Agomelatine
Synonym(s):N-[2-(7-Methoxy-1-naphthalenyl)ethyl]-acetamide;S-20098
- CAS NO.:138112-76-2
- Empirical Formula: C15H17NO2
- Molecular Weight: 243.3
- MDL number: MFCD00916659
- EINECS: 629-727-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-03-12 07:03:40
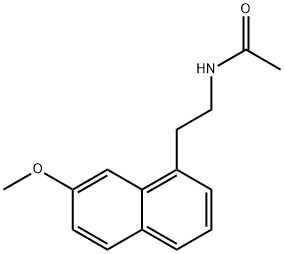
What is Agomelatine?
Absorption
Bioavailability is less than 5%.
Description
Agomelatine is an agonist of melatonin (MT) receptors and a derivative of melatonin . It binds to MT1 and MT2 receptors (Kis = 0.14 and 0.41 nM, respectively) and has an EC50 value of 0.1 nM in a [35S]GTPγS binding assay using CHO cells expressing MT2 receptors. Agomelatine is also an antagonist of the serotonin (5-HT) receptor subtypes 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C (Kis = 0.26 and 0.71 nM, respectively, for the human receptors). Agomelatine (40 mg/kg) inhibits the penile erection response induced by the 5-HT2 agonist Ro 60-0175 in rats. It also increases extracellular levels of noradrenaline and dopamine in the frontal cortex of freely moving rats when administered at doses ranging from 20 to 80 mg/kg. Agomelatine (10 mg/kg) reduces immobility time in the forced swim test and increases the amount of time spent in the open arms of the elevated plus maze in mice, indicating antidepressant-like and anxiolytic-like activity, in a transgenic neuroendocrine model of depression. It also increases the rate of readjustment to circadian activity cycles following an induced phase shift.
Chemical properties
White Solid
The Uses of Agomelatine
Agomelatine is an antidepressant drug. It is classified as a norepinephrine-dopamine disinhibitor (NDDI) due to its antagonism of the 5-HT2C receptor. Activation of 5-HT2C receptors by serotonin inhibits dopamine and norepinephrine release. Antagonism of
The Uses of Agomelatine
Agomelatine is a melatoninergic agonist and selective antagonist of 5-HT2C receptors, and has been shown to be active in several animal models of depression. Agomelatine (S20098) displayed pKi values of 6.4 and 6.2 at native (porcine) and cloned, human (h)5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)2C receptors, respectively.
The Uses of Agomelatine
Agomelatine has been used:
- to study its effects on adult neurogenesis and hippocampus apoptosis using the stress-induced depression model of rats
- to explore its effects on tau protein phosphorylation and to study its neuroprotective mechanism
- to study its effects on intracellular calcium ([Ca2+]i) signaling in peripheral neurons of rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons
What are the applications of Application
Agomelatine is a melatoninergic agonist of the 5-HT2C receptor
Indications
Agomelatine is indicated to treat major depressive episodes in adults.
Background
Agomelatine is structurally closely related to melatonin. Agomelatine is a potent agonist at melatonin receptors and an antagonist at serotonin-2C (5-HT2C) receptors, tested in an animal model of depression. Agomelatine was developed in Europe by Servier Laboratories Ltd. and submitted to the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in 2005. The Committee for Medical Products for Human Use (CHMP) recommended refusal of marketing authorization on 27 July 2006. The major concern was that efficacy had not been sufficiently shown. In 2006 Servier sold the rights to develop Agomelatine in the US to Novartis.
The development for the US market was discontinued in October 2011. It is currently sold in Australia under the Valdoxan trade name.
Definition
ChEBI: Agomelatine is a member of acetamides.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Agomelatine is an extremely potent agonist at both melatonin receptors (MT1 and MT2), with additional antagonism at 5HT2C. It is a novel antidepressant with many desired in vivo properties, including neuroprotection and neurogenesis in depression-sensitive brain areas. Agomelatine′s efficacy appears to be due to both melatonergic and serotonergic properties. In neurogenesis assays, both in vitro and in vivo, the compound effects were differentially affected by antagonists for MT1/MT2 and 5HT2C, demonstrating actions through all three receptors.
Pharmacokinetics
Agomelatine resynchronises circadian rhythms in animal models of delayed sleep phase syndrome and other circadian rhythm disruptions. It increases noradrenaline and dopamine release specifically in the frontal cortex and has no influence on the extracellular levels of serotonin. Agomelatine has shown an antidepressant-like effect in animal depression models, (learned helplessness test, despair test, and chronic mild stress) circadian rhythm desynchronisation, and in stress and anxiety models. In humans, agomelatine has positive phase shifting properties; it induces a phase advance of sleep, body temperature decline and melatonin onset. Controlled studies in humans have shown that agomelatine is as effective as the SSRI antidepressants paroxetine and sertraline in the treatment of major depression
Clinical Use
Antidepressant
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antibacterials: avoid with ciprofloxacin.
Antidepressants: metabolism inhibited by
fluvoxamine.
Antimalarials: avoid with artemether with
lumefantrine and artenimol with piperaquine.
Metabolism
Hepatic (90% CYP1A2 and 10% CYP2C9).
Metabolism
Agomelatine is rapidly metabolised, mainly by the hepatic cytochrome P450 isoenzyme CYP1A2; the isoenzymes CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 also make a minor contribution. The major metabolites, hydroxylated and demethylated agomelatine, are not active and are rapidly conjugated and eliminated in the urine.
References
[1] zupancic m, guilleminault c. agomelatine. cns drugs, 2006, 20(12): 981-992.
Properties of Agomelatine
| Melting point: | 107-109°C |
| Boiling point: | 478.8±28.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.109±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: >50mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 16.17±0.46(Predicted) |
| color | white to off-white |
| Merck | 14,190 |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C15H17NO2/c1-11(17)16-9-8-13-5-3-4-12-6-7-14(18-2)10-15(12)13/h3-7,10H,8-9H2,1-2H3,(H,16,17) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 138112-76-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Agomelatine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H400:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. |
Computed Descriptors for Agomelatine
| InChIKey | YJYPHIXNFHFHND-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C(NCCC1=C2C(C=CC(OC)=C2)=CC=C1)(=O)C |
Agomelatine manufacturer
SETV ASRV LLP
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Agomelatine 99%View Details
Agomelatine 99%View Details -
 Agomelatine 99%View Details
Agomelatine 99%View Details -
 Agomelatine 98% (HPLC) CAS 138112-76-2View Details
Agomelatine 98% (HPLC) CAS 138112-76-2View Details
138112-76-2 -
 Agomelatine 99%View Details
Agomelatine 99%View Details -
 Agomelatin 138112-76-2 95-99%View Details
Agomelatin 138112-76-2 95-99%View Details
138112-76-2 -
 Agomelatine CAS 138112-76-2View Details
Agomelatine CAS 138112-76-2View Details
138112-76-2 -
 Agomelatine 98% CAS 138112-76-2View Details
Agomelatine 98% CAS 138112-76-2View Details
138112-76-2 -
 Agomelatine CAS 138112-76-2View Details
Agomelatine CAS 138112-76-2View Details
138112-76-2
