2-Pyrrolidinone
Synonym(s):γ-Butyrolactam;2-Pyrrolidinone;2-Pyrrolidone;Butyrolactam
- CAS NO.:616-45-5
- Empirical Formula: C4H7NO
- Molecular Weight: 85.1
- MDL number: MFCD00005270
- EINECS: 210-483-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-02-27 17:16:38
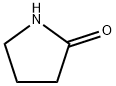
What is 2-Pyrrolidinone?
Chemical properties
2-Pyrrolidinone occurs as a colorless or slightly grayish liquid, as white or almost white crystals, or colorless crystal needles. It has a characteristic odor. miscible with water, alcohol, ether, chloroform, benzene, ethyl acetate and carbon disulfide, insoluble in petroleum ether.
The Uses of 2-Pyrrolidinone
2-Pyrrolidinone is a widely used organic polar solvent for various applications. 2-Pyrrolidinone is also an intermediate in the manufacture of polymers.
The Uses of 2-Pyrrolidinone
2-pyrrolidone widely exists in various physiologically active natural products in nature. For example, it is the main structural unit of gonadotropin releasing hormone. At the same time, 2-pyrrolidone is an important raw material and intermediate of medicine, pesticide, dye, peptide and other chemicals. If it is used as the end chain of peptide, it also plays a stable role in the conformation of the compound. Many polysubstituted 2-pyrrolidones have been used in the synthesis and production of a variety of drugs and applied for patents.
Definition
ChEBI: 2-Pyrrolidinone is the simplest member of the class of pyrrolidin-2-ones, consisting of pyrrolidine in which the hydrogens at position 2 are replaced by an oxo group. The lactam arising by the formal intramolecular condensation of the amino and carboxy groups of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). It has a role as a polar solvent and a metabolite.
Production Methods
The synthesis of 2-pyrrolidone was first reported in 1889 as the product of dehydration of 4-aminobutanoic acid. It is produced commercially by condensation of butyrolactone with ammonia, a method first described in 1936. Other synthetic routes include carbon monoxide insertion into allylamine, hydrolytic hydrogenation of succinonitrile, and hydrogenation of ammoniacal solutions of maleic and succinnic acids (Hort and Anderson 1978).
Preparation
Pyrrolidone is prepared from butyrolactone by a Reppe process, in which acetylene is reacted with formaldehyde.
Reactions
2-Pyrrolidone undergoes the reactions of a typical lactam, e.g. ring opening, attack on the carbonyl group, and replacement of hydrogens alpha to the carbonyl group. Strong acids and bases catalyze the hydrolysis of 2-pyrrolidone to 4-aminobutanoic acid (GABA). The hydrogen atom on the nitrogen atom is easily replaced by alkylation reactions with alkyl halide or sulfates, or reaction with acid anhydrides, acyl halides, ethylene oxide, and styrene. Condensation reactions with secondary amines and alcohols, and O-alkylation reactions occur at the carbonyl group. In the presence of anionic catalyst systems, 2-pyrrolidone is polymerized to polypyrrolidone, nylon-4 (Hort and Anderson 1978).
Health Hazard
Exposure to 2-pyrrolidone produces irritation to the eyes, mucous membranes, and skin. Although reported to be a skin sensitizer in animal tests, there is no indication that 2-pyrrolidone is a skin sensitizer in human exposures (Anon 1975). 2-Pyrrolidone has been reported to enhance the permeability of human skin for methanol, but reduced the permeability for octanol (Southwell et al 1983).
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Pharmaceutical Applications
Pyrrolidone and N-methylpyrrolidone are mainly used as solvents in veterinary injections. Pyrrolidone has been shown to be a better solubilizer than glycerin, propylene glycol, or ethanol. They have also been suggested for use in human pharmaceutical formulations as solvents in parenteral, oral, and topical applications. In topical applications, pyrrolidones appear to be effective penetration enhancers. Pyrrolidones have also been investigated for their application in controlled-release depot formulations.
Industrial uses
2-Pyrrolidone is used as an intermediate for synthesis of l-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone and various TV-methylol derivatives used as textile-finishing agents; as a solvent for various polymers, chlordane and DDT, d-sorbitol, glycerin, and sugars; and as a decolorizing agent for kerosene, fatty oils, and rosins. N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone and 2-pyrrolidone are utilized in petroleum refining to selectively extract aromatics from paraffinic hydrocarbons. 2-Pyrrolidone is used as a plasticizer and coalescing agent for acrylic latices and acrylic/styrene copolymers in emulsion coatings, i.e. floor waxes. A linear high molecular weight polyamide polymer of 2-pyrrolidone, nylon-4, is used as a textile fiber, injection molding compound, and film-forming polymer (Anon. 1975; Hort and Anderson 1978).
Safety
Pyrrolidones are mainly used in veterinary injections and have also
been suggested for use in human oral, topical, and parenteral
pharmaceutical formulations. In mammalian species, pyrrolidones
are biotransformed to polar metabolites that are excreted via the
urine. Pyrrolidone is mildly toxic by ingestion and subcutaneous
routes; mutagenicity data have been reported.
LD50 (guinea pig, oral): 6.5 g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 6.5 g/kg
Metabolism
A metabolite of 2-pyrrolidone, 4-aminobutanoic acid has been identified in animals (Lundgren et al 1980). 2-Pyrrolidone has been reported to be an endogenous constituent in the brains of mice (Callery et al 1978) and bovine (Mori et al 1975). The aliphatic polyamine putrescine has been demonstrated to be metabolized to 2-pyrrolidone in rat liver slices (Lundgren and Hankins 1978; Lundgren et al 1985) and to lesser extent by slices of spleen and lung, but not in tissue slices from kidney, brain, heart, or rear leg muscle (Lundgren and Hankins 1978). The metabolism of putrescine is catalyzed by the microsomal enzyme diamine oxidase (EC 1.4.3.6) to 4-aminobutyraldehyde, which is subsequently oxidized to the neurotransmitter 4-aminobutanoic acid (4-aminobutyric acid, GAB A) or is cyclized to delta1-pyrroline (Seiler 1980; Lundgren et al 1980; Callery et al 1980), which is in turn oxidized to 5-hydroxy-2-pyrrolidone (Lundgren and Fales 1980). There is evidence that 5-hydroxy-2-pyrrolidone is further metabolized to succinimide, malimide, 2- and 3-hydroxysuccinamic acids, maleamic acid, and carbon dioxide (Bandle et al 1984). An enzyme system residing in the soluble fraction of rabbit liver catalyzes the conversion of delta'-pyrroline to ?-aminobutyric acid and its lactam, 2-pyrrolidone (Callery et al 1982). 2-Pyrrolidone has been identified as a urinary metabolite of N-nitrosopyrrolidine (Cottrell et al 1980) and the drug methadone (Kreek 1980).
storage
Pyrrolidone is chemically stable and, if it is kept in unopened original containers, the shelf-life is approximately one year. Pyrrolidone should be stored in a well-closed container protected from light and oxidation, at temperatures below 20°C.
Incompatibilities
Pyrrolidone is incompatible with oxidizing agents and strong acids.
Properties of 2-Pyrrolidinone
| Melting point: | 23-25 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 245 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.12 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 2.9 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 0.04 hPa (20 °C) |
| FEMA | 4829 | 2-PYRROLIDONE |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: miscible (completely) |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | 16.62±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | Clear colorless to pale yellow |
| PH | 9-11 (100g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| explosive limit | 1.8-16.6%(V) |
| Water Solubility | miscible |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,8016 |
| BRN | 105241 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 616-45-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 2-Pyrrolidinone(616-45-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2-Pyrrolidinone (616-45-5) |
Safety information for 2-Pyrrolidinone
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for 2-Pyrrolidinone
| InChIKey | HNJBEVLQSNELDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
2-Pyrrolidinone manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
New Products
2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Strontium Carbonate, 98% Wang resin Sodium hydrogenphosphate, anhydrous 2-Bromo-3-methoxyaniline hydrochloride, 95% (Custom work) 1-Bromo-4-chlorobenzene, 99% Benzocaine, 98% (R)-2-Methylpyrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (De Mepro) Ramipril Sacubitril- Valsartan Boc-his(trt)-OH Fmoc-L-Glu-OtBu Boc-L-Tyr(tBu)-OH Semi carbazide Hydrochloride 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 2-Chloromethyl-4-methyl-quinazoline Trans-4-Aminocyclohexanol [4tac] 2-[1-(Mercaptomethyl)Cyclopropyl]Acetic AcidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


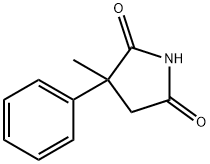
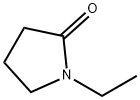
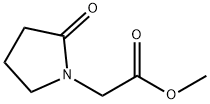
You may like
-
 2-Pyrrolidinone supplierView Details
2-Pyrrolidinone supplierView Details
616-45-5 -
 2 Pyrrolidone 99%View Details
2 Pyrrolidone 99%View Details -
 2-Pyrrolidone pure CAS 616-45-5View Details
2-Pyrrolidone pure CAS 616-45-5View Details
616-45-5 -
 2-Pyrrolidinone CAS 616-45-5View Details
2-Pyrrolidinone CAS 616-45-5View Details
616-45-5 -
 2-Pyrrolidone CAS 616-45-5View Details
2-Pyrrolidone CAS 616-45-5View Details
616-45-5 -
 2-PYRROLIDONE For Synthesis CAS 616-45-5View Details
2-PYRROLIDONE For Synthesis CAS 616-45-5View Details
616-45-5 -
 2-Pyrrolidinone CAS 616-45-5View Details
2-Pyrrolidinone CAS 616-45-5View Details
616-45-5 -
 2-Pyrrolidinone CAS 616-45-5View Details
2-Pyrrolidinone CAS 616-45-5View Details
616-45-5
