CACODYLIC ACID
Synonym(s):Dimethylarsinic acid;Dimethylarsonic acid;Hydroxydimethylarsine oxide
- CAS NO.:75-60-5
- Empirical Formula: C2H7AsO2
- Molecular Weight: 138
- MDL number: MFCD00002095
- EINECS: 200-883-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
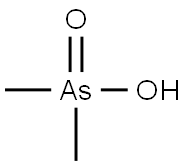
What is CACODYLIC ACID?
Description
Cacodylic acid is a colorless, odorless,crystalline solid arsenic compound. Molecular weight =138.02; Boiling point=200℃; Freezing/Melting point 5192℃. Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704 MRating System): Health 4, Flammability 0, Reactivity 0.[NJ]Highly soluble in water.
Chemical properties
white crystals or powder
The Uses of CACODYLIC ACID
Cacodylic acid is used for dermatologic treatment in cronic eczema, anemia and as a tonic.
The Uses of CACODYLIC ACID
antieczema, dermatologic, herbicide
The Uses of CACODYLIC ACID
A useful arsenic acid for proteomics research. It a good substitute for phosphate in applications to avoid phosphates. Cacodylic Acid is useful for some DNA applications and is also popular in microscopy.
What are the applications of Application
Cacodylic acid is a useful arsinic acid for proteomics research
Definition
ChEBI: The organoarsenic compound that is arsenic acid substituted on the central arsenic atom with two methyl groups.
General Description
A colorless, odorless crystalline solid. Melting point 195-196°C. Toxic by ingestion and irritating to skin and eyes.
Air & Water Reactions
Hygroscopic. Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
CACODYLIC ACID is a weak acid. Dissolves in water to yield solutions containing more hydrogen ions than pure water contains and so having a pH less than 7.0. Is neutralized exothermically by all bases to produce water plus a salt. Reacts (but usually slowly) with active metals to form gaseous hydrogen and a metal salt. Such reactions occur in principle for the solid acid but are quite slow if the solid acid remains dry. The solid may absorb enough water from the air and dissolve sufficiently in CACODYLIC ACID to corrode or dissolve iron, steel, and aluminum parts and containers. Reacts with cyanide salts to generate gaseous hydrogen cyanide. Flammable and/or toxic gases and heat may be generated with diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides. Also may react with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (SO2), to generate flammable and/or toxic gases and heat. Reaction with carbonates and bicarbonates generates a harmless gas (carbon dioxide) but still some heat. Can be oxidized exothermically by strong oxidizing agents and reduced by strong reducing agents; a wide variety of products is possible. May initiate polymerization reactions; may catalyze (increase the rate of) chemical reactions.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion.
Health Hazard
Chemical is essentially non-irritating in contact with skin or eyes. Ingestion causes arsenic poisoning, but symptoms are delayed.
Fire Hazard
Behavior in Fire: May form toxic oxides of arsenic when heated.
Potential Exposure
Used as an herbicide, soil sterilant and intimber thinning. Has been used as a chemical warfare agent.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seekmedical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, getmedical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.Note to physician: For severe poisoning BAL [British AntiLewisite, dimercaprol, dithiopropanol (C3H8OS2)] has beenused to treat toxic symptoms of certain heavy metals poisoning including arsenic. Although BAL is reported to have alarge margin of safety, caution must be exercised, becausetoxic effects may be caused by excessive dosage. Most can beprevented by premedication with 1-ephedrine sulfate (CAS:134-72-5). For milder poisoning penicillamine (not penicillin)has been used, both with mixed success. Side effects occurwith such treatment and it is never a substitute for controllingexposure. It can only be done under strict medical care.
Storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with cacodylicacid you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. A regulated, marked area should be establishedwhere this chemical is handled, used, or stored in compliance with OSHA Standard 1910.1045. Store in tightlyclosed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area away fromoxidizing agents, chemically active metals, strong bases,moisture, fertilizers, seeds, insecticides, and fungicides.
Shipping
UN1572 Cacodylic acid & UN1688 Sodium Cacodylate, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials. UN3465 Organoarsenic compound, solid, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required
Purification Methods
Recrystallise it from warm EtOH (3mL/g) by cooling and filtering. Dry it in a vacuum desiccator over CaCl2. It has also been recrystallised twice from propan-2-ol. [Koller & Hawkridge J Am Chem Soc 107 7412 1985, Beilstein 4 IV 3681.]
Incompatibilities
A strong reducing agent. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Aqueous solution reacts violently with chemically active metals releasing toxic arsenic fumes. Incompatible with oxidizers, sulfuric acid; caustics (strong bases), reducing agents; ammonia, amines, isocyanates, alkylene oxides; epichlorohydrin.
Properties of CACODYLIC ACID
| Melting point: | 195-198 °C |
| Boiling point: | >200 °C |
| storage temp. | Store at RT. |
| solubility | Methanol (Slightly), Water (Slightly) |
| pka | 1.57(at 25℃) |
| form | Powder/Solid |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water (50 mg/ml), water (2000 at 25°C), alcohols, and acetic acid. Insoluble in ether. |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,1604 |
| BRN | 1736965 |
| Stability: | Aqueous solutions react violently with active metals. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 75-60-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 100C) 2012 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cacodylic acid (75-60-5) |
Safety information for CACODYLIC ACID
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H350:Carcinogenicity H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for CACODYLIC ACID
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


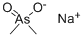


You may like
-
 Cacodylic acid CAS 75-60-5View Details
Cacodylic acid CAS 75-60-5View Details
75-60-5 -
 Cacodylic acid CAS 75-60-5View Details
Cacodylic acid CAS 75-60-5View Details
75-60-5 -
 Cacodylic acid CAS 75-60-5View Details
Cacodylic acid CAS 75-60-5View Details
75-60-5 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
