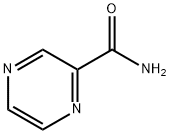
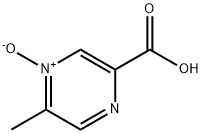
Acipimox
Synonym(s):2-Carboxy-5-methylpyrazine 4-oxide;5-Methylpyrazinecarboxylic acid 4-oxide
- CAS NO.:51037-30-0
- Empirical Formula: C6H6N2O3
- Molecular Weight: 154.12
- MDL number: MFCD00865757
- EINECS: 256-928-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 21:30:31
What is Acipimox?
Description
Acipimox is a nicotinic acid derivate that structurally related to nicotinic acid. Like nicotinic acid, lowers lipids effectively, but unlike nicotinic acid, acipimox is longer acting and therefore much less prone to produce free fatty acid rebounding. It is usually employed in man in the therapy of hypertriglyceridemia. In addition to its lipid lowering activity, it produces a beneficial elevation of the anti-atherogenic high density lipoprotein subfraction, HDL2. Acipimox is recommended as a lipid-lowering agent to treat hyperlipidemia in patients with noninsulin dependent diabetes mellitus.
Chemical properties
Yellow Solid
Originator
Erbamont (Italy)
Characteristics
The advantages of acipimox to niacin are as follows:
Longer duration of inhibition of hormone-sensitive lipase than niacin.
A lower dose (250 mg BD or TDS) of acipimox is required to lower lipid levels and better tolerability with fewer side effects than niacin.
Acipimox increases insulin sensitivity, while niacin causes insulin resistance. Thus, acipimox has a favorable role in patients with dyslipidemia and diabetes, whereas niacin is contraindicated in diabetes.
Acipimox has adjuvant role in the management of PCOD and increases tissuesensitivity to GH, whereas niacin does not.
The Uses of Acipimox
Acipimox is a long-acting antilipemic agent and used for the treatment of hyperlipoproteinemias, in particular hypertriglyceridemias, and as adjunctive therapy for affecting cholesterol metabolism.
What are the applications of Application
Acipimox is a hypolipidaemic agent that is more potent than nicotinic acid and clofibrate
Background
Acipimox is a niacin derivative used as a hypolipidemic agent. It is used in low doses and may have less marked adverse effects, although it is unclear whether the recommended dose is as effective as are standard doses of nicotinic acid. Acipimox inhibits the production of triglycerides by the liver and the secretion of VLDL, which leads indirectly to a modest reduction in LDL and increase in HDL. Long-term administration is associated with reduced mortality, but unwanted effects limit its clinical use. Adverse effects include flushing (associated with Prostaglandin D2), palpitations, and GI disturbances. Flushing can be reduced by taking aspirin 20-30 min before taking Acipimox. High doses can cause disorders of liver function, impair glucose tolerance and precipitate gout.
Indications
Used in the treatment of hyperlipidemias (abnormally elevated levels of any or all lipids and/or lipoproteins in the blood).
Preparation
Synthesis of acipimox: Under cooling and stirring, 78 g of maleic anhydride was dissolved in a solution of 60 ml of chloroform, and 40 ml of 30% hydrogen peroxide was added. After 2 h, 4.8 g of 5-Methyl-2-pyrazinecarboxylic acid was added, and the temperature was kept at 0-5 °C for 2 d. The maleic acid was filtered off. Concentrate to a small volume, add ethyl acetate, and filter to obtain 1.1 g of acipimox, the melting point of which is 178-180 °C.
Definition
ChEBI: 5-methyl-4-oxido-2-pyrazin-4-iumcarboxylic acid is a pyrazinecarboxylic acid.
brand name
OLBETAM
Benefits
1. Act on the liver and adipose tissue, inhibit the lipolysis of adipose tissue, thereby reducing plasma total cholesterol, triglyceride, low-density lipoprotein, and very low-density lipoprotein.
2. Increase high-density lipoprotein in plasma, which is beneficial to the transport and clearance of cholesterol.
3. Increase liver glycogen synthesis and lower blood sugar levels. Asimimox can be used as the first-choice lipid-lowering drug for the treatment of various hyperlipidemias, especially for those with diabetes mellitus with hyperlipidemia.
Biological Activity
Acipimox, also known as olbemox, is a nicotinic acid analog. It functions as an anti-lipolytic drug and vasodilator. Acipimox may be used in various metabolic studies involving insulin and ghrelin. It lowers total cholesterol and total triglycerides, which helps in the treatment of hyperlipidemia.
Clinical Use
Acipimox was introduced in Europe to treat hyperlipidemia in 1985. Acipimox is a weak agonist of GPR109A with micromolar binding and functional activity.Like niacin, acipimox raises HDL-C and triggers vasodilation in humans.However, it remains unclear whether acipimox causes mild hyperglycemia as is observed with niacin.
Side Effects
Adverse effects include flushing (associated with Prostaglandin D2), rash, palpitations, and GI disturbances (nausea, dyspepsia, diarrhoea and upper abdominal pain) . Flushing can be reduced by taking aspirin 20-30 min before taking Acipimox. High doses can cause disorders of liver function, impair glucose tolerance and precipitate gout.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs. It can be combined with powerful hypolipidemic drugs such as fenofibrate and lovastatin to enhance the efficacy and reduce the dose and side effects of the drug. Acyclolimus can improve the efficacy of hypoglycemic drugs, so it is necessary to reduce the dose of hypoglycemic drugs and adjust the dose according to the patient's blood sugar. In antioxidant therapy, it can be used in combination with probucol.
Metabolism
Not Available
Metabolism
Acipimox is not significantly metabolised and is eliminated almost completely intact by the urinary route.
Mode of action
Acipimox is a nicotinic acid derivative (methyl-pyrazine-carboxylic-acid-oxide) that acts on the niacin receptor (GPR109A).The mechanism of action is similar to niacin (inhibition of hormone-sensitive lipase). However,the inhibition of hormone-sensitive lipase by acipimox is remarkably longer (9-12 h) than that of niacin (3 h). Similar to niacin, acipimox also lowers the levels of lp(a).
References
[1] Ana T.M.G. Santomauro, Guenther Boden, Maria E.R. Silva, Dalva M. Rocha, Rosa F. Santos, Mileni J.M. Ursich, Paula G. Strassmann and Bernardo L. Wajchenberg, Overnight Lowering of Free Fatty Acids With Acipimox Improves Insulin Resistance and Glucose Tolerance in Obese Diabetic and Nondiabetic Subjects, Diabetes, 1999, vol. 48, 1836-1841
[2] K. C. Shih, C. F. Kwok, C. M. Hwu, L. C. Hsiao, S. H. Li, Y. F. Liu, L. T. Ho, Acipimox attenuates hypertriglyceridemia in dyslipidemic noninsulin dependent diabetes mellitus patients without perturbation of insulin sensitivity and glycemic control, Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 1997, vol. 36, 113-119
Properties of Acipimox
| Melting point: | 177-180 °C |
| Boiling point: | 539.0±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.44±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in methanol, water (100 mM), DMSO (100 mM), ethanol (<1 mg/ml at 25° C), and 1 M NH4OH (1 mg/ml). |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 2.80±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | Yellow |
| Merck | 14,111 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 51037-30-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Pyrazinecarboxylic acid, 5-methyl-, 4-oxide (51037-30-0) |
Safety information for Acipimox
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Acipimox
| InChIKey | DJQOOSBJCLSSEY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Acipimox manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Acipimox CAS 51037-30-0View Details
Acipimox CAS 51037-30-0View Details
51037-30-0 -
 Acipimox 98% (HPLC) CAS 51037-30-0View Details
Acipimox 98% (HPLC) CAS 51037-30-0View Details
51037-30-0 -
 Acipimox 97% CAS 51037-30-0View Details
Acipimox 97% CAS 51037-30-0View Details
51037-30-0 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8