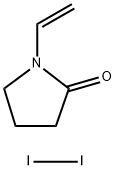
N-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone
Synonym(s):1-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidinone;1-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone
- CAS NO.:88-12-0
- Empirical Formula: C6H9NO
- Molecular Weight: 111.14
- MDL number: MFCD00003197
- EINECS: 201-800-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-07-24 18:12:20
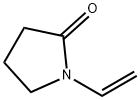
What is N-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone?
Chemical properties
Colorless liquid. Combustible.
The Uses of N-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone
A pyrrolidine used for biochemical research
The Uses of N-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone
1-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidinone is used in the preparation of NMDA receptor antagonists. Also used in the synthesis of copolymers used to stabilize rhodium nanoclusters.
What are the applications of Application
1-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidinone is a pyrrolidine used for biochemical research
Definition
ChEBI: N-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone is a member of pyrrolidin-2-ones.
Production Methods
Industrially, N-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone (NVP) is produced by reacting 2-pyrrolidone with acetylene in highpressure autoclaves at 130–170 ℃ and pressures of up to 2.6 MPa. Vinylation proceeds in the liquid phase and is catalyzed by 2-pyrrolidone–potassium. The salt is obtained by adding 1–5% potassium hydroxide or caustic potash solution to fresh pyrrolidone and removing excess water by vacuum distillation (batchwise or continuously). The vinylation reaction takes place in a liquid-phase tube or loop reactor, or in a gas-phase reactor. To avoid the danger of acetylene explosions, nitrogen or propane mixtures of acetylene are used instead of pure acetylene. After the vinylation, the crude product obtained is purified by multistep vacuum distillation. Unreacted 2-pyrrolidone and derivatives can be recycled. Excess acetylene is removed by distillation and can also be recycled to the process. ?Another industrially important synthetic route is based on N-(1-hydroxyethyl)-2-pyrrolidone (HEP). In this process, HEP is dehydrated in the gas phase in a heterogeneously catalyzed reaction at 320–400 ℃ and 10 kPa. The obtained crude NVP is purified by vacuum distillation or crystallization.
What are the applications of Application
N-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone (NVP) is an important precursor and intermediate for process auxiliaries and additives. The main areas of use are the production of polyvinylpyrrolidone and copolymers, the preferred comonomers being vinyl acetate and methyl acrylate. Ca. 10–15% of the monomer is used in the pharmaceutical industry for the production of a polyvinylpyrrolidone–iodine complex used as a disinfectant. NVP is also used as a reactive solvent for UV-curable resins for the production of printing inks and paints as paper and textile auxiliaries, and as an additive in the cosmetics industry.
General Description
1-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidinone is a colorless to yellow liquid, with a characteristic odor. Its melting point is around 13.5oC and boils at about 90-92oC. VP is completely miscible in water and in most organic solvents but partially miscible in aliphatic hydrocarbons. Industrial production of VP by reacting 2-pyrrolidone with acetylene at high pressure and temperature has been reported. The vinylation process proceeds in liquid phase and is catalyzed by 3-pyrrolidone -potassium hydroxide.
Chemical Reactivity
N-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone (NVP) is stable toward alkalis at room temperature. Above 0 ℃ it is cleaved by aqueous mineral acids into acetaldehyde and 2-pyrrolidone; the latter reacts with an excess of NVP to give 1,1'-ethylidene-bis-2- pyrrolidone. Protic compounds such as amides, thiols, alcohols, and phenols add to the double bond according to the Markovnikov rule, for example, N-(1-phenoxyethyl)-2-pyrrolidone is formed with phenol. Catalytic hydrogenation produces N-ethyl-2-pyrrolidone. Hydroformylation on rhodium catalysts forms 2-N-(2-pyrrolidonyl)-propanal as the major product. On prolonged standing, particularly in warm conditions, NVP tends to polymerize. Industrially, N-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone (NVP) is converted into polyvinylpyrrolidone using radical initiators.
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen. Moderately toxic by ingestion, inhalation, and skin contact. A severe eye irritant. Probably irritating and narcotic in high concentrations. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame; can react vigorously with oxibzing materials. To fight fire, use alcohol foam, CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of NOx.
Storage
N-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone (NVP) must be protected from heat and direct sunlight. Even in closed containers NVP can only be stored for a limited period because it tends to polymerize. Stabilizers are therefore added. N,N'-Bis(1-methylpropyl)-1,4-benzenediamine [101-96-2] is an important, NVP-soluble stabilizer that does not interfere with further processing. Use of this stabilizer allows the product to be stored for ca. 300 d at 20 ℃, and ca. 150 d at 25 ℃. Stabilization with solid sodium hydroxide that can be easily filtered off is not as efficient. Storage at temperatures close to the melting point results in separation of NVP from the stabilizer due to repeated solidification and melting. This shortens the shelf life considerably and can lead to uncontrolled polymerization. Solidified NVP must therefore be molten carefully in a water bath (max. 40 ℃) or at room temperature (max. 30 ℃) and homogenized by continuous agitation.
Properties of N-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone
| Melting point: | 13-14 °C |
| Boiling point: | 92-95 °C11 mm Hg(lit.) |
| Density | 1.04 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 3.8 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 0.1 mm Hg ( 24 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 201 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 52.1g/l soluble |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | -0.34±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | Clear colorless to yellow |
| PH | 9-10 (100g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| explosive limit | 1.4-10%(V) |
| Water Solubility | miscible |
| Merck | 14,7697 |
| BRN | 110513 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 88-12-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | N-Vinylpyrrolidone(88-12-0) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 19, Sup 7, 71) 1999 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | N-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone (88-12-0) |
Safety information for N-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H351:Carcinogenicity H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for N-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone
| InChIKey | WHNWPMSKXPGLAX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 88-12-0 1-Ethenyl-2-pyrrolidinone 98%View Details
88-12-0 1-Ethenyl-2-pyrrolidinone 98%View Details
88-12-0 -
 1-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone (stabilized with N,N'-Di-sec-butyl-p-phenylenediamine) CAS 88-12-0View Details
1-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone (stabilized with N,N'-Di-sec-butyl-p-phenylenediamine) CAS 88-12-0View Details
88-12-0 -
 1-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidinone, ≥99% CAS 88-12-0View Details
1-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidinone, ≥99% CAS 88-12-0View Details
88-12-0 -
 1-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidinone CAS 88-12-0View Details
1-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidinone CAS 88-12-0View Details
88-12-0 -
 1-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone CAS 88-12-0View Details
1-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone CAS 88-12-0View Details
88-12-0 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4
