ARSENIC PENTOXIDE
- CAS NO.:1303-28-2
- Empirical Formula: As2O5
- Molecular Weight: 229.84
- MDL number: MFCD00003434
- EINECS: 215-116-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
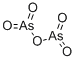
What is ARSENIC PENTOXIDE?
Description
Arsenic pentoxide is an odorless white lumpysolid or powder and nonflammable. It may be shipped as aconcentrated water solution. Molecular weight= 229.84;Specific gravity (H2O:1)= 4.32 at 25℃; 5.73[NIOSH]Boiling point= 499.8℃; Freezing/Melting point= 315℃(decomposes). Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704M Rating System): Health 4, Flammability 0, Reactivity 0.Highly soluble in water; solubility=66 g/100 mL.
Chemical properties
white to off-white powder and chunks
Chemical properties
Arsenic pentoxide is an important commercial compound of arsenic. It is a white, shapeless (amorphous), crystalline, lumpy solid or, hygroscopic powder, and is not combustible. It emits irritating or toxic fumes (or gases) in a fi re. Arsenic pentoxide is used as a solid or as a solution in the manufacture of arsenates, weed killer, metal adhesives, insecticides, fungicide wood preservatives, and colored gases, and in printing and dyeing. It can be synthesized either by burning elemental arsenic in oxygen, or by oxidizing arsenic trioxide with oxidizing agents, such as ozone, hydrogen peroxide, and nitric acid. Arsenic pentoxide decomposes to oxygen and As2O3 on heating, and dissolves readily in water to form arsenic acid, H3AsO4. Arsenic pentoxide reacts violently with bromine pentafl uoride and reducing agents, and attacks many metals in the presence of water or moisture.
Chemical properties
Arsenic pentoxide is an odorless white lumpy solid or powder and nonflammable. It may be shipped as a concentrated water solution.
Physical properties
White amorphous solid; deliquescent; density 4.32 g/cm3; melts at 315°C; dissolves slowly in water but is very soluble (230 g/100g at 20°C); also soluble in alcohol.
Occurrence
Arsenic pentoxide is used to make colored glass; in fungicide formulations; in adhesive for metals; in wood preservatives; in dyeing and printing; and to prepare arsenates.
The Uses of ARSENIC PENTOXIDE
Arsenic pentoxide (As2O5) is manufactured by adding oxygen to the trioxide form and is used to form many arsenic compounds.
The Uses of ARSENIC PENTOXIDE
manufacture of colored glass; in adhesives for metals; in wood preservatives; in weed control; as fungicide.
The Uses of ARSENIC PENTOXIDE
Arsenic(V) oxide is used in the preparation of metal arsenates. It is used for dye and printing industries. Further, it is used in wood preservatives, colored glass and metal adhesives.
Preparation
Arsenic pentoxide is prepared by dehydration of crystalline arsenic acid at 200°C or above. The former is made by treating arsenic metal or arsenious oxide with nitric acid. Also, the pentoxide can be prepared by the reaction of arsenic trioxide with oxygen under pressure.
General Description
A white crystalline solid. Noncombustible. Corrosive to metals in the presence of moisture. Toxic by ingestion.
Air & Water Reactions
Dissolves in water to give solutions of arsenic acid.
Reactivity Profile
ARSENIC PENTOXIDE is an oxidizing acid. Oxidizing acids are generally soluble in water with the release of hydrogen ions. The resulting solutions have pH's of less than 7.0. Materials in this group react with chemical bases (for example: amines and inorganic hydroxides) to form salts. These neutralization reactions occur as the base accepts hydrogen ions that the acid donates. Neutralizations can generate dangerously large amounts of heat in small spaces. The dissolution of acids in water or the dilution of their concentrated solutions with water may generate significant heat. The addition of water acids often generates sufficient heat in the small region of mixing to boil some of the water explosively. The resulting "bumping" spatters acid widely. These materials have significant ability as oxidizing agents. but that ability varies (for example, from high for nitric acid to low for sulfuric acid and most sulfonic acids). They can react with active metals, including iron and aluminum, and also many less active metals, to dissolve the metal and liberate hydrogen and/or toxic gases. Like other acids, materials in this group can initiate polymerization in certain classes of organic compounds. Their reactions with cyanide salts and compounds release gaseous hydrogen cyanide. Flammable and/or toxic gases are also often generated by their reactions with dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, nitriles, sulfides, and weak or strong reducing agents. Additional gas-generating reactions occur with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (SO2), and even carbonates: the carbon dioxide gas from the last is nontoxic but the heat and spattering from the reaction can be troublesome. Acids often catalyze (increase the rate of) chemical reactions.
Hazard
Confirmed carcinogen.
Health Hazard
ARSENIC PENTOXIDE is extremely toxic; the probable oral lethal dose for humans is 5-50 mg/kg, or between 7 drops and 1 teaspoonful for a 150-lb. person. It is irritating to eyes, nose, and throat. Chronic exposure may cause nerve damage to the extremities, alter cellular composition of the blood, and cause structural changes in blood components. There is sufficient evidence that inorganic arsenic compounds are skin and lung carcinogens in humans.
Health Hazard
Exposures to arsenic pentoxide dust causes eye irritation, itching, burning, mild temporary redness and/or infl ammation of the eye membrane (conjunctivitis), lacrimation, diplopia (temporary double vision), photophobia (abnormal sensitivity to light), vision dimness, and other transient eye damage or lesion formation (ulceration), cough, redness, sore throat, headache, dizziness, weakness, shortness of breath, and pain in chest. There may be a delay in the appearance of the symptoms of poisoning. Ingestion of arsenic pentoxide causes vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, severe thirst, muscular cramps, and shock. Arsenic pentoxide causes adverse health effects to the eyes, infl ammation and redness of the skin (erythroderma) with skin shedding (exfoliative dermatitis) may result from hyperkeratosis, pulmonary edema, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and respiratory failure. Cardiovascular disturbances (heart rate, sinus tachycardia, and ventricular dysrhythmias), acute degenerative disease or dysfunction of the brain (encephalopathy) may develop and progress over several days, leading to delirium, and confusion. Severe exposures to arsenic pentoxide cause seizures, brain swelling (cerebral edema) and brain vessel bleeding (micro-hemorrhages) and damage in, peripheral nervous system, bone marrow (hematopoietic changes), liver, and lungs. Exposure far above the occupational exposure limits (OEL) may result in death.
Fire Hazard
Fire may produce irritating or poisonous gases. Reacts with metal and may give off toxic arsine gas. Hazardous polymerization may not occur.
Safety Profile
Confirmed human carcinogen. Poison by ingestion and intravenous routes. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. Reacts vigorously with Rb2C2. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of arsenic. See also ARSENIC COMPOUNDS.
Potential Exposure
Arsenic pentoxide is used in production of metal arsenates; as an herbicide, defoliant on cotton; as a chemical intermediate; as an ingredient in wood preservatives; and in glass. Other possible uses are as an insecticide and soil sterilant.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.Note to physician: For severe poisoning BAL [British AntiLewisite, Dimercaprol, dithiopropanol (C3H8OS2)] has beenused to treat toxic symptoms of certain heavy metals poisoning—including arsenic. Although BAL is reported to have alarge margin of safety, caution must be exercised, becausetoxic effects may be caused by excessive dosage. Most can beprevented by premedication with 1-ephedrine sulfate (CAS:134-72-5). For milder poisoning penicillamine (not penicillin)has been used, both with mixed success. Side effects occurwith such treatment and it is never a substitute for controllingexposure. It can only be done under strict medical care.
storage
Arsenic pentoxide should be kept stored separately from strong bases, reducing substances, food, and feedstuffs and dry and safe area.
Shipping
UN1559 Arsenic pentoxide, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Incompatibilities
Decomposes above 315 C, forming oxygen and arsenic trioxide fumes. Arsenic pentoxide is an oxidizer; reacts violently with bromine pentafluoride and reducing agents. The solution in water is a weak acid. Incompatible with acids, strong alkalis; halogens, rubidium carbide, zinc. Corrosive to metals in the presence of moisture. Contact with acids or acid mists releases deadly arsine gas.
Waste Disposal
Dissolve in a minimum of concentrated hydrochloric acid. Dilute with water until white precipitate forms. Add HCl to dissolve. Saturate with H2S; filter and wash precipitate and return to supplier. Alternatively, precipitate with heavy metals, such as lime or ferric hydroxide in lieu of H2S. If needed, seek professional environmental engineering assistance from the United States Environmental Protection Agency Environmental Response Team at (908) 548-8730 (24-hour response line). Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/ mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Precautions
During handling and use of arsenic pentoxide, occupational workers should use protective gloves, protective clothing, safety goggles or eye protection in combination with breathing protection if using powder, and workers should not eat, drink, or smoke in the area. The worker should NOT wash away the spillage/waste into the sewer. The containers of arsenic pentoxide may explode when heated
Properties of ARSENIC PENTOXIDE
| Melting point: | 315 °C |
| Density | 4,32 g/cm3 |
| storage temp. | Poison room |
| solubility | very soluble in ethanol |
| form | Powder |
| Specific Gravity | 4.32 |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water and alcohol. |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,798 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1303-28-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Arsenic(V) pentoxide (1303-28-2) |
Safety information for ARSENIC PENTOXIDE
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H331:Acute toxicity,inhalation H350:Carcinogenicity H400:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for ARSENIC PENTOXIDE
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
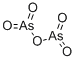
You may like
-
 Arsenic(V) oxide CAS 1303-28-2View Details
Arsenic(V) oxide CAS 1303-28-2View Details
1303-28-2 -
 Arsenic(V) oxide CAS 1303-28-2View Details
Arsenic(V) oxide CAS 1303-28-2View Details
1303-28-2 -
 Arsenic pentoxide CAS 1303-28-2View Details
Arsenic pentoxide CAS 1303-28-2View Details
1303-28-2 -
 Arsenic pentoxide, pract CAS 1303-28-2View Details
Arsenic pentoxide, pract CAS 1303-28-2View Details
1303-28-2 -
 ARSENIC(V)OXIDE CASView Details
ARSENIC(V)OXIDE CASView Details -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1