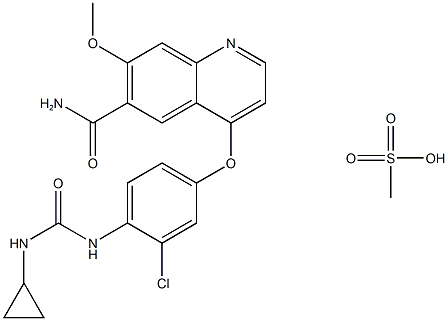
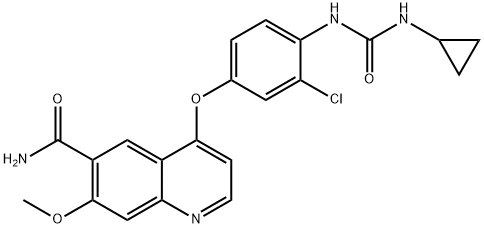
Afatinib
- CAS NO.:850140-72-6
- Empirical Formula: C24H25ClFN5O3
- Molecular Weight: 485.94
- MDL number: MFCD12407405
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-25 07:49:43
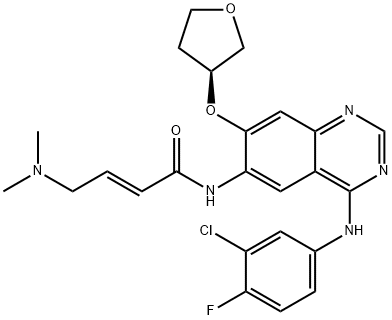
What is Afatinib?
Absorption
Following oral administration, time to peak plasma concentration (Tmax) is 2 to 5 hours . Maximum concentration (Cmax) and area under the concentration-time curve from time zero to infinity (AUC0-∞) values increased slightly more than dose proportional in the range of 20 to 50 mg . The geometric mean relative bioavailability of 20 mg tablets was 92% as compared to an oral solution .
Additionally, systemic exposure to afatinib is decreased by 50% (Cmax) and 39% (AUC0-∞), when administered with a high-fat meal compared to administration in the fasted state . Based on population pharmacokinetic data derived from clinical trials in various tumor types, an average decrease of 26% in AUCss was observed when food was consumed within 3 hours before or 1 hour after taking afatinib .
Toxicity
Most common adverse reactions (≥20%) are diarrhea, rash/dermatitis, acneiform, stomatitis, paronychia, dry skin, decreased appetite, pruritus .
Conversely, overdose in 2 healthy adolescents involving the ingestion of 360 mg each of afatinib (as part of a mixed drug ingestion) was associated with adverse events of nausea, vomiting, asthenia, dizziness, headache, abdominal pain and elevated amylase (< 1.5 times ULN) . Both individuals recovered from these adverse events .
Description
Afatinib (850140-72-6) is a clinically useful kinase inhibitor approved for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. It is a potent and highly selective inhibitor of mutant and wild-type EGFR (IC50= 0.5 nM) and HER2 (IC50?= 14 nM).
Chemical properties
Class: receptor tyrosine kinase
Treatment: NSCLC
Elimination half-life = 37 h
Protein binding = 95%
The Uses of Afatinib
Afatinib is a tyrosine kinase receptor inhibitor that is used to treat metastatic (cancer that has already spread) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that has certain types of abnormal epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) genes in patients who have not received any treatments for cancer that has already spread to other parts of the body. This medicine is also used to treat patients with metastatic squamous NSCLC who have received medicines containing platinum but did not work well.
Indications
Afatinib is a kinase inhibitor indicated as monotherapy for the first-line treatment of (a) Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) TKI (tyrosine kinase inhibitor)-naive adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumours have non-resistant EGFR mutations as detected by an FDA-approved test , and (b) adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC of squamous histology progressing on or after platinum-based chemotherapy .
Recently, as of January 2018, the US FDA approved a supplemental New Drug Application for Boehringer Ingelheim's Gilotrif (afatinib) for the first line treatment of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors have non-resistant epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations as detected by an FDA-approved test . The new label includes data on three additional EGFR mutations: L861Q, G719X and S768I .
Background
Afatinib is a 4-anilinoquinazoline tyrosine kinase inhibitor in the form of a dimaleate salt available as Boehringer Ingelheim's brand name Gilotrif . For oral use, afatinib tablets are a first-line (initial) treatment for patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with common epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations as detected by an FDA-approved test . Gilotrif (afatinib) is the first FDA-approved oncology product from Boehringer Ingelheim .
Definition
ChEBI: Afatinib is a quinazoline compound having a 3-chloro-4-fluoroanilino group at the 4-position, a 4-dimethylamino-trans-but-2-enamido group at the 6-position, and an (S)-tetrahydrofuran-3-yloxy group at the 7-position. Used (as its dimaleate salt) for the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. It has a role as a tyrosine kinase inhibitor and an antineoplastic agent. It is a member of quinazolines, a member of furans, an organofluorine compound, an enamide, an aromatic ether, a tertiary amino compound, a member of monochlorobenzenes and a secondary carboxamide.
Indications
The collection of ibrutinib (Imbruvica(R), Pharmacyclics Inc.), afatinib, and osimertinib represents the small, yet expanding, group of covalent SMKIs. Ibrutinib is a non-receptor Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor approved for the treatment of relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Afatinib, approved for NSCLC in 2013 and squamous NSCLC in 2016, is a second-generation irreversible EGFR inhibitor that targets wild-type EGFR, the mutant T790M EGFR, and HER2. Osimertinib (AZD9291), which was approved by FDA in November 2015, is a third-generation irreversible EGFR inhibitor that selectively targets the mutant T790M EGFR. Rociletinib, which shares a high degree of structural similarity with that of osimertinib, is a promising covalent EGFR inhibitor developed by Clovis Oncology aimed for the treatment of patients with EGFR T790M-mutated NSCLC, until the company terminated its development in May 2016 following a negative vote fromthe FDA’sOncologic Drugs Advisory Committee.
Pharmacokinetics
Aberrant ErbB signaling triggered by receptor mutations, and/or amplification, and/or receptor ligand overexpression contributes to the malignant phenotype . Mutation in EGFR defines a distinct molecular subtype of lung cancer .
In non-clinical disease models with ErbB pathway deregulation, afatinib as a single agent effectively blocks ErbB receptor signaling resulting in tumor growth inhibition or tumor regression . NSCLC tumors with common activating EGFR mutations (Del 19, L858R) and several less common EGFR mutations in exon 18 (G719X) and exon 21 (L861Q) are particularly sensitive to afatinib treatment in non-clinical and clinical settings . Limited non-clinical and/or clinical activity was observed in NSCLC tumors with insertion mutations in exon 20 .
The acquisition of a secondary T790M mutation is a major mechanism of acquired resistance to afatinib and gene dosage of the T790M-containing allele correlates with the degree of resistance in vitro . The T790M mutation is found in approximately 50% of patients' tumors upon disease progression on afatinib, for which T790M targeted EGFR TKIs may be considered as a next line treatment option . Other potential mechanisms of resistance to afatinib have been suggested preclinically and MET gene amplification has been observed clinically .
At the same time, the effect of multiple doses of afatinib (50 mg once daily) on cardiac electrophysiology and the QTc interval was evaluated in an open-label, single-arm study in patients with relapsed or refractory solid tumors . Ultimately, no large changes in the mean QTc interval (i.e., >20 ms) were detected in the study .
Clinical Use
Protein kinase inhibitor:
Treatment of non-small cell lung cancer
Enzyme inhibitor
This oral quinazoline derivative and EGFR/HER2-directed protein kinase inhibitor (FW = 485.94; CASs = 439081-18-2 (free base), 936631-70-8 (maleic acid salt), 1254955-21-9 (HCl salt); Solubility (at 25°C): 197 mg/mL DMSO, 1 mg/mL Water), also known by its code name BIBW2992, its trade names Gilotrif? Tomtovok?, Tovok?, and its systematic name (S,E)-N-(4-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl-amino)-7-(tetrahydrofuran- 3-yloxy)quinazolin-6-yl)-4-(dimethylamino)but-2-enamide, irreversibly inactivates EGFRwt, EGFRL858R, EGFRL858R/T790M and HER2with IC50 values of 0.5 nM, 0.4 nM, 10 nM and 14 nM, respectively. Mode of Action: The irreversible binding of afatinib to HER2 inactivates its interactions with a preferred partner of EGFR, and blocking the HER2- EGFR heterodimerization reduces their intrinsic tyrosine kinase activities. Irreversible inhibitors (such as afatinib and dacomitinib) that target all ErbB family receptor tyrosine kinases are intended to confer sustained disease control in ErbB-dependent cancers. Because nearly all EGFRmutated patients eventually develop resistance to reversible EGFR-TKIs after a median of 14 months, tafatinib’s irreversible action is thought to be a promising feature of its mode of action. Pharmacokinetics: Afatinib’s PK profile is best described by a two-compartment disposition model, with first-order absorption and linear elimination. There was a slightly more than proportional increase in exposure with increasing dose, most likely due to dose-dependent relative bioavailability. For the therapeutic dose of 40 mg, the estimated apparent total clearance rate at steady state was 734 mL/min.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antipsychotics: avoid with clozapine - increased risk
of agranulocytosis.
Ciclosporin: concentration of afatinib possibly
increased, separate administration by 6-12 hours.
Tacrolimus: concentration of afatinib possibly
increased, separate administration by 6-12 hours.
Metabolism
Enzyme-catalyzed metabolic reactions play a negligible role for afatinib in vivo . Covalent adducts to proteins were the major circulating metabolites of afatinib .
Metabolism
Enzyme-catalysed metabolic reactions play a negligible role for afatinib in vivo. Covalent adducts to proteins were the major circulating metabolites of afatinib. Excreted mainly in the faeces.
References
1) Li?et al. (2008),?BIBW2992, an irreversible EGFR/HER2 inhibitor highly effective in preclinical lung cancer models; Oncogene,?27?4702
Properties of Afatinib
| Melting point: | 102 °C |
| Boiling point: | 676.9±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.380 |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (up to 25 mg/ml) or in Ethanol (up to 25 mg/ml). |
| form | Yellow powder. |
| pka | 11.79±0.43(Predicted) |
| color | Pale yellow |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20°C for up to 2 months. |
Safety information for Afatinib
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P311:Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for Afatinib
Afatinib manufacturer
Sai Life Sciences Ltd
Shreyaa Medilife Private Limited
Myosynth Laboratories Pvt Ltd
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

![4-QuinazolinaMine, N-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-6-nitro-7-[[(3S)-tetrahydro-3-furanyl]oxy]-](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/314771-88-5.gif)

You may like
-
 850140-72-6 98%View Details
850140-72-6 98%View Details
850140-72-6 -
 Afatinib 99%View Details
Afatinib 99%View Details
850140-72-6 -
 850140-72-6 Afatinib 98%View Details
850140-72-6 Afatinib 98%View Details
850140-72-6 -
 850140-72-6 98%View Details
850140-72-6 98%View Details
850140-72-6 -
 Afatinib 98%View Details
Afatinib 98%View Details
850140-72-6 -
 Afatinib 850140-72-6 98%View Details
Afatinib 850140-72-6 98%View Details
850140-72-6 -
 Afatinib CAS 850140-72-6View Details
Afatinib CAS 850140-72-6View Details
850140-72-6 -
 850140-72-6 Afatinib 98%View Details
850140-72-6 Afatinib 98%View Details
850140-72-6