Selenium dioxide
Synonym(s):NSC 56753;Selenious anhydride, Selenium(IV) oxide;Selenium dioxide;Selenium oxide
- CAS NO.:7446-08-4
- Empirical Formula: O2Se
- Molecular Weight: 110.96
- MDL number: MFCD00003562
- EINECS: 231-194-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
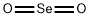
What is Selenium dioxide ?
Chemical properties
Yellowish white to reddish powder or crystals. It is soluble in water and hygroscopic and absorbs moisture or water from the air. Selenium oxide is incompatible with strong oxidising agents, reducing agents, strong acids, ammonia, organics, and phosphorus trichloride.
Chemical properties
Selenium dioxide is white to slightly reddish crystalline solid or yellow liquid which forms a yellowgreen vapor. It has a sour and pungent odor. Odor threshold in air50.0002 milligram per cubic meter.
The Uses of Selenium dioxide
Selenium dioxide (SeO2) is used as an oxidizing agent, as a catalyst, and as an antioxidant for lubricating oils and grease.
The Uses of Selenium dioxide
In the manufacture of other selenium compounds; as a reagent for alkaloids; as oxidizing agent: L. F. Fieser, M. Fieser, Reagents for Organic Chemistry vol. 1 (New York, Wiley, 1967) p 992.
The Uses of Selenium dioxide
It is used in the manufacture of other selenium compounds. Selenium dioxide is an oxidizing agent mostly used in the allylic oxidation of alkenes to produce allylic alcohols. It is used in creating colorless glass and toner in photographic developing.
Production Methods
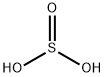
While selenium dioxide, SeO2, can be produced by direct reaction of the element with oxygen activated by passage through HNO3, the compound is easily made by heating selenious acid, H2SeO3. Selenium dioxide sublimes at 315–317 °C (599–603 °F), and is readily reduced by SO2 to elemental selenium.
General Description
A white or creamy-white volatile lustrous crystal or crystalline powder with a pungent sour smell. Melting point 340 deg C. Density 3.954 g / cm3 . Toxic by ingestion and inhalation.
Air & Water Reactions
In presence of water will corrode most metals [USCG, 1999]. Readily soluble in water forming selenious (selenous) acid.
Reactivity Profile
Inorganic oxidizing agents, such as Selenium dioxide , react with reducing agents to generate heat and products that may be flammable, combustible, or otherwise reactive. Selenium dioxide reacts with water, particularly hot water, to give selenious (selenous) acid, a weak acid that is corrosive. Stable to light and heat. Rapidly absorbs dry hydrogen fluoride, hydrogen chloride, hydrogen bromide to form the corresponding selenium oxohalide. A good oxidizing agent. Reacts oxidatively with ammonia to form dinitrogen gas and selenium [Merck]. Oxidizes many organic substances.
Hazard
Toxic by inhalation, ingestion, and skin absorption.
Health Hazard
Absorption of selenium may be demonstrated by presence of the element in the urine and by a garlic-like odor of the breath. Inhalation of dust can cause bronchial spasms, symptoms of asphyxiation, and pneumonitis. Acute symptoms of ingestion include sternal pain, cough, nausea, pallor, coated tongue, gastrointestinal disorders, nervousness, and conjunctivitis. Contact with eyes causes irritation.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Sublimes and forms toxic vapors when heated in fire.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Potential Exposure
Selenium dioxide is used in the manufacture of selenium compounds, a reagent for alkaloids; an oxidizing agent; in paint and ink pigments; in metal “blueing” and etching; as a chemical catalyst; in photographic toners; in electric and photoelectric components; and others.
Shipping
UN3283Selenium compound, solid, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous material, Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
Purify it by sublimation at 315o, or by solution in HNO3, precipitation of selenium which, after standing for several hours or boiling, is filtered off, then re-oxidised by HNO3 and cautiously evaporated to dryness below 200o. The dioxide is dissolved in H2O and again evaporated to dryness. In H2O it forms selenious acid (see selenious acid above). Its solubility in H2O is 70%w/w at 20o, and it is soluble in EtOH. [Waitkins & Clark Chem Rev 36 235 1945, Fehér in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry (Ed Brauer) Academic Press Vol I p 421 1963.]
Incompatibilities
Selenium dioxide is and inorganic oxidizer; reacts, possibly violently, with reducing agents such as hydrides, nitrides, alkali metals, and sulfides. Contact with strong acids may cause release of toxic hydrogen selenide gas. Water solution is a medium-strong acid (selenious acid). Rapidly absorbs dry hydrogen fluoride, hydrogen bromide, hydrogen chloride, to form corresponding selenium oxohalides. Reacts with many substances producing toxic selenium vapors. Attacks many metals in presence of water.
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform to EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal.
Properties of Selenium dioxide
| Melting point: | 315 °C (subl.)(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 684.9 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 4.81 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 157 °C) |
| refractive index | nD20 <1.76 |
| Flash point: | 315°C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| form | powder |
| Specific Gravity | 3.95 |
| color | white |
| PH | 2 (10g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Water Solubility | 38.4 g/100 mL (14 ºC) |
| Sublimation | 315 ºC |
| Merck | 14,8434 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.2 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 1 mg/m3; TWA 0.2 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with organic materials, strong acids, ammonia, nitric acid, halogen acids. Protect from moisture. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7446-08-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Selenium dioxide(7446-08-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Selenium dioxide (7446-08-4) |
Safety information for Selenium dioxide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. |
Computed Descriptors for Selenium dioxide
Selenium dioxide manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
ARRAKIS INDUSTRIES LLP
New Products
4-Piperidinemethanol Ethyl 2,4-Dihydroxy-6-methylnicotinate Ethyl isonicotinate 3-pyridine methanol N-Methyl 4-chloro-pyridine-2-carboxamide 5,6 Dimethoxy-1-indanone 3-Iodophenylacetic acid 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole N Ethylmethylamine Ethyl Methanesulfonate N N' DimethylEthylenediamine Lead II Bromide Variamine Blue B Diazonium salt N N N'Trimethyl ethylenediamine Radiator Flux Zinc Chloride Solution (All Grades) Levetiracetam Fmoc-Gln-OH Boc Phenyl Alanine Alpha Lipoic Acid*Related products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Selenium(IV) oxide CAS 7446-08-4View Details
Selenium(IV) oxide CAS 7446-08-4View Details
7446-08-4 -
 Selenium(IV) oxide CAS 7446-08-4View Details
Selenium(IV) oxide CAS 7446-08-4View Details
7446-08-4 -
 Selenium(IV) oxide CAS 7446-08-4View Details
Selenium(IV) oxide CAS 7446-08-4View Details
7446-08-4 -
 Selenium Dioxide pure CAS 7446-08-4View Details
Selenium Dioxide pure CAS 7446-08-4View Details
7446-08-4 -
 Selenium dioxide CASView Details
Selenium dioxide CASView Details -
 SELENIUM DIOXIDE 99%View Details
SELENIUM DIOXIDE 99%View Details -
 SELENIUM DIOXIDE (SUBLIMED) Extra Pure CASView Details
SELENIUM DIOXIDE (SUBLIMED) Extra Pure CASView Details -
 Selenium ICP standard CASView Details
Selenium ICP standard CASView Details
