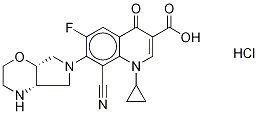
3-Quinolinecarboxylic acid, 8-cyano-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-[(4aS,7aS)-hexahydropyrrolo[3,4-b]-1,4-oxazin-6(2H)-yl]-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-
Synonym(s):8-Cyano-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-[(4aS,7aS)-hexahydropyrrolo[3,4-b][1,4]oxazin-6(2H)-yl]-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid
- CAS NO.:209342-40-5
- Empirical Formula: C20H19FN4O4
- Molecular Weight: 398.39
- MDL number: MFCD13185157
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-28 23:16:16
![3-Quinolinecarboxylic acid, 8-cyano-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-[(4aS,7aS)-hexahydropyrrolo[3,4-b]-1,4-oxazin-6(2H)-yl]-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo- Structural](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/209342-40-5.gif)
What is 3-Quinolinecarboxylic acid, 8-cyano-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-[(4aS,7aS)-hexahydropyrrolo[3,4-b]-1,4-oxazin-6(2H)-yl]-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-?
Toxicity
-Finafloxacin was shown to be genotoxic and clastogenic in vitro, with and without metabolic activation, and in vivo. -General toxicity studies in rats have confirmed sperm toxicity following oral and intravenous dosing. -At 500 mg/kg/day, males were completely infertile, presumably due to low sperm count and sperm immobility.
Description
Finafloxacin, an antimicrobial agent of the 8-cyano subclass of fluoroquinolones, was approved by the US FDA in December 2014 for treatment of acute otitis externa, commonly known as swimmer’s ear, caused by susceptible strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Finafloxacin was developed by MerLion Pharmaceuticals in partnership with Bayer Health Care Pharmaceuticals, and the drug was licensed by Mer- Lion to Alcon (a division of Novartis) for development and commercialization for ear infections in North America. In contrast to other marketed fluoroquinolones, which display reduced activity in slightly acidic environments, finafloxacin exhibits increased antibacterial activity at pH 5–6, with minimum inhibitory concentration values that are 4- to 8-fold lower than at neutral pH. It is highly selective for bacterial type II topoisomerases, which are involved in bacterial DNA replication, transcription, repair, and recombination, and has broad spectrum antibacterial activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative strains, including ciprofloxacin-resistant strains.
The Uses of 3-Quinolinecarboxylic acid, 8-cyano-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-[(4aS,7aS)-hexahydropyrrolo[3,4-b]-1,4-oxazin-6(2H)-yl]-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-
Used for the preparation of naphthyridonecarboxylic acid derivatives as drugs for therapy of Helicobacter pylori infections and associated gastroduodenal illnesses.
Indications
Finafloxacin is indicated for the treatment of acute otitis externa (AOE) with or without an otowick, caused by susceptible strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus in patients age 1 year and older.
Background
Finafloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic indicated in the treatment of acute otitis externa (swimmer's ear) caused by the bacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Finafloxacin is marketed by Novartis under the brand Xtoro?, and was approved by the FDA in December 2014.
Definition
ChEBI: A quinolone that is 4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid which is substituted at positions 1, 6, 7 and 8 by cyclopropyl, fluoro, hexahydropyrrolo[3,4-b][1,4]oxazin-6-yl and cyano groups respectively; an antibiotic used for treatment of acute otitis externa (swimmer's ear) caused by the bacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Finafloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic approved by the FDA in 2014 for treating swimmer′s ear. Its mechanism of action involves the inhibition of bacterial type II topoisomerase enzymes, DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV
Synthesis
Synthesis of finafloxacin has been reported on kilogram scale
starting from 5-fluoro-1,3-xylene (104). Catalytic
chlorination through the use of FeCl3 in 1,2-dichloroethane (DCE)
was followed by a photochemical chlorination at elevated temperatures
to generate the polychlorinated intermediate 105 in 45%
yield over two steps. The polychlorinated system 105 was then
hydrolyzed with concentrated sulfuric acid to arrive at 3-formylbenzoic
acid 106. Conversion of the formyl group to nitrile and
the acid to the acid chloride was achieved in two steps, via condensation
of the aldehyde with hydroxylamine hydrochloride in the
presence of 45% NaOH and subsequent treatment with refluxing
thionyl chloride to afford 107 in 62% yield for the two steps. Acid
chloride 107 was converted to quinolone 109 through the following
4-step sequence, which was conducted without isolation of
intermediates?a107 was first coupled with ethyl 3-dimethylamino-
acrylate 108 in DCM in the presence of DIPEA followed
by condensation with cyclopropylamine in the presence of acetic
acid. This was followed by treatment with potassium carbonate
in warm NMP and, upon acidification, ethyl ester 109 was furnished
in a remarkable 90% yield over the sequence. Acidic hydrolysis
of ester 109 generated acid 110, which underwent coupling
with pyrrolo-oxazine 111 in the presence of triethylamine (TEA) and warm acetonitrile
to provide finafloxacin (XIV) in 90% yield from 109.
The synthesis of pyrrolo-oxazine fragment 111 commenced
with (Z)-butene-1,4-diol (112).120 Mesylation of this
diol followed by reaction with tosylamide under phase transfer
conditions afforded dihydropyrrole 113. Epoxidation of the olefin
using 3-chloroperoxybenzoic acid (m-CPBA) to give 114, followed
by subjection to ethanolamine affected an epoxide ring opening
to give rise to the trans aminoalcohol rac-115. Tosylation and
cyclization upon treatment with methanolic sodium hydroxide
gave the bis-toluenesulfonamide 116, which was resolved at this
point to >99% ee by chiral chromatography to arrive at the desired
(S,S)-enantiomer. Removal of the tosyl protecting groups within
116 using hydrobromic acid in glacial acetic acid preceded treatment
with KOH to finally furnish pyrrolo-oxazine 111.

Metabolism
Not Available
Properties of 3-Quinolinecarboxylic acid, 8-cyano-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-[(4aS,7aS)-hexahydropyrrolo[3,4-b]-1,4-oxazin-6(2H)-yl]-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-
| Boiling point: | 686.2±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.57±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO : 6.4 mg/mL (16.06 mM) |
| form | powder |
| pka | 6.38±0.50(Predicted) |
| color | white to beige |
Safety information for 3-Quinolinecarboxylic acid, 8-cyano-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-[(4aS,7aS)-hexahydropyrrolo[3,4-b]-1,4-oxazin-6(2H)-yl]-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H340:Germ cell mutagenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for 3-Quinolinecarboxylic acid, 8-cyano-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-[(4aS,7aS)-hexahydropyrrolo[3,4-b]-1,4-oxazin-6(2H)-yl]-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-
3-Quinolinecarboxylic acid, 8-cyano-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-[(4aS,7aS)-hexahydropyrrolo[3,4-b]-1,4-oxazin-6(2H)-yl]-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo- manufacturer
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Finafloxacin CAS 209342-40-5View Details
Finafloxacin CAS 209342-40-5View Details
209342-40-5 -
 55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 -
 N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
13162-05-5 -
 Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 207557-35-5 99%View Details
207557-35-5 99%View Details
207557-35-5 -
 2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0 -
 181228-33-1 (S)-Methyl 3-amino-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)propanote Hydrochloride (DAP-OMe. HCl) 99%View Details
181228-33-1 (S)-Methyl 3-amino-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)propanote Hydrochloride (DAP-OMe. HCl) 99%View Details
181228-33-1