5-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione
Synonym(s):5-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthlenedione, 5-Hydroxy- p-naphthoquinone;5-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone;Juglone;Juglone - CAS 481-39-0 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:481-39-0
- Empirical Formula: C10H6O3
- Molecular Weight: 174.15
- MDL number: MFCD00001684
- EINECS: 207-567-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-15 14:23:52
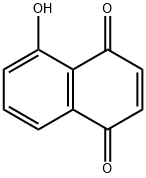
What is 5-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione?
Description
Juglone (5-hydroxynapthoquinone), is found in the leaves and other parts of walnut, hickory and pecan (1,2). Juglone is synthesized from isochorismic acid (a product of the shikimic acid pathway) and 2-oxo-glutaric acid (3). In plant tissue juglone exists as a free compound or as a glycoside (3,4). Action of a glucosidase releases 1,4,5-trihydroxynapthalene, which is then oxidized to juglone (3,4).
Description
Juglone (5-hydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione) is a naturally occurring naphthoquinone derivative that has been known for more than a century. In 1905, French scientists M. Brissemoret and R. Combes reported that juglone exists in the green portions of walnut trees (leaves, stems, and husks). Their report cites articles from 1884. In 1887, German chemists August Bernthsen and August Semper described juglone’s structure and its synthesis from naphthalene.
Juglone is found in many species of the walnut family (Juglandaceae), particularly in eastern American black walnut (Juglans nigra). The compound serves as a defense mechanism against surrounding plants: It can stunt their growth, a process known as allelopathy. Since its discovery, juglone has occasionally been used as an herbicide and an anthelmintic (a group of antiparasitic drugs). It is also ichthyotoxic, and some cultures catch fish by throwing walnut husks into the water.
Juglone is more frequently used as a dye. In its pure form, it has a yellow color; but when it is exposed to oxygen, it turns orange, red, or, mainly, brown. As a dye, it is known as C.I. Natural Brown 7, a classification of the database Colour Index International. It is used to dye fabrics, cosmetics, and even foods, despite its properties listed in the hazard information table. It is chemically related to henna.
To learn how the naphthalene-like structure of juglone is biosynthesized, read the 2018 Horticulture Research article by Joshua R. Widhalm and co-workers at Purdue University.
Description
Juglone is a natural naphthoquinone found in the black walnut (J. nigra) and other plants in the Juglandaceae family. It has allelopathic actions, suppressing growth, photosynthesis, and respiration in plants and other organisms, although some bacteria can metabolize juglone. Juglone also irreversibly inhibits peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerases of the parvulin family, including human Pin1, yeast Ess1/Ptf1, and E. coli parvulin (Ki = 55.9 nM). Juglone also blocks transcription by RNA polymerases I, II, and III (IC50s = 2-7 μM) and attenuates kidney fibrosis in rats treated with unilateral ureteral obstruction, both through Pin1-independent mechanisms.
Chemical properties
Orange to brown crystalline powder
The Uses of 5-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione
antineoplastic, antifungal, antioxidant, Pin 1 inhibitor
The Uses of 5-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione
Juglone (CI Natural Brown 7; CI 75500) was isolated from the husks of walnuts in 1856. Juglone occurs in walnuts as a glycoside of its reduced form, 1,4,5-trihydroxynaphthalene. Its structure is (3) Juglone is most readily synthesized by Bernthsen s method. It is a fungicide and as such finds use in the treatment of skin diseases. Its toxic properties have been made use of in catching fish. Juglone has been used to detect very small amount of nickel salts since it gives a deep violet color with such salts.
The Uses of 5-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione
5-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone is used as a natural dye in cloth, fabrics, wool and ink. It is a coloring agent for food and cosmetics. It is involved in the synthesis of poly(hydroxyl-1,4-naphthoquinone) stabilized gold nanoparticles (AuNQ NPs), which is used for nonenzymatic electrochemical detection of glucose.
What are the applications of Application
Juglone is a compound that inhibits RNA polymerases
Definition
ChEBI: A hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone that is 1,4-naphthoquinone in which the hydrogen at position 5 has been replaced by a hydroxy group.
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 48, p. 5160, 1983 DOI: 10.1021/jo00174a003
Synthetic Communications, 15, p. 1177, 1985 DOI: 10.1080/00397918508077262
Synthesis, p. 644, 1977 DOI: 10.1055/s-1977-24517
General Description
This substance is a primary reference substance with assigned absolute purity (considering chromatographic purity, water, residual solvents, inorganic impurities). The exact value can be found on the certificate. Produced by PhytoLab GmbH & Co. KG
Pharmacology
Juglone is probably best known as the allelochemical produced by black walnut. The glucoside of juglone leaches from the leaves and branches of black walnut, where it is converted to juglone in the soil. Juglone is toxic to certain plant species and also inhibits the germination of seeds (4). Thus its allelopathic activity may be the result of both phytotoxicity and a germination inhibitor. Juglone is also antifungal (1,5) and attempts to correlate its presence with disease resistance in pecan, black walnut, and hickory to several fungal pathogens have been reported (1,2,5,6). Positive correlations have been found for resistance of juvenile leaves of black walnut to anthracnose caused by Gnomia leptostyla (5) and of some Carya species to the scab pathogen Cladosporium carygenum (2). In some pecans (C. illinoensis), juglone may act as both a preformed and an induced defense factor because concentrations of juglone increase after infection by fungi (2). No correlation between juglone glycoside concentration in pecan leaves and resistance pecan to C. carygenum has been reported (6). Free juglone and the glycosides increase after infection, but these increases could not be correlated with scab resistance (6).
Purification Methods
Crystallise Juglone from *benzene/pet ether or pet ether. [Beilstein 8 III 2558, 8 IV 2368.]
Properties of 5-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione
| Melting point: | 161-163 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 265.11°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.2346 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5036 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | 2–5 g/l (est.) |
| solubility | DMSO: 10 mg/ml; Ethanol: 10 mg/ml |
| pka | 6.59±0.20(Predicted) |
| form | Crystalline Powder |
| appearance | yellow to brown crystals or powder |
| color | Orange to brown |
| Water Solubility | SOLUBLE IN HOT WATER |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,5269 |
| BRN | 1909764 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 481-39-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 1,4-Naphthalenedione, 5-hydroxy-(481-39-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1,4-Naphthalenedione, 5-hydroxy- (481-39-0) |
Safety information for 5-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for 5-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 5-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone CAS 481-39-0View Details
5-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone CAS 481-39-0View Details
481-39-0 -
 5-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone CAS 481-39-0View Details
5-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone CAS 481-39-0View Details
481-39-0 -
 Juglone CAS 481-39-0View Details
Juglone CAS 481-39-0View Details
481-39-0 -
 Juglone CAS 481-39-0View Details
Juglone CAS 481-39-0View Details
481-39-0 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
