Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate
Synonym(s):Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate;APM;Ammonium phosphate monobasic;Ammonium Phosphate, Monobasic;Ammonium dihydrogenphosphate
- CAS NO.:7722-76-1
- Empirical Formula: H6NO4P
- Molecular Weight: 115.03
- MDL number: MFCD00003396
- EINECS: 231-764-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:56
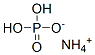
What is Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate?
Chemical properties
Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate is soluble in water and crystallizes from it as the anhydrous salt in the tetragonal system, as elongated prisms or needles. It is practically insoluble in ethanol.
Physical properties
White crystalline powder; odorless; density 1.80 g/cm3; readily dissolves in water (40 g/ 100 g); pH of 0.2 molar solution 4.2; slightly soluble in alcohol; insoluble in acetone.
Physical properties
Electrooptic coefficient (cm/stat-volt): γ63=-2.54×10-7, γ41=62×10-7
Dielectric constants: ε0=56.4–55.9 (102 –108 Hz, E⊥C), 16.4–13.7 (102 –10 Hz, E//C).
The Uses of Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate
Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate is a general purpose food additive which is readily soluble in water. A 1% solution has a ph of 4.3–5.0. It is used as a dough strengthener and leavening agent in baked goods and as a firming agent and ph control agent in condiments and puddings. It is also used in baking powder with sodium bicarbonate and as a yeast food.
Definition
ChEBI: The ammonium salt of phosphoric acid (molar ratio 1:1).
Preparation
Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate is obtained by reaction of equimolar amounts of ammonia and phosphoric acid:
NH3 + H3PO4 → (NH4)H2PO4.
General Description
Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (APM) is an inorganic salt widely used in fertilizer, baking powder and yeast production. It is also employed as an agent to control pH of a solution and in corrosion inhibition. APM can be prepared by reacting phosphoric acid with anhydrous ammonia maintaining the pH below 5.8. The change in some of the physical characteristics on its addition to a high carbonate containing unfired and fired illitic shale has been studied.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Agricultural Uses
Ammonium phosphate fertilizers are highly soluble in water and fast acting in soil to give nitrogen and phosphorus in a chemical combination. They form an important base for many compound fertilizers. Ammonium phosphates, particularly Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate(DAP), are the most popular phosphate fertilizers worldwide because of their high utility and good physical properties. The standard commodity grade of diammonium phosphate is 18-46-0. Pure and completely soluble ammonium phosphates are used mainly as liquid fertilizers.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate exhibits non-linear optical (NLO) and electro-optic (EO) properties.
Potential Exposure
Used in fireproofing of textiles; wood and paper; in soldering flux; as a fertilizer; a buffer; in baking powder and food additives.
Shipping
There are no DOT/UN listed requirements.
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from water (0.7mL/g) between 100o and 0o.
Incompatibilities
Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate is incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Contact with air causes this chemical to produce anhydrous ammonia fumes.
Waste Disposal
May be flushed to sewer with huge volumes of water.
Properties of Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate
| Melting point: | 190 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 87.4 °C |
| Density | 1.02 g/mL at 20 °C |
| vapor pressure | 0.066 hPa (125 °C) |
| RTECS | TC6587000 |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature |
| solubility | H2O: 0.1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | Solid |
| color | White or colorless |
| Specific Gravity | 1.803 |
| PH | 3.8-4.4 (25℃, 50mg/mL in H2O) |
| PH Range | 3.8 - 4.4 |
| Odor | brilliant wh. cryst. or powd., odorless |
| Water Solubility | 368 g/L (20 ºC) |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: ≤0.059 λ: 280 nm Amax: ≤0.050 |
| Merck | 14,543 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7722-76-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Monoammonium phosphate (7722-76-1) |
Safety information for Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate
| InChIKey | LFVGISIMTYGQHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Buradon Inc.
Helm India Pvt. Ltd.
R.D. Chemical & Fertilizers
Destiny Chemicals
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Ammonium Phosphate Mono Basic 98%View Details
Ammonium Phosphate Mono Basic 98%View Details -
 Ammonium Phosphate 99%View Details
Ammonium Phosphate 99%View Details -
 Mono ammonium Phosphate 99%View Details
Mono ammonium Phosphate 99%View Details -
 Mono ammonium phosphate 99%View Details
Mono ammonium phosphate 99%View Details -
 Ammonium phosphate, monobasic 99%View Details
Ammonium phosphate, monobasic 99%View Details -
 Ammonium phosphate, monobasic 98%View Details
Ammonium phosphate, monobasic 98%View Details -
 Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate Matrix Modifier Solution CASView Details
Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate Matrix Modifier Solution CASView Details -
 Ammonium Phosphate PowderView Details
Ammonium Phosphate PowderView Details
12027-67-7
