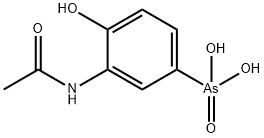
ACETARSONE
- CAS NO.:97-44-9
- Empirical Formula: C8H10AsNO5
- Molecular Weight: 275.09
- MDL number: MFCD00019936
- EINECS: 202-582-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-21 10:59:17
What is ACETARSONE?
Absorption
The absorption seems to be very minimal but there are reports of allergic reactions after vaginal administration of acetarsol.
Toxicity
The administration of inorganic arsenic is highly carcinogenic and thus acetarsol if thought to be dangerous when absorbed. Some reports indicate that acetarsol can produce effects in the eyes such as optic neuritis and optic atrophy.
Originator
Acetarsol ,Cyklo Pharma Chem Pvt. Ltd.
The Uses of ACETARSONE
antiprotozoal; diethylamine salt as antiphilitic
Background
Acetarsol, with the molecular formula N-acetyl-4-hydroxy-m-arsanilic acid, is a pentavalent arsenical compound with antiprotozoal and antihelmintic properties. It was first discovered in 1921 by Ernest Fourneau at the Pasteur Institute. It was developed by Neolab Inc, and approved by Health Canada as an antifungal on December 31, 1964. It has been canceled and withdrawn from the market since August 12, 1997.
What are the applications of Application
Acetarsone is an antiifective agent used as an antiprotozoal
Indications
Acetarsol has been used for the treatment of different diseases such as syphilis, amoebiasis, yaws, trypanosomiasis, and malaria. Acetarsol was used commonly for the treatment of vaginitis due to Trichomonas vaginalis and Candida albicans. When orally administered, acetarsol can be used for the treatment of intestinal amoebiasis and in the form of suppositories it has been researched for the treatment of proctitis.
Protozoan infections are parasitic diseases characterized to be caused by organisms classified in the kingdom Protozoa which is formed by a great diversity of organisms.
Definition
ChEBI: Acetarsol is a member of acetamides and an anilide.
Manufacturing Process
1 part of 4-chloroaniline is dissolved with 2 parts of concentrated hydrochloric
acid (specific gravity 1.16) and 10 parts of water, and diazotised in the usual
manner. 3 parts of sodium arsenite are introduced into the diazo solution thus
obtained, the sodium arsenite being dissolved in 5 parts of water and 1 part
of 96% ethanol. The solution is heated slowly to 70°C. When evolution of
nitrogene ceased, it is filtered from separated oil and the addition of
hydrochloric acid precipitates the 4-chlorophenylarsonic acid, which
crystallizes out in the form of white needles.
By action HNO3/H2SO4 on 4-chlorophenylarsonic acid is obtained 4-chloro-3-
nitrophenylarsonic acid which is converted at 100°C with 33% aqueous
solution of sodium hydroxide to 4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenylarsonic acid. After
reduction of NO2 group of 4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenylarsonic acid by the action
of Na2S2O3 or Fe/NaOH is obtained 3-amino-4-hydroxyphenylarsonic acid.
From 3-amino-4-hydroxyphenylarsonic acid and acetic anhydride is prepared
N-acetyl-4-hydroxy-m-arsanilic acid.
brand name
190 f;Acetarsolum;Amarson;Arsabott;Auryphan;Chrlich 594;Collarsin;Edoiacolo;Ehrlich 594;F 190;Fluryl;Fourneau 190;Kharophene;Neo-vagex;Pallacid;Trichovan;Vagipurin;Vagisep;Vagival.
Therapeutic Function
Antiprotozoal, Tonic
World Health Organization (WHO)
Acetarsol, which has antiprotozoal and antitrichomonal activity, has largely been discarded for systemic use because of its potential to cause systemic poisoning. However, topical preparations for vaginal trichomoniasis are still available and it is included in low concentrations (equal to or less than 0.45%) in some medicated toothpastes.
Pharmacokinetics
Some reports indicate a certain infection remission with the use of acetarsol but this reports also demonstrate the absorption of systemic arsenic which can be physiologically dangerous.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and intravenous routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: respiratory system, endocrine system, dermatitis, and fever. Human systemic effects by intravagmal route: hallucinations, dlstorted perceptions, convulsions, nausea or vomiting, decreased urine volume, and fever. Mutation data reported. See also ARSENIC COMPOUNDS. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx, and As
Metabolism
This pharmacokinetic property was not addressed.
Purification Methods
It crystallises from water in colourless prisms. It decomposes slowly on prolonged boiling in H2O or dilute alkalis. The N-propionyl derivative recrystallises from H2O with m 228-229o(dec). [Raiziss & Fisher J Am Chem Soc 48 1323 1926, Hewitt & King J Chem Soc 823 1926, Beilstein 16 I 491, 16 II 521, 16 III 1129.]
Properties of ACETARSONE
| Melting point: | 220.5°C |
| Boiling point: | 72.17°C |
| Density | 1.0325 g/cm3(Temp: 15 °C) |
| storage temp. | Store at RT |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly, Heated, Sonicated) |
| pka | pKa 3.73 (H2O t=26) (Uncertain);7.9 (Uncertain); 9.3(H2O) (Uncertain) |
| form | solid |
| color | Crystalline material |
| Merck | 13,53 |
Safety information for ACETARSONE
Computed Descriptors for ACETARSONE
Abamectin manufacturer
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 97-44-9 Acetarsone 98%View Details
97-44-9 Acetarsone 98%View Details
97-44-9 -
 97-44-9 99%View Details
97-44-9 99%View Details
97-44-9 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4