ARSENIC(III) CHLORIDE
Synonym(s):Arsenic trichloride
- CAS NO.:7784-34-1
- Empirical Formula: AsCl3
- Molecular Weight: 181.28
- MDL number: MFCD00014165
- EINECS: 232-059-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:52
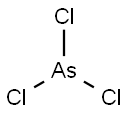
What is ARSENIC(III) CHLORIDE?
Description
Arsenous trichloride is a noncombustible, colorless or pale yellow oily, fuming liquid. The odor is describedas pungent and acrid. Molecular weight= 181.27; Boilingpoint=130.2℃; Freezing/Melting point= -16℃; Specificgravity= 2.156 at 25℃; Latent heat of vaporization=49.06 cal/g; Heat of solution=(estimate) 2 0.42 3 105 J/kg;Vapor pressure= 8.4 mmHg. Decomposes in water, forminghydrogen chloride.
Chemical properties
colourless oily liquid
Chemical properties
Arsenous trichloride is a noncombustible, colorless or pale yellow oily, fuming liquid. The odor is described as pungent and acrid.
Physical properties
Colorless oily liquid; fumes in air; density 2.163 g/ml at 20°C; refractive index 1.621 at 14°C; melts at 0.16°C; boils at 130.2°C; vapor pressure 9.75 torr at 25°C; decomposes in water; soluble in alcohol, ether, HCl and HBr.
The Uses of ARSENIC(III) CHLORIDE
Arsenic Trichloride is an highly toxic inorganic compounds and is an intermediate in the manufacture of organoarsenic compounds.
The Uses of ARSENIC(III) CHLORIDE
In the ceramic industry; in syntheses of chlorine-contg arsenicals, e.g., chloro derivatives of arsine.
The Uses of ARSENIC(III) CHLORIDE
Arsenic trichloride (AsCl3), also known as arsenic chloride, is used in the pharmaceutical industry and to make insecticides and ceramics.
Definition
ChEBI: A arsenic molecular entity that consists of a single arsenic atom bearing three chloro substituents.
Definition
A poisonous oily liquid. It fumesin moist air due to hydrolysis with water
vapor:AsCl3 + 3H2O = As2O3 + 6HCl
Arsenic(III) chloride is covalent and exhibits nonmetallic properties.
Preparation
The compound is generally made from arsenic trioxide by (i) passing chlorine over it or (ii) treating the trioxide with sulfur monochloride, S2Cl2. Alternatively it is prepared from arsenic trioxide by distillation with either concentrated hydrochloric acid or a mixture of sulfuric acid and a metal chloride. Arsenic trichloride may also be prepared by combination of arsenic and chlorine.
General Description
A colorless to yellow oily fuming liquid. ARSENIC(III) CHLORIDE is irritating to the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Very toxic by inhalation and ingestion.
Air & Water Reactions
Fumes in air. Reacts with water to form hydrochloric acid and As(OH)3.
Reactivity Profile
When ARSENIC CHLORIDE is heated to decomposition or on contact with mineral acids, ARSENIC(III) CHLORIDE emits highly toxic fumes of hydrogen chloride and of metallic arsenic. Explodes with Na, K, and Al on impact [Sax, 9th ed., 1996, p. 275]. The interaction of hexafluoroisopropylideneaminolithium with a range of chlorinated and /or fluorinated derivatives of arsenic, boron, phosphorus, silicon, and sulfur yielded a violently exothermic reaction.
Hazard
Strong irritant to eyes and skin.
Health Hazard
ARSENIC(III) CHLORIDE can cause death. In acute exposures, it is extremely toxic and caustic, owing not only to the poisonous nature of arsenic, but also to the release of hydrochloric acid in the presence of water. Exposure to the skin causes local irritation and blisters. Inhalation or ingestion causes hemorrhagic gastroenteritis resulting in loss of fluids and electrolytes, collapse, shock and death. Chronic poisoning can lead to peripheral nerve damage, skin conditions, liver damage and it has been implicated in the induction of skin and lung cancer. The fatal human dose is 70-180 mg depending on the weight of the victim.
Fire Hazard
When in contact with active metals such as arsenic, iron, aluminum, zinc, or when heated to decomposition, ARSENIC(III) CHLORIDE emits highly toxic fumes of arsenic. Upon contact with water hydrogen chloride is produced. Water causes ARSENIC(III) CHLORIDE to decompose to yield arsenic acid and hydrochloric acid. Avoid active metals such as arsenic, iron, aluminum, zinc, decomposed by water to form arsenic hydroxide and hydrogen chloride. Avoid air, ultraviolet light. Hazardous polymerization may not occur.
Safety Profile
Confirmed human carcinogen. A poison via inhalation. See also ARSENIC COMPOUNDS and CHLORIDES. Very poisonous; fumes in air. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of As and Cl-. Highly reactive. Explodes with Na, K, and Al on impact.
Synthesis
The direct synthesis of AsCl3 is uneconom ical. An old commercial production method is the Glauber process using arsenic trioxide:
As2O3 +6NaCl+3H2SO4?→ 2AsCl3+3Na2SO4+3H2O
However, AsCl3 is easier to produce by react ing As2O3 with gaseous hydrogen chloride at 180–200℃.
Potential Exposure
Arsenic chloride is used in the ceramics industry; in the synthesis of chlorine-containing arsenicals; as a chemical intermediate for arsenic insecticides, pharmaceuticals; and has been used in chemical warfare agents.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention.Note to physician: For severe poisoning BAL [British AntiLewisite, Dimercaprol, dithiopropanol (C3H8OS2)] has beenused to treat toxic symptoms of certain heavy metalspoisoning including arsenic. Although BAL is reported tohave a large margin of safety, caution must be exercised,because toxic effects may be caused by excessive dosage.Most can be prevented by premedication with 1-ephedrinesulfate (CAS: 134-72-5). For milder poisoning penicillamine(not penicillin) has been used, both with mixed success. Sideeffects occur with such treatment and it is never a substitutefor controlling exposure. It can only be done under strictmedical care.
storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Store ina secure poison location. Prior to working with this chemicalyou should be trained on its proper handling and storage.Arsenous trichloride, AsCl3, should be stored in tightlyclosed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area away fromheat, water, and any possible contact with active metals orother incompatible materials. A regulated, marked areashould be established where this chemical is handled, used,or stored in compliance with OSHA Standard 1910.1045.
Shipping
UN1560 Arsenic trichloride, Hazard class 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poison Inhalation Hazard, Inhalation Hazard Zone B.
Purification Methods
Reflux the trichloride with arsenic for 4hours, then fractionally distil it. The middle fraction is stored with sodium wire for two days, then again distilled [Lewis & Sowerby J Chem Soc 336 1957]. It fumes in moist air forming the solid hydroxy-chloride [AsCl(OH)2] and is readily hydrolysed by H2O to form arsenious acid. POISONOUS. [Schenk in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry (Ed. Brauer) Academic Press Vol I p 596 1963.]
Incompatibilities
Contact with sodium, potassium, or powdered aluminum may cause a violent reaction. It is decomposed in water, forming arsenic hydroxide and hydrogen chloride. Exposure to light forms toxic gas. Violent reaction with anhydrous ammonia, strong acids; strong oxidizers and halogens. Incompatible with alkali metals; active metals, such as arsenic, iron, aluminum, zinc. Corrodes metals in the presence of moisture and forms flammable and explosive hydrogen gas.
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. Dissolve in a minimum of concentrated hydrochloric acid. Dilute with water until white precipitate forms. Add HCl to dissolve. Saturate with H2S; filter and wash precipitate and return to supplier. Alternatively, precipitate with heavy metals, such as lime or ferric hydroxide in lieu of H2S.If needed, seek professional environmental engineering assistance from the United States Environmental Protection Agency Environmental Response Team at (908) 548-8730 (24-hour response line). In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Properties of ARSENIC(III) CHLORIDE
| Melting point: | −16 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 130.2 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 2.15 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 6.25 |
| refractive index | 1.6006 (589.3 nm 20℃) |
| Flash point: | 130.2°C |
| solubility | reacts with H2O; very soluble in chloroform,ctc, ethyl ether |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Colorless to yellow-brown |
| Water Solubility | Decomposes in water with formation of As(OH)<sub>3</sub> and HCl. Increasing dilutions in water result in As<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> precipitation |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,801 |
| Dielectric constant | 12.4(21℃) |
| Stability: | Stability Reacts with water. Corrodes many metals. Reacts violently on contact with potassium, sodium and aluminium. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7784-34-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Arsenic(III) chloride (7784-34-1) |
Safety information for ARSENIC(III) CHLORIDE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H331:Acute toxicity,inhalation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P262:Do not get in eyes, on skin, or on clothing. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for ARSENIC(III) CHLORIDE
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Arsenic trichloride, 99.5% CAS 7784-34-1View Details
Arsenic trichloride, 99.5% CAS 7784-34-1View Details
7784-34-1 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1