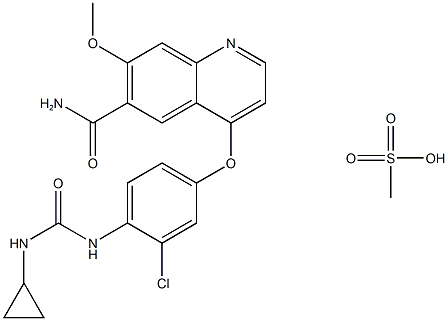
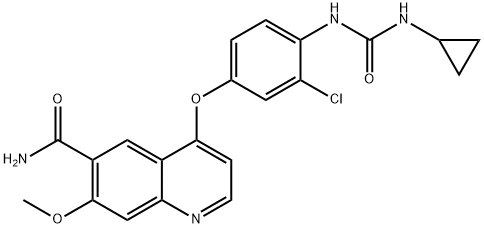
lenvatinib Mesylate
Synonym(s):4-[3-Chloro-4-(N’-cyclopropylureido)phenoxy]-7-methoxyquinoline-6-carboxamide methanesulfonate;4-[3-Chloro-4-[(cyclopropylaminocarbonyl)amino]phenoxy]-7-methoxy-6-quinolinecarboxamide mesylate;4-[3-chloro-4-[[(cyclopropylamino)carbonyl]amino]phenoxy]-7-methoxy-6-Quinolinecarboxamide methanesulfonate (1:1);Lenvatinib methanesulfonate
- CAS NO.:857890-39-2
- Empirical Formula: C22H23ClN4O7S
- Molecular Weight: 522.95862
- MDL number: MFCD18633219
- EINECS: 812-398-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 15:53:33
What is lenvatinib Mesylate?
Description
Lenvatinib mesylate (lenvatinib) is an orally available, receptor‐type tyrosine kinase inhibitor, which was developed at Eisai in 2015. It was approved by the FDA in 2015 for the treatment of differentiated thyroid cancer that is either locally recurrent, metastatic, or progressive and did not respond to radioactive iodine treatment. In May 2016, the FDA approved the drug as a combination therapy with everolimus for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma. Because VEGF (and fibroblast growth factor receptors, known as FGFRs) are thought to play a role in cardiovascular signaling pathways, VEGF2R and FGFR inhibition are thought to be the mechanisms behind the primary side effect of lenvatinib mesylate, which is hypertension.
The Uses of lenvatinib Mesylate
Lenvatinib Mesylate is used in preparation of anti-human CTLA4xPD-1 bispecific antibodies for diagnosis, prevention and treatment of tumor or anemia.
The Uses of lenvatinib Mesylate
E7080 (Lenvatinib) is a multi-target inhibitor of VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 with IC50 of 4 nM and 5.2 nM, respectively.
Definition
ChEBI: Lenvatinib mesylate is a methanesulfonate salt obtained by reaction of lenvatinib with one molar equivalent of methanesulfonic acid. A multi-kinase inhibitor and orphan drug used (as its mesylate salt) for the treatment of various types of thyroid cancer that do not respond to radioiodine. It has a role as an EC 2.7.10.1 (receptor protein-tyrosine kinase) inhibitor, a fibroblast growth factor receptor antagonist, an orphan drug, a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor antagonist and an antineoplastic agent. It contains a lenvatinib(1+).
Mechanism of action
Lenvatinib mesylate works by blocking proteins that signal cancer cells to multiply. It also blocks proteins that signal the formation of new blood vessels that are needed to support tumor growth. Blocking these signals keeps cancer cells from growing.
Pharmacokinetics
Lenvatinib is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with tmax typically observed at 1 to 4 hours postdose. Food does not affect the extent of absorption but slows the rate of absorption. When administered with food to healthy subjects, peak plasma concentrations are delayed by 2 hours.
In vitro binding of lenvatinib to human plasma proteins was high and ranged from 98% to 99% (0.3 – 30 μg/mL, lenvatinib Mesylate). This binding was mainly to albumin with minor binding to α1-acid glycoprotein and γ-globulin. In vitro, the lenvatinib blood-to-plasma concentration ratio ranged from 0.589 to 0.608 (0.1 - 10 μg/mL, lenvatinib Mesylate). Lenvatinib is a substrate for P-gp and BCRP. Lenvatinib is not a substrate for OAT1, OAT3, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OCT1, OCT2, or the BSEP.
Side Effects
The most prevalent AEs were hypertension (77.8%), fatigue (55.6%), weight loss (51.9%).In addition, there may be fatigue or tiredness, rashes, redness, itching or peeling of the palms and soles of the feet, diarrhoea, nausea, constipation and heartburn.
Synthesis
Starting from commercial aniline
193, a substitution reaction under neutral conditions in warm
isopropyl alcohol with a commercial vinyl methoxy derivative of
Meldrum?ˉs acid (194) produced enamine 195 in good yield.
Next, subjection of 195 to DOWTHERM A at 190 ??C affected
an intramolecular cyclizative substitution reaction, followed by
loss of acetone, and a decarboxylation reaction to furnish
quinolone 196. This cyclization reaction, which is a variant of
the Conrad-Limpach reaction, is particularly noteworthy
given the temperature and pH at which it takes place. Conrad-
Limpach cyclizations typically proceed under basic conditions
at temperatures well above 240 ??C. However, a process was
developed by Zeneca in 2004 which involved subjecting 195 to
the DOWTHERM heat transfer fluid (commercially available
from Dow and Sigma-Aldrich, consisting of a eutectic mixture
of biphenyl and diphenyl oxide) allowed the team to lower
the temperature required for the reaction, clearly observe
bubbling of gas indicating the progress of the reaction, and
simple cooling and treatment with ether to facilitated
precipitate formation. The resulting solid could be collected
by filtration and required no additional purification on scale in
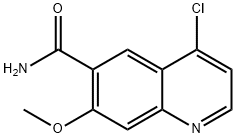
80% yield. Quinoline 196 was then converted to the
corresponding chloride using thionyl chloride in refluxing
DMF, and the resulting ester 197 was converted to the
corresponding amide through the use of 28% aqueous
ammonia in warm ethanol, which ultimately produced the
key chloroquinoline lenvatinib subunit 198 in 80% yield from
197.

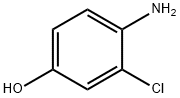
Commercial aminophenol 199 was
converted to the corresponding carbamate through the use of
phenyl chloroformate in essentially quantitative yield prior to
subjection to cyclopropylamine in chilled DMF, which
ultimately furnished urea 201 in 77% overall yield from 200.
Next, exposure of phenol 201 to chloroquinoline 198 in the presence of potassium t-butoxide followed by
treatment with methanesulfonic acid and acetic acid resulted in
clean formation of lenvatinib mesylate (XXV) in 96% yield
across the two-step sequence.
Solubility in water
lenvatinib Mesylate is a white powder sparingly soluble in acetic acid and slightly soluble in water. It is very slightly soluble in 1,3-dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone and practically insoluble in acetonitrile, dehydrated ethanol, 1-propanol, 2-propanol, 1-octanol, and isopropyl acetate. In aqueous solutions, lenvatinib mesylate is slightly soluble in 0.1 mol/L HCl and practically insoluble in Britton-Robinson buffer, pH 3-11.
Properties of lenvatinib Mesylate
| Melting point: | >220°C (dec.) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
Safety information for lenvatinib Mesylate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for lenvatinib Mesylate
| InChIKey | HWLFIUUAYLEFCT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(N)C1C=C2C(N=CC=C2OC2C=C(Cl)C(NC(=O)NC3CC3)=CC=2)=CC=1OC.CS(=O)(O)=O |
lenvatinib Mesylate manufacturer
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 857890-39-2 Lenvatinib Mesylate (Form C and MIBK Solvate) 98%View Details
857890-39-2 Lenvatinib Mesylate (Form C and MIBK Solvate) 98%View Details
857890-39-2 -
 857890-39-2 98%View Details
857890-39-2 98%View Details
857890-39-2 -
 Lenvatinib mesylate 98%View Details
Lenvatinib mesylate 98%View Details
857890-39-2 -
 Lenvatinib mesylate 95% CAS 857890-39-2View Details
Lenvatinib mesylate 95% CAS 857890-39-2View Details
857890-39-2 -
 Lenvatinib mesylate CAS 857890-39-2View Details
Lenvatinib mesylate CAS 857890-39-2View Details
857890-39-2 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8