Hexamethylene Diisocyanate
Synonym(s):Hexamethylene diisocyanate;1,6-Diisocyanatohexane;4,4′-Diisocyanato-methylenedicyclohexane;4,4′-HMDI;4,4′-Methylene-bis(cyclohexyl isocyanate)
- CAS NO.:822-06-0
- Empirical Formula: C8H12N2O2
- Molecular Weight: 168.19
- MDL number: MFCD00002047
- EINECS: 212-485-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-10 11:56:18
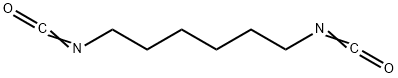
What is Hexamethylene Diisocyanate?
Description
This diisocyanate compound is used in the manufacture of various polyurethane products: elastic and rigid foams, paints, lacquers, adhesives, bin ding agents, synthetic rubbers, and elastomeric fibers.
Chemical properties
Hexamethylene diisocyanate is a colorless liquid. Sharp, irritating odor.
Chemical properties
Hexamethylene diisocyanate is a liquid with a volatility of the same order as that of tolylene diisocyanate. It is respiratory irritant and also has powerful effects on the skin and eyes.
The Uses of Hexamethylene Diisocyanate
Hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI) is one of the most common aliphatic disocyanates, It is a monomer used in the production of polyurethane foams and exceptionally high-quality coatings, and is found in some industrial paints and spray painting operations. It is a compound which reacts readily with water and alcohols (Von Burg 1993). It has a vapor pressure of 0.05 mm Hg at room temperature, but can be present in aerosol form allowing a potentially higher exposure to individuals. The HDI-BT trimer is often present for similar industrial uses. It would be expected to have a lower vapor pressure; however, the aerosol form can also be present, allowing potentially higher exposure of HDI-BT to individuals. Hexamethylene diisocyanate reacts slowly with water to form carbon dioxide (HSDB 1996). The base-catalyzed reaction of Hexamethylene diisocyanate with alcohols should be carried out in inert solvents; the reaction may occur with explosive violence in the absence of solvents (NFPA 1994).
The Uses of Hexamethylene Diisocyanate
1,6-Hexamethylenediisocyanate is a chemical intermediate used in the production of urethane products.
The Uses of Hexamethylene Diisocyanate
Cross-linking agent (hardener) in the production of polyurethane materials such as car paints, dental materials, and contact lenses
Definition
ChEBI: A diisocyanate compound with the two isocyanates linked by a hexane-1,6-diyl group.
Preparation
Hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI) is prepared by the phosgenation of hexamethylenediamine (section lO.2.2(b)):
H2N-(CH2)6-NH2--COCl2-->OCN-(CH2)6-NCO
Hexamethylene diisocyanate is a liquid with a volatility of the same order as that of tolylene diisocyanate. It is respiratory irritant and also has powerful effects on the skin and eyes. Hexamethylene diisocyanate was one of the first diisocyanates utilized for making polyurethanes, being used to prepare fibres and moulding compounds. These applications are no longer of importance but hexamethylene diisocyanate now finds use mainly in coatings which are more light stable than those based on aromatic isocyanates.
What are the applications of Application
Hexamethylene diisocyanate is an aliphatic diisocyanate monomer typically used to produce oligomers and prepolymers that when combined with a polyol produce light-stable polyurethane.
Highly reactive 1,6-hexamethylene diisocyanate (HMDI) was used to synthesize lactic acid polymers from oligomers by the addition of 2,2′-bis(2-oxazoline) (BOX) as chain extenders. Self-healing ability was rendered to polyurethane elastomer by synthesizing alkoxyamine-based diol and reacting it with tri-functional homopolymer of HMDI and polyethylene glycol (PEG). Plastic optical fiber (POF) was prepared by the bulk homopolymerization of HMDI catalyzed by Tin(II)-2 ethylhexanoate (SnOct).
General Description
A colorless crystalline solid. Toxic by ingestion and is strongly irritating to skin and eyes. 1,6-Diisocyanatohexane is used to make nylon.
Air & Water Reactions
Contact with moisture or temperatures over 399°F may cause polymerization. Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
1,6-Diisocyanatohexane reacts with water. Base-catalyzed reactions of 1,6-Diisocyanatohexane with alcohols may be explosively violent in the absence of diluting solvents. 1,6-Diisocyanatohexane is incompatible with strong bases, amines, acids and strong oxidizers. 1,6-Diisocyanatohexane is also incompatible with metal compounds and surface active materials. .
Hazard
Combustible.
Health Hazard
HDI is moderately toxic by inhalation. Inhumans the acute toxic symptoms could bewheezing, dyspnea, sweating, coughing, dif-ficulty in breathing, and insomnia. In addition, this compound can produce irritationof the skin, eyes, nose, and respiratory tract.Chronic exposure may cause obstruction ofairways and asthma.
The lethal concentration for rats frominhalation of this compound for 4 hourswas 60 mg/m3. The oral toxicity of thiscompound was found to be low in testanimals. The toxicity order was much higherwhen given intravenously.
LD50 value, oral (mice): 350 mg/kg
LD50 value, intravenous (mice): 5.6 mg/kg
There is no report of any carcinogenic orteratogenic study for this compound.
Fire Hazard
Combustible material: may burn but does not ignite readily. Substance will react with water (some violently) releasing flammable, toxic or corrosive gases and runoff. When heated, vapors may form explosive mixtures with air: indoors, outdoors and sewers explosion hazards. Most vapors are heavier than air. They will spread along ground and collect in low or confined areas (sewers, basements, tanks). Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated or if contaminated with water.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Contact allergens
This diisocyanate compound is used in the manufac ture of various polyurethane products: elastic and rigid foams, paints, lacquers, adhesives, binding agents, synthetics rubbers, and elastomer fibers.
Safety Profile
Poison by inhalation and intravenous routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion and skin contact. Potentially explosive reaction with alcohols + base. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. See also CYANATES.
Potential Exposure
Used to make other chemicals, coat ings, and polyurethane. It is also used as a hardener in automobile and airplane paints.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek med-ical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and washimmediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, includ-ing resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.Medical observation is recommended for 24-48 h afterbreathing overexposure, as pulmonary edema may bedelayed. As first aid for pulmonary edema, a doctor orauthorized paramedic may consider administering a cortico-steroid spray.
Environmental Fate
HDI is not readily soluble (low mg l-1 range) in water. However, upon contact with water, reactivity is rapid with a half-life of 0.23 h at 23 ℃. This nonhomogeneous reaction is expected to produce principally polyureas. In the occupational environment, an aerosol can be formed by nebulization; however, with a vapor pressure of 0.007 hPa, HDI is expected to exist in the ambient atmosphere in its vapor state. As a vapor, HDI is expected to degrade in the atmosphere by reaction with hydroxyl radicals (half-life approximately 2 days). In direct contact with water, its rapid hydrolysis reduces the likelihood for HDI to bioaccumulate in the aquatic compartment or transfer to groundwater. Therefore, the rapid hydrolysis in an aquatic environment and relatively rapid degradation in atmosphere limits the ability of this substance to be bioaccumulative or persistent.
Storage
Color Code- Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with thischemical you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. Before entering confined space where this chemicalmay be present, check to make sure that an explosive con-centration doesnot exist. Hexamethylene diisocyanateshould be stored away from moisture or water. This contactwill causeit to polymerize? andIexplode its container.Hexamethylene diiso-cyanate must be stored to avoid con-tact with amines, carboxylic acids, strong bases, and alco-hols since violent reactions occur. Store in tightly closedcontainers in a cool, well-ventilated area at temperaturesbelow 93℃/200°F.
Shipping
UN2281 Hexamethylene diisocyanate, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Toxicity evaluation
Toxicity predominantly results from direct interaction of HDI with tissues or macromolecules at the portal of entry. HDI reacts with biologic macromolecules containing nucleophilic –NH, –SH, –OH, or –COOH groups, and these interactions are thought to account for acute irritation to skin and mucus membranes, sensory irritation, and dermal sensitization. Less clear is the etiology of HDI-induced occupational asthma. A number of mechanisms, including immunologic, neurologic, and pharmacologic, have been postulated without a clear resolution. Overall, these mechanisms account for the principal effects associated with HDI that lead to toxicity at the portal of entry with no evidence of primary systemic organ toxicity.
Incompatibilities
May form explosive mixture with air. Isocyanates are highly flammable and reactive with many compounds, even with themselves. Incompatible with oxi dizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, per chlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Reaction with moist air, water or alcohols may form amines and insoluble polyureas and react exothermically, releasing toxic, corrosive or flamma ble gases, including carbon dioxide; and, at the same time, may generate a violent release of heat increasing the con centration of fumes in the air. Incompatible with amines, aldehydes, alkali metals, ammonia, carboxylic acids, capro lactum, alkaline materials, glycols, ketones, mercaptans, hydrides, organotin catalysts, phenols, strong acids, strong bases, strong reducing agents such as hydrides, urethanes, ureas. Elevated temperatures or contact with acids, bases, tertiary amines, and acyl-chlorides may cause explosive polymerization. Attacks some plastics, rubber and coatings. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. May accumulate static electrical charges, and may cause ignition of its vapors. Temperatures above 200℃ can cause polymerization. Attacks copper.
Waste Disposal
Disposal is by chemical incineration of HDIsolution in a combustible solvent.
Properties of Hexamethylene Diisocyanate
| Melting point: | -55°C |
| Boiling point: | 82-85 °C/0.1 mmHg |
| Density | 1.047 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.)
1.047 g/mL at 20 °C |
| vapor pressure | 0.05 mm Hg ( 25 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 248 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Clear colorless to slightly yellow |
| Specific Gravity | 1.05 |
| explosive limit | 0.9-9.5%(V) |
| Water Solubility | Reacts |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| BRN | 956709 |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 0.0343 mg/m3 (0.005 ppm)
(ACGIH). |
| Stability: | Stable. Moisture sensitive. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases, amines, acids. May react explosively with alcohols in the presence of base without a diluting solvent. Heating above 200 C may cause polymerization. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 822-06-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 1,6-Hexamethylene diisocyanate(822-06-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Hexamethylene-1,6-diisocyanate (822-06-0) |
Safety information for Hexamethylene Diisocyanate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H330:Acute toxicity,inhalation H334:Sensitisation, respiratory H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Hexamethylene Diisocyanate
| InChIKey | RRAMGCGOFNQTLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Hexamethylene Diisocyanate manufacturer
Triveni Interchem Private Limited (Group Of Triveni Chemicals)
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 1,6-Diisocyanatohexane CAS 822-06-0View Details
1,6-Diisocyanatohexane CAS 822-06-0View Details
822-06-0 -
 1,6-Diisocyanatohexane CAS 822-06-0View Details
1,6-Diisocyanatohexane CAS 822-06-0View Details
822-06-0 -
 Hexamethylene Diisocyanate CAS 822-06-0View Details
Hexamethylene Diisocyanate CAS 822-06-0View Details
822-06-0 -
 Hexamethylene diisocyanate, 98% CAS 822-06-0View Details
Hexamethylene diisocyanate, 98% CAS 822-06-0View Details
822-06-0 -
 Hexamethylene diisocyanate CAS 822-06-0View Details
Hexamethylene diisocyanate CAS 822-06-0View Details
822-06-0 -
 Hexamethylene diisocyanate CAS 822-06-0View Details
Hexamethylene diisocyanate CAS 822-06-0View Details
822-06-0 -
 Hexamethylene diisocyanate CAS 822-06-0View Details
Hexamethylene diisocyanate CAS 822-06-0View Details
822-06-0 -
 Liquid Hexamethylene Diisocyanate, For Bacterial Infections, Packaging Type: DrumView Details
Liquid Hexamethylene Diisocyanate, For Bacterial Infections, Packaging Type: DrumView Details
822-06-0
