Sucralfate
Synonym(s):Sucralfate;Sucrose octasulfate–aluminum complex
- CAS NO.:54182-58-0
- Empirical Formula: C11H52Al16O75S8-16
- Molecular Weight: 2072.71
- MDL number: MFCD00145339
- EINECS: 259-018-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-13 11:39:26
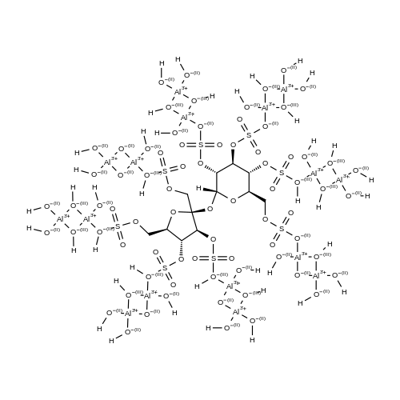
What is Sucralfate?
Absorption
This drug is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract in very minimal quantities. The adsorbed sulfated disaccharide is excreted in the urine . This drug contains aluminum and after the administration of 1 g of sucralfate 4 times per day, about 0.001% to 0.017% of this aluminum content is absorbed in patients with normal renal function. This number is expected to increase in those with impaired renal function.
Toxicity
Overdose
Overdosage has never been observed with sucralfate . It is unlikely, as administering a maximum dose of up to 12 g/kg/body weight in several animal species did not result in death. The lethal dose could not be determined in these studies . It is likely that overdose of sucralfate in humans would result in constipation, and supportive treatment would be advised .
Use in pregnancy
This drug is considered a pregnancy Category B drug. Studies have been performed in rodents and rabbits at doses up to 50 times the recommended human dose. No harm to the fetus has been observed in the abovementioned studies. Sufficient and well-controlled clinical trials have not been performed in pregnant women. Due to the fact that the results of animal studies are not always relevant to human response, sucralfate should be used during pregnancy only if it is deemed essential for the mother's health .
Use in nursing
Whether this drug is excreted in human milk is currently unknown. Many drugs are excreted in breast milk, therefore, if sucralfate is administered to a lactating and nursing woman, caution should be observed .
Carcinogenesis
24 month toxicity studies were performed in rodents, and the dose of sucralfate reached up to 1 g/kg (equivalent to 12 times the recommended human dose). No signs of sucralfate-related tumors were noted.
Description
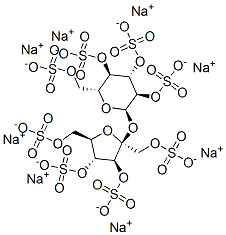
Sucralfate is a complex of the sulfuric acid ester of sucrose and aluminum hydroxide. Secondary polymerization with aluminum hydroxide forms intermolecular bridges between molecules of sulfate esters with aluminum. Limited dissociation of the complex occurs in gastric acid, but these anionic sulfate esters form insoluble adherent complexes with the proteinaceous exudate at the abraded surface of a crater of the ulcerated area in the stomach. This physical complex protects the ulcer from the erosive action of pepsin and bile salts. Sucralfate also stimulates synthesis and release of prostaglandins, bicarbonate, and epidermal and fibroblast growth factors. Significant ulcer healing effects are noted in placebo-controlled trials. Only small amounts of sucralfate are absorbed systemically. In renal impairment, there is a risk of accumulation of absorbed aluminum from the drug. Sucralfate reduces absorption of other drugs, including H2 antihistamines, quinolone antibiotics, phenytoin, and perhaps, warfarin
Description
Sucralfate is a basic aluminum sucrose sulfate complex that has gastroprotective activity. It inhibits rat pepsin in a concentration-dependent manner and pepsin activity in isolated human gastric juice. It also inhibits ulcer formation induced by pyloric ligation, indomethacin , or cysteamine in rats. Sucralfate (5,600 mg/animal) is protective against neutral ethanol and acidified taurocholic acid-induced damage in a rat model of hydrochloric acid-induced gastric mucosal damage, increasing the pH and reducing the disappearance of hydrogen ions. Formulations containing sucralfate have been used as antacids in the treatment of duodenal ulcer.
Chemical properties
White Powder
Originator
Antepsin,Baldacci,Italy,1975
The Uses of Sucralfate
Sucralfate, an aluminum salt of sucrose octasulfate, is used as an antacid and antiulcer medication. Bis- and tris-platinum complexes of sucrose show promise as antitumor agents. Sucrose monoesters are used in some pharmaceutical preparations.
The Uses of Sucralfate
An inhibitor of peptic hydrolysis and stomach acidity. Used as an antiulcerative
The Uses of Sucralfate
antineoplastic, antileukemia
Indications
The sucralfate suspension and tablet are used for the treatment of active duodenal ulcer for up to 8 weeks. The tablet form may be used at a lower dose for healed duodenal ulcers, for the purpose of maintaining healing and preventing recurrence .
Sucralfate is also used in the prevention and/or treatment of gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD), gastritis, peptic ulcer disease, stress ulcer, in addition to dyspepsia .
Background
Sucralfate is a medication that is widely used to prevent and treat a number of diseases in the gastrointestinal tract such as duodenal ulcers , gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD), gastritis, peptic ulcer disease, stress ulcer, in addition to dyspepsia . It is considered a cytoprotective agent, protecting cells in the gastrointestinal tract from damage caused by agents such as gastric acid, bile salts, alcohol, and acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin), among other substances .
Sucralfate has been shown to be a well-tolerated and safe drug. It is sold under many brands and is available in both tablet and suspension forms. It was approved by the FDA 1982 in tablet form, and in 1994 for the suspension form .
What are the applications of Application
Sucrose octasulfate-aluminum complex is an inhibitor of peptic hydrolysis
Indications
Sucralfate (Carafate) is an aluminum hydroxide–sulfated sucrose complex that is only minimally absorbed from the GI tract. After exposure to gastric acid, the compound becomes negatively charged, creating a viscous adherent complex. This complex is believed to inhibit back-diffusion of H .Other effects are a direct reduction in pepsin activity and a slight rise in tissue prostaglandin levels. Stimulation of a cytoprotection mechanism may therefore assist mucosal healing. The drug has no acid-buffering capacity.
Manufacturing Process
A disaccharide is added to a pyridine SO3 complex solution, which is prepared by reacting 5 to 6 times the molar amount of liquid SO3 as much as that of disaccharide with 5 to 10 times the amount of pyridine as that of the disaccharide at 0°C to 5°C, for sulfation at 50°C to 70°C for 3 to 7 hours. After the completion of sulfation, the greater part of pyridine is removed by decantation. The obtained solution exhibits an acidity that is so strong that it is improper to apply the reaction with aluminum ion and, therefore, sodium hydroxide is added for neutralization. After the remaining pyridine is removed by concentration, 100 unit volumes of water per unit volume of the residue is added thereto. To the solution is then added aluminum ion solution mainly containing aluminum dihydroxychloride, the pH of which is 1.0 to 1.2, in such an amount that the aluminum ion is present in an amount of 4 to 6 molar parts of the amount of disaccharide to provide a pH of 4 to 4.5. The mixture is reacted under stirring at room temperature and the formed disaccharide polysulfate-aluminum compound is allowed to precipitate. After filtration, the residue is washed with water and dried.
brand name
Carafate (Axcan Scandipharm).
Therapeutic Function
Antiulcer
General Description
Sucralfate, 3,4,5,6-tetra-(polyhydroxyaluminum)-α-D-glucopyranosyl sulfate-2,3,4,5-tetra-(polyhydroxyaluminum)-β-D-fructofuranoside sulfate (Carafate), isthe aluminum hydroxide complex of the octasulfate ester ofsucrose. It is practically insoluble in water and soluble instrong acids and bases. It has a pKa value between 0.43 and1.19.
Sucralfate is minimally absorbed from the GI tract by design,and thus exerts its antiulcer effect through local ratherthan systemic action. It has negligible acid-neutralizing orbuffering capacity in therapeutic doses. Although its mechanismof action has not been established, studies suggestthat sucralfate binds preferentially to the ulcer site to form aprotective barrier that prevents exposure of the lesion to acidand pepsin. In addition, it adsorbs pepsin and bile salts.Either would be very desirable modes of action.
The simultaneous administration of sucralfate may reducethe bioavailability of certain agents (e.g., tetracycline, phenytoin,digoxin, or cimetidine). It further recommends restorationof bioavailability by separating administration of theseagents from that of sucralfate by 2 hours. Presumably, sucralfatebinds these agents in the GI tract. The most frequentlyreported adverse reaction to sucralfate is constipation (2.2%).Antacids may be prescribed as needed but should not be takenwithin 0.5 hour before or after sucralfate.
Pharmacokinetics
This drug aids in the healing of duodenal ulcers, relieving painful inflammation by creating a protective mechanical barrier between the lining or skin of the gastrointestinal tract and damaging substances . In addition, sucralfate acts to increase levels of growth factors locally, and also causes an increase in prostaglandins which are important in the healing of the mucosa (lining) of the gastrointestinal tract .
Clinical Use
Sucralfate is frequently used for prophylaxis of stress-induced gastritis in patients in intensive care units. It has also been successfully used in small numbers of patients as a suspension enema to treat radiation proctitis.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Sucralfate has been used in the treatment of oral, esophageal, gastric, and duodenal ulcers. It has also been employed to prevent drug-induced (e.g., aspirin) gastric erosions, but efficacy for this is somewhat sporadic. Sucralfate has been used in human patients with hyperphosphatemia secondary to renal failure and potentially could be useful for this in animals as well.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Reduced absorption of digoxin, tetracyclines,
quinolones, coumarins, fosphenytoin and phenytoin
- give 2 hours after sucralfate.
Metabolism
This drug is absorbed in very small quantities and is not significantly metabolized .
Metabolism
Sucralfate is only slightly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract after oral doses. However, there can be some release of aluminium ions and of sucrose sulphate; small quantities of sucrose sulphate may then be absorbed and excreted, mainly in the urine; some absorption of aluminium may also occur.
Properties of Sucralfate
| Melting point: | >220°C (dec.) |
| Boiling point: | 1990℃ at 101.325kPa |
| Density | 0.338 at 20℃ |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,2-8°C |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, in ethanol (96 per cent) and in methylene chloride. It dissolves in dilute solutions of mineral acids and alkali hydroxides. |
| form | neat |
| pka | pKa = 0.43 to 1.19(at 25℃) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White |
Safety information for Sucralfate
Computed Descriptors for Sucralfate
Sucralfate manufacturer
REXIN Laboratories (Redson Group)
Inventys Research Company Pvt Ltd
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

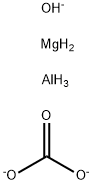

You may like
-
 Sucralfate 99%View Details
Sucralfate 99%View Details -
 54182-58-0 98%View Details
54182-58-0 98%View Details
54182-58-0 -
 Sucralfate 16.5 to 18.7% Al CAS 54182-58-0View Details
Sucralfate 16.5 to 18.7% Al CAS 54182-58-0View Details
54182-58-0 -
 Sucralfate 54182-58-0 100View Details
Sucralfate 54182-58-0 100View Details
54182-58-0 -
 Sucralfate 99%View Details
Sucralfate 99%View Details
54182-58-0 -
 54182-58-0 98%View Details
54182-58-0 98%View Details
54182-58-0 -
 Sucrose Octasulphate Aluminium Salt (Sucralfate) extrapure CAS 54182-58-0View Details
Sucrose Octasulphate Aluminium Salt (Sucralfate) extrapure CAS 54182-58-0View Details
54182-58-0 -
 Sucrose octasulfate–aluminum complex CAS 54182-58-0View Details
Sucrose octasulfate–aluminum complex CAS 54182-58-0View Details
54182-58-0