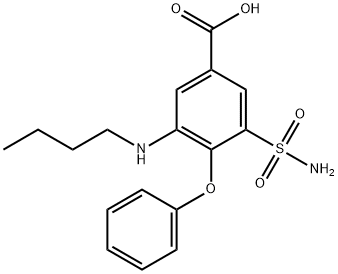
Bumetanide
Synonym(s):3-(Aminosulfonyl)-5-(butylamino)-4-phenoxybenzoic acid
- CAS NO.:28395-03-1
- Empirical Formula: C17H20N2O5S
- Molecular Weight: 364.42
- MDL number: MFCD00078949
- EINECS: 249-004-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32
What is Bumetanide?
Absorption
Bumetanide is completely absorbed (80%), and the absorption is not altered when taken with food. Bioavailability is almost complete.
Toxicity
Overdosage can lead to acute profound water loss, volume and electrolyte depletion, dehydration, reduction of blood volume and circulatory collapse with a possibility of vascular thrombosis and embolism. Electrolyte depletion may be manifested by weakness, dizziness, mental confusion, anorexia, lethargy, vomiting and cramps. Treatment consists of replacement of fluid and electrolyte losses by careful monitoring of the urine and electrolyte output and serum electrolyte levels.
Chemical properties
Crystalline Solid
Originator
Burinex,Leo,UK,1973
The Uses of Bumetanide
Bumetanide is a diuretic.
The Uses of Bumetanide
antineoplastic, alkylating agent
The Uses of Bumetanide
Bumetanide is used for relieving edema associated with cardiac insufficiency, for liver and kidney diseases including nephrotic syndrome, for ascites, and hypertension.
What are the applications of Application
Bumetanide (Ro 10-6338) is a specific inhibitor of Na+-K+-2Cl- cotransporter NKCC1
Background
Bumetanide is a sulfamyl diuretic.
Indications
For the treatment of edema associated with congestive heart failure, hepatic and renal disease including the nephrotic syndrome.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of benzoic acids that is 4-phenoxybenzoic acid in which the hydrogens ortho to the phenoxy group are substituted by butylamino and sulfamoyl groups. Bumetanide is a diuretic, and is used for treatment of oedema associated with congestive heart failure, hepatic and renal disease.
Manufacturing Process
Preparation of 3-Nitro-4-Phenoxy-5-Sulfamylbenzoic Acid: A mixture of 4-
chloro-3-nitro-5-sulfamylbenzoic acid (140 grams), phenol (100 grams),
sodium hydrogencarbonate (170 grams), and water (1.000 ml) was heated to
85°C while stirring and kept at this temperature for 16 hours. After cooling to
4°C, the precipitated sodium salt of 3-nitro-4-phenoxy-5-sulfamylbenzoic acid
was filtered off and washed with ice water. The sodium salt was dissolved in
boiling water (3,000 ml), and the 3-nitro-4-phenoxy-5-sulfamylbenzoic acid
was precipitated by addition of 4N hydrochloric acid. After cooling, the acid
was isolated by suction and dried. The melting point was 255°-256°C.
Preparation of 3-Amino-4-Phenoxy-5-Sulfamylbenzoic Acid: A suspension of 3-
nitro-4-phenoxy-5-sulfamylbenzoic acid (20 grams) in water (100 ml) was
adjusted to pH 8 by addition of 1N lithium hydroxide. The resulting solution
was hydrogenated at room temperature and 1.1 atmospheres hydrogen
pressure after addition of Pd on carbon catalyst (0.6 grams catalyst containing
10% Pd). After the hydrogen uptake had become negligible, the catalyst was
removed by filtration, and the 3-amino-4-phenoxy-5-sulfamylbenzoic acid was
precipitated from the filtrate by addition of 4N hydrochloric acid to pH 2.5.
After recrystallization from aqueous ethanol and drying, the melting point was
255°-256°C.
Preparation of 3-n-Butylamino-4-Phenoxy-5-Sulfamylbenzoic Acid: To a
suspension of 3-amino-4-phenoxy-5-sulfamyibenzoic acid (10 grams) in nbutanol
(200 ml), concentrated sulfuric acid (2 ml) was added while stirring.
The reaction mixture was heated under reflux under conditions in which the
water formed during the reaction could be removed. When, after dilution with n-butanol, the NMR-spectrum of a sample of the reaction mixture showed at
the two doublets of the aromatic protons in ring A that the butyl-3-amino-4-
phenoxy-5-sulfamylbenzoate formed as an intermediate was more than 90%
converted to the corresponding 3-n-butylaminobenzoate, 2 N sodium
hydroxide (200 ml) was added and the boiling was continued for 45 minutes.
After the saponification, the reaction mixture was neutralized to pH 8 by
addition of concentrated hydrochloric acid.
By cooling, the sodium salt of 3-n-butylamino-4-phenoxy-5-sulfamylbenzoic
acid precipitated. It was filtered off and recrystallized from water (100 ml).
The sodium salt, crystallizing with 3 molecules of water, was then dissolved in
boiling water (200 ml), 1N hydrochloric acid was added to pH 2.5, and after
cooling the precipitated 3-n-butylamino-4-phenoxy-5-sulfamylbenzoic acid was
collected by filtration. After recrystallization from aqueous ethanol and drying,
the pure compounds were obtained with melting point 230°-231°C.
brand name
Bumex (Roche).
Therapeutic Function
Diuretic
Biological Activity
Loop diuretic that inhibits the Na + /2Cl - /K + (NKCC) cotransporter. More potent than furosemide (5-(Aminosulfonyl)-4-chloro-2-([2-furanylmethyl]amino)benzoic acid ).
Biochem/physiol Actions
Inhibitor of Na+/K+/Cl- cotransporter.
Pharmacokinetics
Bumetanide is a loop diuretic of the sulfamyl category to treat heart failure. It is often used in patients in whom high doses of furosemide are ineffective. There is however no reason not to use bumetanide as a first choice drug. The main difference between the two substances is in bioavailability. Bumetanide has more predictable pharmacokinetic properties as well as clinical effect. In patients with normal renal function, bumetanide is 40 times more effective than furosemide.
Clinical Use
A diuretic structurally related to furosemide is bumetanide. This compound also functions as a high-ceiling diuretic in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle. It has a duration of action of approximately 4 hours. The uses of this compound are similar to those described for furosemide. The dose of bumetanide is 0.5 to 2 mg/day given as a single dose.
Synthesis
Bumetanide, 3-butylamino-4-phenoxy-5-sulfamoylbenzoic acid (21.4.6), is synthesized from 4-chlorobenzoic acid. In the first stage of synthesis, it undergoes sulfonylchlorination by chlorosulfonic acid, forming 4-chloro-3-chlorosulfonylbenzoic acid (21.4.1), which is further nitrated with nitric acid to 4-chloro-3-chlorosulfonyl-5-nitrobenzoic acid (21.4.2). Reacting this with ammonia gives 5-aminosulfonyl-4-chloro-3-nitrobenzoic acid (21.4.3), which when reacted with sodium phenolate is transformed into 5-amino-sulfonyl-3-nitro-5-phenoxybenzoid acid (21.4.4). Reduction of the nitro group in this product by hydrogen using a palladium on carbon catalyst gives 3-amino-5-aminosulfonyl- 5-phenoxybenzoic acid (21.4.5). Finally, reacting this with butyl alcohol in the presence of sulfuric acid gives the desired bumetanide (21.4.6).

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Analgesics: increased risk of nephrotoxicity with
NSAIDs; antagonism of diuretic effect with
NSAIDs.
Anti-arrhythmics: risk of cardiac toxicity with
anti-arrhythmics if hypokalaemia occurs; effects of
lidocaine and mexiletine antagonised.
Antibacterials: increased risk of ototoxicity with
aminoglycosides, polymyxins and vancomycin; avoid
with lymecycline.
Antidepressants: increased risk of hypokalaemia
with reboxetine; enhanced hypotensive effect with
MAOIs; increased risk of postural hypotension with
tricyclics.
Antiepileptics: increased risk of hyponatraemia with
carbamazepine.
Antifungals: increased risk of hypokalaemia with
amphotericin.
Antihypertensives: enhanced hypotensive effect;
increased risk of first dose hypotensive effect
with alpha-blockers; increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with sotalol if hypokalaemia occurs.
Antipsychotics: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with amisulpride or pimozide if
hypokalaemia occurs - avoid with pimozide;
enhanced hypotensive effect with phenothiazines.
Atomoxetine: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias if hypokalaemia occurs.
Cardiac glycosides: increased toxicity if hypokalaemia
occurs.
Cytotoxics: increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
due to hypokalaemia with arsenic trioxide; increased
risk of nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity with platinum
compounds.
Lithium: risk of toxicity.
Metabolism
45% is secreted unchanged. Urinary and biliary metabolites are formed by oxidation of the N-butyl side chain.
Metabolism
About 80% of a dose of bumetanide is excreted in the urine, about 50% as unchanged drug, and 10-20% in the faeces. No active metabolites are known. In patients with chronic renal failure the liver takes more importance as an excretory pathway although the duration of action is not markedly prolonged.
storage
Store at RT
Properties of Bumetanide
| Melting point: | 230-2310C |
| Boiling point: | 571.2±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.2812 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6510 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, soluble in acetone and in alcohol, slightly soluble in methylene chloride. It dissolves in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides. |
| form | neat |
| pka | pK1 3.6, pK2 7.7(at 25℃) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Light Yellow |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in ethanol (10 mg/ml), DMSO (25 mg/ml), acetone, benzene, methanol, propylene glycol, and water (<1 mg/ml). |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 28395-03-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Benzoic acid, 3-(aminosulfonyl)-5-(butylamino)-4-phenoxy- (28395-03-1) |
Safety information for Bumetanide
Computed Descriptors for Bumetanide
Bumetanide manufacturer
Solara Active Pharma Sciences Ltd
Vijaya Pharma And Life Science
Medilux Laboratories Pvt Ltd
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 Bumetanide 98%View Details
Bumetanide 98%View Details -
 28395-03-1 96%View Details
28395-03-1 96%View Details
28395-03-1 -
 28395-03-1 Bumetanide 98%View Details
28395-03-1 Bumetanide 98%View Details
28395-03-1 -
 Bumetanide 28395-03-1 98%View Details
Bumetanide 28395-03-1 98%View Details
28395-03-1 -
 Bumetanide 98%View Details
Bumetanide 98%View Details
28395-03-1 -
 Bumetanide 28395-03-1 98%View Details
Bumetanide 28395-03-1 98%View Details
28395-03-1 -
 Bumetanide 98% CAS 28395-03-1View Details
Bumetanide 98% CAS 28395-03-1View Details
28395-03-1 -
 Bumetanide CAS 28395-03-1View Details
Bumetanide CAS 28395-03-1View Details
28395-03-1