Glipizide
Synonym(s):1-Cyclohexyl-3-{4-[2-(5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxamido)ethyl]phenylsulfonyl}urea;Glipizide
- CAS NO.:29094-61-9
- Empirical Formula: C21H27N5O4S
- Molecular Weight: 445.54
- MDL number: MFCD00072159
- EINECS: 249-427-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-16 16:15:04
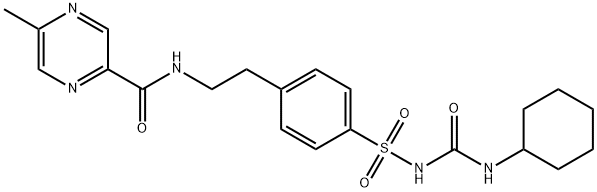
What is Glipizide?
Absorption
Gastrointestinal absorption of glipizide is uniform, rapid, and essentially complete. The absolute bioavailability of glipizide in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving a single oral dose was 100%. The maximum plasma concentrations are expected to be reached within 6 to 12 hours following initial dosing. The steady-state plasma concentrations of glipizide from extended-release oral formulations are maintained over the 24-hour dosing interval. In healthy volunteers, the absorption of glipizide was delayed by the presence of food but the total absorption was unaffected.
Toxicity
In rats, the oral LD50 is reported to be greater than 4000 mg/kg and the intraperitoneal LD50 is 1200 mg/kg. The lowest published toxic dose (TDLo) via oral route in child was 379 μg/kg.
Symptoms of overdose in sulfonylureas, including glipizide, may be related to severe hypoglycemia and may include coma, seizure, or other neurological impairment. These are symptoms of severe hypoglycemia and require immediate treatment with glucagon or intravenous glucose and close monitoring for a minimum of 24 to 48 hours since hypoglycemia may recur after apparent clinical recovery. Mild hypoglycemic symptoms without loss of consciousness or neurologic findings should be treated with oral glucose.
Chemical properties
Crystalline Solid
Originator
Minidiab,Carlo Erba,Italy,1973
The Uses of Glipizide
Labelled Glipizide . A sulfonylurea hypoglycemic agent. Used as an antidiabetic.;Labeled Glipizide, intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of Glipizide by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry.
The Uses of Glipizide
A hypoglycemic agent that enhances insulin secretion.
Background
Glipizide is an oral hypoglycemic agent in the second-generation sulfonylurea drug class that is used to control blood sugar levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. It was first introduced in 1984 and is available in various countries including Canada and the U.S. According to the 2018 Clinical Practice Guidelines by Diabetes Canada, sulfonylurea drugs are considered a second-line glucose-lowering therapy following metformin. Because sulfonylureas require functional pancreatic beta cells for their therapeutic effectiveness, sulfonylureas are more commonly used for early-stage type 2 diabetes when there is no progressed pancreatic failure. Compared to the first-generation sulfonylureas, such as tolbutamide and chlorpropamide, second-generation sulfonylureas contain a more non-polar side chain in their chemical structure, which enhances their hypoglycemic potency. Compared to other members of the sulfonylurea drug group, glipizide displays rapid absorption and onset of action with the shortest half-life and duration of action, reducing the risk for long-lasting hypoglycemia that is often observed with blood glucose-lowering agents. Glipizide was first approved by the FDA in 1994 and is available in extended-release tablets under the brand name Glucotrol?, as well as in combination with metformin under the brand name Metaglip?.
Indications
Indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Definition
ChEBI: An N-sulfonylurea that is glyburide in which the (5-chloro-2-methoxybenzoyl group is replaced by a (5-methylpyrazin-2-yl)carbonyl group. An oral hypoglycemic agent, it is used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Manufacturing Process
5-Methyl pyrazine-2-carboxylic acid is refluxed with thionyl chloride in
anhydrous benzene for approximately 12 hours. Benzene and thionyl chloride
excess is removed by distillation. Then some anhydrous dioxane is added and
this acid chloride solution is allowed to drop into p-(β-aminoethyl)-
benzenesulfonamide suspension in dioxane and anhydrous pyridine. The
resulting mixture is then refluxed for 3 hours. Dioxane is removed by
distillation and then the residue is washed with water and acetic acid. The raw
acylated sulfonamide is then filtered and crystallized from 95% ethanol, thus
obtaining a product of MP 200° to 203°C.
This product is then reacted with cyclohexyl isocyanate to give glipizide.
brand name
Glucotrol (Pfizer).
Therapeutic Function
Oral hypoglycemic
General Description
Glipizide is N-[2-[4-[[[(cyclohexylamino)carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]phenyl]ethyl]-5-methyl-2-pyrazinecarboxamide;this compound can also be named as the urea—seepreceding discussion (Glucotrol, generic). In the UnitedStates, combinations are available with metformin (Metaglip,generic; tablets, mg glipizide/mg metformin as hydrochloride:2.5/250, 2.5/500, 5/500). Extended-release tablets are available(Glucotrol XL, generic). The pyrazine moiety within thisstructure renders the molecule significantly more hydrophilicthan the similar molecule glyburide, albeit also moderatelyless potent on a dosage as well as target-level basis.
General Description
Glipizide, 1-cyclohexyl-3-[[p-(2-(5-methylpyrazinecarboxamido)ethyl]phenyl]sulfonyl]urea(Glucotrol), is an off-white, odorless powder with a pKa of5.9. It is insoluble in water and alcohols, but soluble in 0.1 NNaOH. Even though on a weight basis, it is approximately100 times more potent than tolbutamide, the maximal hypoglycemiceffects of these two agents are similar. It is rapidlyabsorbed on oral administration, with a serum half-life of 2 to4 hours, whereas the hypoglycemic effects range from 12 to24 hours. Metabolism of glipizide is generally through oxidationof the cyclohexane ring to the p-hydroxy and m-hydroxymetabolites. A minor metabolite that occurs involves theN-acetyl derivative, which results from the acetylation of theprimary amine following hydrolysis of the amide system byamidase enzymes.
General Description
Structurally, glipizide, 1-cyclohexyl-3-[[p-[2(methylpyrazinecarboxamido)ethyl]phenyl]sulfonyl]urea(Glucotrol), is a cyclohexylsulfonylurea analog similar toacetohexamide and glyburide. The drug is absorbed rapidlyon oral administration. Its serum half-life is 2 to 4 hours, andit has a hypoglycemic effect that ranges from 12 to 24 hours.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 1 (KCNJ1) plays a vital role in potassium balance. It is an ATP-dependent K+?channel blocker. The encoded protein is liable for the elimination of potassium in exchange for the absorption of sodium by the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC). Mutation in KCNJ1 is linked with several diseases, such as, antenatal Bartter syndrome and diabetes. Glipizide helps to repress the development of tumors and metastasis by preventing angiogenesis.
Pharmacokinetics
Glipizide is a blood glucose-lowering agent. The initial onset of blood glucose-lowering effect occurs around 30 minutes post-administration with the duration of action lasting for about 12 to 24 hours. While the chronic use of glipizide does not result in elevations in the fasting insulin levels over time, the postprandial insulin response, or insulin response to a meal, is observed to be enhanced, even after 6 months of treatment. The main therapeutic actions of glipizide primarily occur at the pancreas where the insulin release is stimulated, but glipizide also mediates some extrapancreatic effects, such as the promotion of insulin signaling effects on the muscles, fat, or liver cells. Due to its action on the endogenous cells, sulfonylureas including glipizide is associated with a risk for developing hypoglycemia and weight gain in patients receiving the drug. Chronic administration of glipizide may result in down-regulation of the sulfonylurea receptors on pancreatic beta cells, which are molecular targets of the drug, leading to a reduced effect on insulin secretion.
Like other sulfonylureas, glipizide may work on pancreatic delta (δ) cells and alpha (α) cells to stimulate the secretion of somatostatin and suppress the secretion of glucagon, which are peptide hormones that regulate neuroendocrine and metabolic pathways. Other than its primary action on the pancreas, glipizide also exerts other biological actions outside of the pancreas, or "extrapancreatic effects", which is similar to other members of the sulfonylurea drug class. Glipizide may enhance the glucose uptake into the skeletal muscles and potentiate the action of insulin in the liver. Other effects include inhibited lipolysis in the liver and adipose tissue, inhibited hepatic glucose output, and increased uptake and oxidation of glucose. It has also been demonstrated by several studies that the chronic therapeutic use of sulfonylureas may result in an increase in insulin receptors expressed on monocytes, adipocytes, and erythrocytes.
Clinical Use
Non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus
Synthesis
Glipizide, 1-cyclohexyl-3-[[p-[2-(5-methylpyrazincarboxamido)ethyl]phenyl] sulfonyl]urea (26.2.13), differs from glyburide in the structure of the amide region of the molecule, in which the 2-methoxy-5-chlorobenzoic acid part is replaced with 6- methylpyrazincarboxylic acid. It is also synthesized by a synthesis alternative to those described above. In the given scheme, 6-methylpyrazincarboxylic acid is initially reacted with thionyl chloride, resulting in the corresponding chloride, which undergoes further action with 4-(2-aminoethyl)benzenesulfonamide, forming the corresponding amide 26.2.12. The resulting sulfonamide is reacted in a traditional scheme with cyclohexylisocyanate, forming the desired glipizide (26.2.13).

Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Glipizide may be of benefit in treating cats with type II diabetes if
they have a population of functioning beta cells. It has been suggested
that there are two situations when glipizide can be recommended,
1) If an owner refuses to consider using insulin usually
due to a fear of needles, and 2) the cat appears to be relatively well
controlled on quite small doses of insulin and the owner would
strongly prefer to no longer give insulin (Feldman 2005b).
While glipizide potentially could be useful in treating canine patients
with type II or III diabetes, however, by the time dogs present
with hyperglycemia, they are absolutely or relatively insulinopenic
and glipizide would unlikely be effective.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Analgesics: effects enhanced by NSAIDs.
Antibacterials: effects enhanced by chloramphenicol,
sulphonamides, tetracyclines and trimethoprim;
effect reduced by rifamycins.
Anticoagulants: effect possibly enhanced by
coumarins; also possibly changes to INR.
Antifungals: concentration increased by fluconazole,
posaconazole and miconazole and possibly
voriconazole - avoid with miconazole.
Ciclosporin: may increase ciclosporin levels.
Lipid-regulating drugs: possibly additive
hypoglycaemic effect with fibrates.
Sulfinpyrazone: enhanced effect of sulphonylureas.
Metabolism
Glipizide is subject to hepatic metabolism, in which its major metabolites are formed from aromatic hydroxylation. These major metabolites are glipizide are reported to be pharmacologically inactive. In contrast, an acetylaminoethyl benzine derivative is formed as a minor metabolite which accounts for less than 2% of the initial dose and is reported to have one-tenth to one-third as much hypoglycemic activity as the parent compound.
Metabolism
The metabolism of glipizide is extensive and occurs mainly in the liver. The primary metabolites are inactive hydroxylation products and polar conjugates and are excreted mainly in the urine.
Properties of Glipizide
| Melting point: | 208-209°C |
| Density | 1.34±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | methanol: 1.9 mg/mL |
| form | solid |
| pka | pKa 5.9 (Uncertain) |
| color | white |
| Merck | 14,4442 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 29094-61-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2-Pyrazinecarboxamide, N-[2-[4-[[[(cyclohexylamino)carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]phenyl]ethyl]-5-methyl- (29094-61-9) |
Safety information for Glipizide
Computed Descriptors for Glipizide
Glipizide manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 29094-61-9 Glipizide 99%View Details
29094-61-9 Glipizide 99%View Details
29094-61-9 -
 Glipizide 98%View Details
Glipizide 98%View Details -
 Glipizide 29094-61-9 99%View Details
Glipizide 29094-61-9 99%View Details
29094-61-9 -
 Glipizide 99%View Details
Glipizide 99%View Details
29094-61-9 -
 Glipizide CAS 29094-61-9View Details
Glipizide CAS 29094-61-9View Details
29094-61-9 -
 Glipizide 95.00% CAS 29094-61-9View Details
Glipizide 95.00% CAS 29094-61-9View Details
29094-61-9 -
 Glipizide 99% (HPLC) CAS 29094-61-9View Details
Glipizide 99% (HPLC) CAS 29094-61-9View Details
29094-61-9 -
 Glipizide CAS 29094-61-9View Details
Glipizide CAS 29094-61-9View Details
29094-61-9
