1,3-Dioxolane
Synonym(s):1,3-Dioxacyclopentane, Formaldehyde ethylene acetal, Ethylene glycol methylene ether;1,3-Dioxolane;Ethylene glycol methylene ether;Formaldehyde ethylene acetal
- CAS NO.:646-06-0
- Empirical Formula: C3H6O2
- Molecular Weight: 74.08
- MDL number: MFCD00003207
- EINECS: 211-463-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:53
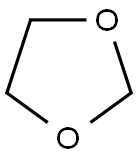
What is 1,3-Dioxolane?
Description
Dioxolane is a water-white liquid. Molecularweight= 74.09; Boiling point = 74℃; Flash point = 2℃(oc). Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704 M RatingSystem): Health 2, Flammability 4, Reactivity 2. Soluble inwater
Chemical properties
Colourless Liquid. Miscible with water, soluble in alcohol, ether and benzene. The azeotrope formed with water, the azeotrope is 70-73°C, and the water content is 6.7%. Decolorize bromine water.
The Uses of 1,3-Dioxolane
1,3-Dioxolane is an intermediate for the preparation of Acyclovir (A192400). Also, 1,3-Dioxolane is used in the synthesis of new Vandetanib (V097100) analogs.
What are the applications of Application
1,3-Dioxolane is used in the synthesis of new Vandetanib (V097100) analogs
Definition
ChEBI: 1,3-dioxolane is a cyclic acetal that is pentane in which the carbon atoms at positions 1 and 3 are replaced by oxygen atoms respectively. It is a dioxolane and a cyclic acetal.
What are the applications of Application
1,3-Dioxolane (DOXL) is a cyclic ether. It is a green solvent. It undergoes reaction with C60 to afford an epoxide and 1,3-dioxolane derivative. Reaction has been reported to proceed via a diradical mechanism. A mixture of tetra(ethylene glycol) dimethyl ether (TEGDME) and DOXL has been used to compose the binary electrolyte for use in lithium-sulfur battery. Its efficacy as a solvent in a non-aqueous redox flow battery system has been tested. 1,3-Dioxolane may be used in the fabrication of batteries and capacitors. It may be used as one of the co-solvent to prepare the electrolyte for lithium-sulfur batteries.
General Description
A clear colorless liquid. Flash point 35°F. Slightly denser than water. Vapors heavier than air.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. When exposed to air 1,3-Dioxolane undergoes autooxidation with formation of peroxides. In the distillation process peroxides will concentrate causing violent explosion. Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Ethers, such as 1,3-Dioxolane, can act as bases. They form salts with strong acids and addition complexes with Lewis acids. The complex between diethyl ether and boron trifluoride is an example. Ethers may react violently with strong oxidizing agents. In other reactions, which typically involve the breaking of the carbon-oxygen bond, ethers are relatively inert.
Health Hazard
Inhalation or contact with material may irritate or burn skin and eyes. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Vapors may cause dizziness or suffocation. Runoff from fire control may cause pollution.
Health Hazard
The acute inhalation and oral toxicity of1,3-dioxolane is low in test animals. Thevapor is irritant to eyes and respiratory tract.Application of the liquid produced severeirritation in rabbits’ eyes and mild action onthe animals’ skin. The information on thetoxicity of this compound in humans is notknown.
The inhalation LC50 value of 4-hour exposurein rats is in the range of 20,000 mg/m3,and the oral LD50 is 3000 mg/kg (NIOSH1986).
Fire Hazard
HIGHLY FLAMMABLE: Will be easily ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Vapors may form explosive mixtures with air. Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Most vapors are heavier than air. They will spread along ground and collect in low or confined areas (sewers, basements, tanks). Vapor explosion hazard indoors, outdoors or in sewers. Runoff to sewer may create fire or explosion hazard. Containers may explode when heated. Many liquids are lighter than water.
Flammability and Explosibility
Highly flammable
Industrial uses
1,3-Dioxolane is used to dissolve a wide spectrum of polymeric materials such as acrylates, alkyds, cellulosics, epoxies, polycarbonates, polyesters, urethanes, and vinyl resins. In many cases, 1,3-dioxolane solvent can replace the chlorinated solvents that were used previously to dissolve many of these polymers. The excellent solvency of 1,3-dioxolane for polymeric compositions makes this cyclic ether a valuable component in paint remover formulations. 1,3-Dioxolane is used to treat polyester fibers for improved dye retention, application of cross-linking agents to cellulosic fibers, and bonding of acrylonitrile polymers. 1,3-Dioxolane is used in metal working and electroplating formulations, as a complexing solvent for organometallic and inorganic salts, and in the preparation of lithium battery electrolyte solutions. 1,3-Dioxolane is a valuable reactant in the polymerization reactions to produce polyacetals. Polymerization reactions of dioxolane with itself or with aldehydes and ethers are catalyzed by a Lewis acid to yield the polyacetal polymers. The methylene group (CH2) bonded to the two oxygen atoms in dioxolane is susceptible to radical abstraction of a hydrogen atom and the resultant dioxolane radical species can be added across various double bond configurations.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Mildly toxic by skin contact and inhalation. A shin and severe eye irritant. Mutation data reported. A very dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat or flame; can react with oxidizers. Used in lithium batteries. Potentially explosive reaction with lithium perchlorate. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Potential Exposure
It is a low-boiling solvent and used forextraction of oils, fats, waxes, dyes, and cellulose derivatives.May be used as a cross-linking agent in phenolic resins.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, getmedical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit
Storage
Color Code—Red: Flammability Hazard: Store ina flammable liquid storage area or approved cabinet awayfrom ignition sources and corrosive and reactive materials.Prior to working with this chemical you should be trainedon its proper handling and storage. Store in tightly closedcontainers in a cool, well-ventilated area away from oxidizers and reducing agents. Where possible, automaticallypump liquid from drums or other storage containers to process containers.
Shipping
This compound requires a shipping label of“FLAMMABLE LIQUID.” It falls in Hazard Class 3 andPacking Group II
Purification Methods
Dry it with solid NaOH, KOH or CaSO4, and distil it from sodium or sodium amalgam. Barker et al. [J Chem Soc 802 1959] heated 34mL of dioxalane under reflux with 3g of PbO2 for 2hours, then cooled and filtered. After adding xylene (40mL) and PbO2 (2g) to the filtrate, the mixture is fractionally distilled. Addition of xylene (20mL) and sodium wire to the main fraction (b 70-71o) led to a vigorous reaction, following which the mixture was again fractionally distilled. Xylene and sodium additions are made to the main fraction (b 73-74o) before it is finally distilled. [Beilstein 19/1 V 6.]
Incompatibilities
Forms explosive mixture with air. Contactwith oxidizers may cause fire and explosion hazard.
Properties of 1,3-Dioxolane
| Melting point: | -95 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 75-76 °C/1.013 hPa |
| Density | 1.06 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 2.6 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 70 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 35 °F |
| storage temp. | Store at <= 20°C. |
| solubility | 1000g/l soluble |
| form | Liquid |
| color | White to off-white |
| explosive limit | 2.1-20.5%(V) |
| Water Solubility | SOLUBLE |
| BRN | 102453 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 20 ppm |
| Stability: | Below 4°C |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 646-06-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 1,3-Dioxolane(646-06-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1,3-Dioxolane (646-06-0) |
Safety information for 1,3-Dioxolane
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H360:Reproductive toxicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for 1,3-Dioxolane
| InChIKey | WNXJIVFYUVYPPR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
1,3-Dioxolane manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 1,3-Dioxolane, Stabilized CAS 646-06-0View Details
1,3-Dioxolane, Stabilized CAS 646-06-0View Details
646-06-0 -
 1,3-Dioxolane, Stabilized CAS 646-06-0View Details
1,3-Dioxolane, Stabilized CAS 646-06-0View Details
646-06-0 -
 1,3-Dioxolane, Stabilized CAS 646-06-0View Details
1,3-Dioxolane, Stabilized CAS 646-06-0View Details
646-06-0 -
 1 3 Dioxolane CASView Details
1 3 Dioxolane CASView Details -
 1,3 DioxolaneView Details
1,3 DioxolaneView Details
646-06-0 -
 1,3 DioxolaneView Details
1,3 DioxolaneView Details
646-06-0 -
 1 3 DioxolaneView Details
1 3 DioxolaneView Details
646-06-0 -
 Liquid Grade Standard: Laboratory Grade 1,3-Dioxolane - 13D / CAS No.646-06-0View Details
Liquid Grade Standard: Laboratory Grade 1,3-Dioxolane - 13D / CAS No.646-06-0View Details
646-06-0
