Acetohydroxamic acid
Synonym(s):AHA
- CAS NO.:546-88-3
- Empirical Formula: C2H5NO2
- Molecular Weight: 75.07
- MDL number: MFCD00009994
- EINECS: 208-913-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-16 17:24:19
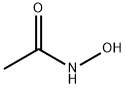
What is Acetohydroxamic acid?
Absorption
Well absorbed from the GI tract following oral administration.
Toxicity
Oral, rat: LD50 = 4.8gm/kg. Symptoms of overdose include anorexia, malaise, lethargy, diminished sense of wellbeing, tremor, anxiety, nausea, and vomiting.
Description
Acetohydroxamic acid is a potent, non-competitive and irreversible inhibitor of bacterial urease (Ki≈lO-7M). This enzyme, which is widely distributed in plants and bacteria, but not in mammalian cells, catalyzes the decomposition of urea to ammonia. Elevated urinary ammonia levels can reduce the antibacterial effectiveness of a number of agents. Thus, acetohydroxamic acid is useful as adjunctive therapy to decrease urinary ammonia and alkalinity in patients with chronic urea-splitting urinary infection. Such infections are a leading cause of recurring complications and death in paraplegics.
Chemical properties
White Crystalline Solid
Originator
Research Organics; Baylor Unk. (USA)
The Uses of Acetohydroxamic acid
Urease inhibitorAcetohydroxamic acid acts as a drug, as an inhibitor of bacterial and plant urease, which is used for urinary tract infections. It is also used in organic synthesis. It acts as an antiurolithic and antibacterial agent. It is involved in the study of complexation of iron(III) with acetohydroxamic acid as well as in the inhibition study of lansoprazole and omeprazole on Helicobacter pyloni. It plays an important role in the insitu generation of nitrosocarbonylmethane as a Diels-Alder dienophile. In addition to this, it is used in the treatment of kidney stones and urinary tract infections.
The Uses of Acetohydroxamic acid
Acetohydroxamic acid is a potent inhibitor of bacterial urease activity and reduces urinary ammonia levels. 2-Acetohydroxamic acid loaded floating microspheres forms an efficient drug delivery system for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori.
Acetohydroxamic acid was used:
to study the mechanism of complexation of iron (III) with acetohydroxamic acid.
to study the inhibitory mechanism of lansoprazole and omeprazole on Helicobacter pyloni.
in urease inhibition studies.
for in situ generation of nitrosocarbonylmethane as a Diels-Alder dienophile.
Used in urease inhibition studies and for in situ generation of nitrosocarbonylmethane as a Diels-Alder dienophile.
The Uses of Acetohydroxamic acid
A urease inhibitor. Used in the synthesis
What are the applications of Application
Acetohydroxamic Acid is An inhibitor of urease.
Indications
Used, in addition to antibiotics or medical procedures, to treat chronic urea-splitting urinary infections.
Background
Acetohydroxamic Acid, a synthetic drug derived from hydroxylamine and ethyl acetate, is similar in structure to urea. In the urine, it acts as an antagonist of the bacterial enzyme urease. Acetohydroxamic Acid has no direct antimicrobial action and does not acidify urine directly. It is used, in addition to antibiotics or medical procedures, to treat chronic urea-splitting urinary infections.
Definition
ChEBI: Acetohydroxamic acid is a member of the class of acetohydroxamic acids that is acetamide in which one of the amino hydrogens has been replaced by a hydroxy group. It has a role as an EC 3.5.1.5 (urease) inhibitor and an algal metabolite. It is functionally related to an acetamide. It is a tautomer of a N-hydroxyacetimidic acid.
Manufacturing Process
3 Methods of producing of acetohydroxamic acid:
1. Ethyl acetic acid ether was treated with hydroxylamine and
acetohydroxamic acid was obtained.
2. Acetohydroxamic acid was obtained in the result of reaction of acetamide
with hydroxylamine.
3. Acetohydroxamic acid was obtained by treatment of acetaldehyde with
nitrohydroxylamine.
brand name
Lithostat (Mission).
Therapeutic Function
Urease inhibitor
General Description
Acetohydroxamic acid is a potent inhibitor of bacterial urease activity and reduces urinary ammonia levels. 2-Acetohydroxamic acid loaded floating microspheres forms an efficient drug delivery system for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori.
Pharmacokinetics
Acetohydroxamic Acid, a synthetic drug derived from hydroxylamine and ethyl acetate, is similar in structure to urea. In the urine, it acts as an antagonist of the bacterial enzyme urease. Acetohydroxamic Acid has no direct antimicrobial action and does not acidify urine directly.
Side Effects
Get emergency medical help if you have any of these signs of an allergic reaction: hives; difficulty breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Call your doctor at once if you have:
pounding heartbeats or fluttering in your chest;
signs of a blood clot in your leg --pain, swelling, warmth, or redness in one or both legs;
signs of a red blood cell disorder --pale or yellowed skin, dark colored urine, fever, confusion or weakness.
Common side effects may include:
headache during the first 2 days of treatment;
skin rash, warmth, tingling or redness (especially if you drink alcohol while taking acetohydroxamic acid);
upset stomach, nausea, loss of appetite;
depressed mood;
anxiety, tremors, nervousness;
hair loss.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by intraperitonealroute. An experimental teratogen. Other experimentalreproductive effects. Mutation data reported. When heatedto decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Acetohydroxamic acid can be used in dogs as adjunctive therapy in some cases of recurrent urolithiasis or in the treatment of persistent urinary tract infections caused by the following bacteria: E. coli, Klebsiella, Morganella morganii, Staphylococci spp., and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Adverse effects limit its usefulness.
Metabolism
35-65% of oral dose excreted unchanged in urine (which provides the drug's therapeutic effect).
Properties of Acetohydroxamic acid
| Melting point: | 88-90 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 133.7°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.2269 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4264 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Room temperature |
| solubility | Methanol (Sparingly), Water (Sparingly) |
| pka | 8.70(at 25℃) |
| form | Crystalline Solid |
| color | White to pale yellow |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water. |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,63 |
| BRN | 1739019 |
| Stability: | Moisture and Temperature Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 546-88-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Acetamide,N-hydroxy(546-88-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Acetohydroxamic acid (546-88-3) |
Safety information for Acetohydroxamic acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H360:Reproductive toxicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Acetohydroxamic acid
| InChIKey | RRUDCFGSUDOHDG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Acetohydroxamic acid manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Acetohydroxamic acid CAS 546-88-3View Details
Acetohydroxamic acid CAS 546-88-3View Details
546-88-3 -
 Acetohydroxamic Acid CAS 546-88-3View Details
Acetohydroxamic Acid CAS 546-88-3View Details
546-88-3 -
 Acetohydroxamic acid 96% CAS 546-88-3View Details
Acetohydroxamic acid 96% CAS 546-88-3View Details
546-88-3 -
 Acetohydroxamic acid, 98% CAS 546-88-3View Details
Acetohydroxamic acid, 98% CAS 546-88-3View Details
546-88-3 -
 Acetohydroxamic acid CAS 546-88-3View Details
Acetohydroxamic acid CAS 546-88-3View Details
546-88-3 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
