1,5-Naphthalene diisocyanate
- CAS NO.:3173-72-6
- Empirical Formula: C12H6N2O2
- Molecular Weight: 210.19
- MDL number: MFCD00039588
- EINECS: 221-641-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
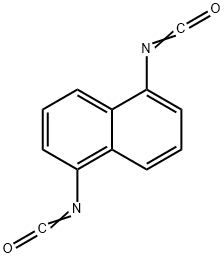
What is 1,5-Naphthalene diisocyanate?
Description
Naphthalene diisocyanate (NDI) occurs as white to lightyellow crystalline flakes with a characteristic odor. NDI is incompatible with many classes of compounds, reacting exothermically to release toxic gases. Reactions with amines, aldehydes, alcohols, alkali metals, ketones, mercaptans, strong oxidizers, hydrides, phenols, and peroxides can cause vigorous releases of heat. Acids and bases initiate polymerization reactions. NDI can react with water to form amines and liberate carbon dioxide.
Chemical properties
Naphthylene 1,5-diisocyanate is a solid, m.p. 128°C. It has a lower vapour pressure than tolylene diisocyanate and is therefore less toxic in use; it does, however, have sensitizing properties.
The Uses of 1,5-Naphthalene diisocyanate
Manufacture of polyurethane solid elastomers.
The Uses of 1,5-Naphthalene diisocyanate
NDI is used as a curing agent in the manufacture of elastomers.
The Uses of 1,5-Naphthalene diisocyanate
Naphthylene 1,5-diisocyanate is mainly used for the production of elastomers.
Preparation
Naphthylene 1,5-diisocyanate (NDI) is prepared from naphthalene as follows:

Definition
ChEBI: 1,5-Naphthalene diisocyanate is a member of naphthalenes.
General Description
White to light-yellow crystalline flakes.
Reactivity Profile
Isocyanates and thioisocyanates, such as 1,5-Naphthalene diisocyanate, are incompatible with many classes of compounds, reacting exothermically to release toxic gases. Reactions with amines, aldehydes, alcohols, alkali metals, ketones, mercaptans, strong oxidizers, hydrides, phenols, and peroxides can cause vigorous releases of heat. Acids and bases initiate polymerization reactions in these materials. Some isocyanates react with water to form amines and liberate carbon dioxide. Base-catalysed reactions of isocyanates with alcohols should be carried out in inert solvents. Such reactions in the absence of solvents often occur with explosive violence, [Wischmeyer(1969)].
Hazard
Irritant. Questionable carcinogen.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Safety Profile
A powerful allergen. An irritant. Questionable carcinogen. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Environmental Fate
NDI is a synthetic organic chemical. It is a natural derivative of primary amines with the general formula R–N]C]O which does not occur naturally in the environment. At room temperature it can be a liquid or crystal. It is miscible with alcohol, diglycol, monoethyl ether, ether, acetone, carbon tetrachloride, benzene, chlorobenzene, kerosene, and olive oil; however, it may react violently with alcohol, water, acid, bases, and strong alkaline materials and tertiary amines and generate enough heat to self-ignite and release toxic combustion products. NDI is not readily biodegradable; however, it reacts with water and most acids producing unstable carbonic acids, which subsequently decarboxylate yielding relatively chemically inert and insoluble polymeric urea. While these polyureas are persistent, studies have indicated that they pose virtually no potential for adverse impacts on the aquatic environment. Due to hydrolysis in water, bioaccumulation of NDI is not expected. Since the hydrolysis products formed are irritants, there is a potential for inhalation exposure. The degree stability is a function of humidity.
Toxicity evaluation
The toxicological properties of isocyanates are attributed to the –N=C=O group. It is thought to react vigorously and exothermically with water forming an unstable carbamic acid that dissociates to form a primary amine with liberation of CO2. Hence, the primary amine will react further generating a urea derivative. Isocyanates also react readily with all organic compounds resulting in polymerization. Such reactions denature proteins, form abnormal crosslinkages, and generally disorganize the protein resulting in alteration of its normal function. This reactivity with proteins can account for its potency as a sensitizing agent. An IgE- or IgG-mediated mechanism has been proposed, but has not been definitively linked to isocyanate exposure. There is also evidence that inflammation and morphological changes of the bronchia mucosa and direct neurogenic mechanisms could be involved in the mechanics of toxicity. Thus, more than one reaction may occur in a system at a given time.
Properties of 1,5-Naphthalene diisocyanate
| Melting point: | 130°C |
| Boiling point: | 244°C (100 torr) |
| Density | 1.45 |
| vapor pressure | 0.001Pa at 25℃ |
| refractive index | 1.6000 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly) |
| form | powder to lump |
| color | White to Light yellow |
| Water Solubility | soluable |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 3173-72-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 19, Sup 7, 71) 1999 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Naphthalene, 1,5-diisocyanato-(3173-72-6) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1,5-Naphthalene diisocyanate (3173-72-6) |
Safety information for 1,5-Naphthalene diisocyanate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H330:Acute toxicity,inhalation H334:Sensitisation, respiratory H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P284:Wear respiratory protection. P405:Store locked up. P403+P233:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for 1,5-Naphthalene diisocyanate
| InChIKey | SBJCUZQNHOLYMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![5-Chloro-2-[(2,4-dichlorophenyl)sulfonyl]benzoic acid](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/5101-68-8.gif)

You may like
-
 1,5-Diisocyanatonaphthalene CAS 3173-72-6View Details
1,5-Diisocyanatonaphthalene CAS 3173-72-6View Details
3173-72-6 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8