhibitor. It was originally developed as an antilepic drug, and was shown to significantly reduce plasma total triglyceride and VLDL-cholesterol, but later clinical trials were disappointing. ACAT has also been investigated as a potential therapeutic target for Alzheimer′s disease. Recent studies have looked at the effects of avasimibe in reducing amyloid pathology by limiting generation and increasing clearance of diffusible amyloid-beta (Abeta).
storage
Store at +4°C
References
[1] llaverías g, laguna jc, alegret m. pharmacology of the acat inhibitor avasimibe (ci-1011). 2003 spring;21(1):33-50.
[2] huttunen hj, peach c, bhattacharyya r, barren c, pettingell w, hutter-paier b, windisch m, berezovska o, kovacs dm. inhibition of acyl-coenzyme a: cholesterol acyl transferase modulates amyloid precursor protein trafficking in the early secretory pathway. faseb j. 2009 nov;23(11):3819-28.
Properties of Avasimibe
| Melting point: | 178-180° (Lee); mp 169.5-170.4° (Dozeman) |
| Density | 1.072±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | DMSO: ≥40mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 1.97±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | white to tan |
Safety information for Avasimibe
Computed Descriptors for Avasimibe
| InChIKey | PTQXTEKSNBVPQJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

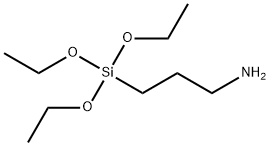
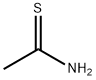
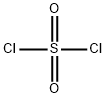
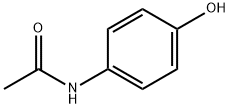
You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8