Aceclofenac
Synonym(s):2-[(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)amino]benzeneacetic acid carboxymethyl ester;;Aceclofenac
- CAS NO.:89796-99-6
- Empirical Formula: C16H13Cl2NO4
- Molecular Weight: 354.18
- MDL number: MFCD00864296
- EINECS: 641-844-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
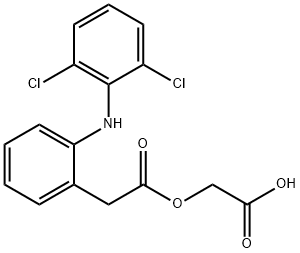
What is Aceclofenac?
Absorption
Aceclofenac is rapidly and completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and circulates mainly as unchanged drug following oral administration. Peak plasma concentrations are reached around 1.25 to 3 hours post-ingestion, and the drug penetrates into the synovial fluid where the concentration may reach up to 60% of that in the plasma . There is no accumulation in regular dosing, with similar maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) and time to reach peak plasma concentration (Tmax) after single and multiple doses .
Toxicity
Some common adverse effects include gastro-intestinal disorders (dyspepsia, abdominal pain, nausea), rash, ruber, urticaria, symptoms of enuresis, headache, dizziness, and drowsiness . Oral LD50 value in rats is 130 mg/kg .
Description
Aceclofenac is a nonsteroidal antiinflammatory agent with analgesic and antipyretic properties. It is reported to be useful in the treatment of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and pain associated with minor surgical procedures. Compared to ketoprofen in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, aceclofenac is substantially faster acting.
Originator
Prodes (Prodesfarma) (Spain)
The Uses of Aceclofenac
Labeled Aceclofenac, intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of Aceclofenac by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry.
The Uses of Aceclofenac
Aceclofenac is a non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with potent inhibitory activity in several models of inflammation. It is used for the treatment of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. It is a Biopharmaceutics classification system class II (BCS class I) drug which has an intermediate half-life of 3-4h and undergoes substantial first pass metabolism. aceclofenac is available either in oral form (tablet) or in topical form (gel).
What are the applications of Application
Aceclofenac is an anti-inflammatory and analgesic agent
Indications
Aceclofenac is indicated for the relief of pain and inflammation in osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis.
Background
Aceclofenac is a potent NSAID with significant anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, effectively treating conditions like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. It has been shown to outperform or at least match traditional NSAIDs in clinical studies. The drug's efficacy is attributed to its strong inhibition of the COX enzyme, which is crucial for prostaglandin synthesis, a key player in inflammation and pain. Despite its poor aqueous solubility, classified under BCS Class II, aceclofenac exhibits high permeability, reaching synovial joints to alleviate symptoms of joint degeneration. Additionally, it has demonstrated effectiveness in dental and gynaecological pain. Developed in 1991 as a Diclofenac analog, aceclofenac was designed to enhance gastrointestinal tolerability, making it a widely prescribed medication in Europe.
Definition
ChEBI: Aceclofenac is a monocarboxylic acid that is the carboxymethyl ester of diclofenac. A non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug related to diclofenac, it is used in the management of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. It has a role as an EC 1.14.99.1 (prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase) inhibitor, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug and a non-narcotic analgesic. It is a monocarboxylic acid, a carboxylic ester, a secondary amino compound, an amino acid and a dichlorobenzene. It derives from a diclofenac.
brand name
Airtal; Gerbin
Biochem/physiol Actions
Non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), with selectivity for COX-2 over COX-1.
Pharmacokinetics
Aceclofenac is a NSAID that inhibits both isoforms of COX enzyme, a key enzyme involved in the inflammatory cascade. COX-1 enzyme is a constitutive enzyme involved in prostacyclin production and protective functions of gastric mucosa whereas COX-2 is an inducible enzyme involved in the production of inflammatory mediators in response to inflammatory stimuli. Aceclofenac displays more selectivity towards COX-2 (IC50 of 0.77uM) than COX-1 (IC50 of >100uM), which promotes its gastric tolerance compared to other NSAIDs. The primary metabolite, 4'-hydroxyaceclofenac, also minimally inhibits COX-2 with IC50 value of 36uM . Although the mode of action of aceclofenac is thought to mainly arise from the inhibition of synthesis of prostaglandins (PGE2), aceclofenac also inhibits the production of inflammatory cytokines, interleukins (IL-1β, IL-6), and tumor necrosis factors (TNF) . It is also reported that aceclofenac also affects the cell adhesion molecules from neutrophils . Aceclofenac also targets the synthesis of glycosaminoglycan and mediates chrondroprotective effects .
Clinical Use
NSAID and analgesic
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
ACE inhibitors and angiotensin-II antagonists:
antagonism of hypotensive effect; increased risk of
nephrotoxicity and hyperkalaemia.
Analgesics: avoid concomitant use of 2 or more
NSAIDs, including aspirin (increased side effects);
avoid with ketorolac (increased risk of side effects
and haemorrhage).
Antibacterials: possible increased risk of convulsions
with quinolones.
Anticoagulants: effects of coumarins and
phenindione enhanced; possibly increased risk of
bleeding with heparins, dabigatran and edoxaban -
avoid long term use with edoxaban.
Antidepressants: increased risk of bleeding with
SSRIs and venlaflaxine.
Antidiabetic agents: effects of sulphonylureas enhanced.
Antiepileptics: possibly increased phenytoin
concentration.
Antivirals: increased risk of haematological toxicity
with zidovudine; concentration possibly increased by
ritonavir.
Ciclosporin: may potentiate nephrotoxicity
Cytotoxics: reduced excretion of methotrexate;
increased risk of bleeding with erlotinib.
Diuretics: increased risk of nephrotoxicity;
antagonism of diuretic effect, hyperkalaemia with
potassium-sparing diuretics.
Lithium: excretion decreased.
Pentoxifylline: increased risk of bleeding.
Tacrolimus: increased risk of nephrotoxicity.
Metabolism
4'-hydroxyaceclofenac is the main metabolite detected in plasma however other minor metabolites include diclofenac, 5-hydroxyaceclofenac, 5-hydroxydiclofenac, and 4'-hydroxydiclofenac . It is probable that the metabolism of aceclofenac is mediated by CYP2C9 .
Side Effects
Common side effects of Aceclofenac include: abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting, rash, dizziness, flatulence, stomach pain, loss of appetite, heartburn, and visual disturbances. Severe gastrointestinal bleeding, ulcers and perforations, and severe bronchospasm may occur. Kidney failure and liver damage are possible in overdose.
Properties of Aceclofenac
| Melting point: | 149-153°C |
| Boiling point: | 486.0±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.455±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| RTECS | CY1577900 |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| pka | 2.60±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | powder |
| color | off-white to light tan |
| Water Solubility | 32mg/L(32 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,22 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 89796-99-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Benzeneacetic acid, 2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino]-, carboxymethyl ester (89796-99-6) |
Safety information for Aceclofenac
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Aceclofenac
| InChIKey | MNIPYSSQXLZQLJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Aceclofenac manufacturer
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Aceclofenac 98%View Details
Aceclofenac 98%View Details -
 Aceclofenac 99%View Details
Aceclofenac 99%View Details -
 Aceclofenac 98% CAS 89796-99-6View Details
Aceclofenac 98% CAS 89796-99-6View Details
89796-99-6 -
 Aceclofenac 99%View Details
Aceclofenac 99%View Details -
 Aceclofenac CAS 89796-99-6View Details
Aceclofenac CAS 89796-99-6View Details
89796-99-6 -
 89796-99-6 98%View Details
89796-99-6 98%View Details
89796-99-6 -
 Aceclofenac CAS 89796-99-6View Details
Aceclofenac CAS 89796-99-6View Details
89796-99-6 -
 Aceclofenac CAS 89796-99-6View Details
Aceclofenac CAS 89796-99-6View Details
89796-99-6
