1,3-Dichlorobenzene
Synonym(s):1,3-Dichlorobenzene
- CAS NO.:541-73-1
- Empirical Formula: C6H4Cl2
- Molecular Weight: 147
- MDL number: MFCD00000573
- EINECS: 208-792-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32
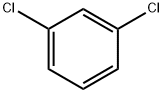
What is 1,3-Dichlorobenzene?
Chemical properties
There are three isomeric forms of dichlorobenzene (DCB): m-DCB is a flammable liquid and vapor.
Physical properties
1,3-Dichlorobenzene is a clear, colorless liquid with a disinfectant or musty-type odor. Soluble in alcohol, ether, insoluble in water. At 40 °C, the average odor threshold concentration and the lowest concentration at which an odor was detected were 170 and 177 μg/L, respectively. At 25 °C, the lowest concentration at which a taste was detected was 190 μg/L, respectively (Young et al., 1996).
The Uses of 1,3-Dichlorobenzene
1,3-Dichlorobenzene is used in organic synthesis that can synthesize fungicides imazalil, propiconazole, epiconazole, and insecticides insectaphos. It is also used in the synthesis of 1,2-diaminobenzene, in addition, it is also used as a solvent in the fields of dyes, medicine, resin, rubber and so on.
The Uses of 1,3-Dichlorobenzene
1,3-Dichlorobenzene is used in medicine, and dyes. And it is also used to study the effect of solvent vapor pressure on the vertical nanowire of C60 molecules1. 1,3-Dichlorobenzene, a chlorinated aromatic hydrocarbon, can be detected in environmental samples using an advanced Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy-attenuated total reflectance (FTIR-ATR) sensor.
Definition
ChEBI: 1,3-dichlorobenzene is a dichlorobenzene carrying chloro substituents at positions 1 and 3. Used as a fumigant, insecticide, and chemical intermediate.
What are the applications of Application
1,3-Dichlorobenzene was used to study the effect of solvent vapor pressure on the vertical nanowire of C60 molecules. 1,3-Dichlorobenzene, a chlorinated aromatic hydrocarbon, can be detected in environmental samples using an advanced Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy-attenuated total reflectance (FTIR-ATR) sensor.
Preparation
1,3-Dichlorobenzene is prepared from o-chloroaniline through diazotization and displacement reaction.
Add o-chloroaniline and hydrochloric acid into the reaction pot, mix evenly below 25°C, cool to 0°C, drop in sodium nitrite solution, control the temperature at 0-5°C, stop adding when the potassium iodide starch indicator turns blue, and obtain diazonium salt solution. Then add the diazonium salt solution into the hydrochloric acid solution of cuprous chloride at 0~5℃, stir well, heat up to 60~70℃ and react for 1h, after cooling, let stand for stratification, and use 5% sodium hydroxide for the oil layer. Repeated washing with water, dehydration with anhydrous calcium chloride, fractional distillation, and collection of fractions at 177-183 °C to obtain the product 1,3-dichlorobenzene.
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 48, p. 250, 1983 DOI: 10.1021/jo00150a020
General Description
Colorless liquid. Sinks in water.
Air & Water Reactions
1,3-Dichlorobenzene is sensitive to moisture. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
1,3-Dichlorobenzene is incompatible with oxidizing agents and aluminum and its alloys. Above the flash point, explosive vapor-air mixtures may be formed.
Health Hazard
INHALATION: Causes headache, drousiness, unsteadiness. Irritating to mucous membranes. EYES: Severe irritation. SKIN: Severe irritation. INGESTION: Irritation of gastric mucosa, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramps and cyanosis.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Irritating vapors including hydrogen chloride are produced.
Flammability and Explosibility
Flammable
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by intraperitoneal route. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl-. See also oDICHLOROBENZENE and p DICHLOROBENZENE.
Potential Exposure
The major uses of o-DCB are as a process solvent in the manufacturing of toluene diisocyanate and as an intermediate in the synthesis of dyestuffs, herbicides, and degreasers. p-Dichlorbenzene is used primarily as a moth repellant, a mildew control agent; space deodorant; and in insecticides, which accounts for 90% of the total production of this isomer. Information is not available concerning the production and use of m-DCB. However, it may occur as a contaminant of o-or p-DCB formulations. Both o-and p-isomers are produced almost entirely as by-products during the production of monochlorobenzene
Environmental Fate
Biological. When 1,3-dichlorobenzene was statically incubated in the dark at 25 °C with yeast
extract and settled domestic wastewater inoculum, significant biodegradation with gradual
acclimation was followed by a deadaptive process in subsequent subcultures. At a concentration of
5 mg/L, 59, 69, 39, and 35% losses were observed after 7, 14, 21, and 28-d incubation periods,
respectively. At a concentration of 10 mg/L, percent losses were virtually unchanged. After 7, 14,
21, and 28-d incubation periods, percent losses were 58, 67, 31, and 33, respectively (Tabak et al.,
1981).
Photolytic. The sunlight irradiation of 1,3-dichlorobenzene (20 g) in a 100-mL borosilicate
glass-stoppered Erlenmeyer flask for 56 d yielded 520 ppm trichlorobiphenyl (Uyeta et al., 1976).
Chemical/Physical. Anticipated products from the reaction of 1,3-dichlorobenzene with
atmospheric ozone or OH radicals are chlorinated phenols, ring cleavage products, and nitro
compounds (Cupitt, 1980). Based on an assumed base-mediated 1% disappearance after 16 d at 85
oC and pH 9.70 (pH 11.26 at 25 oC), the hydrolysis half-life was estimated to be >900 yr
(Ellington et al., 1988). 1,3-Dichlorobenzene (0.17–0.23 mM) reacted with OH radicals in water
(pH 8.7) at a rate of 5.0 x 109/M·sec (Haag and Yao, 1992).
Shipping
m-DCB: UN2810 Toxic liquids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. United States DOT Regulated Marine Pollutant. UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solis, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical NameRequired. UN3082 Environmentally hazardous substances, liquid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required
Purification Methods
Wash it with aqueous 10% NaOH, then with water until neutral, dry and distil it. Conductivity material (ca 10-10 mhos) has been prepared by refluxing over P2O5 for 8hours, then fractionally distilling, and storing with activated alumina. m-Dichlorobenzene dissolves rubber stoppers. [Beilstein 5 IV 657.]
Incompatibilities
For o-DCB and m-DCB: acid fumes, chlorides, strong oxidizers; hot aluminum, or aluminum alloys. For p-DCB: Strong oxidizers; although, incompatibilities for this chemical may also include other materials listed for o-DCB.
Waste Disposal
Incineration, preferably after mixing with another combustible fuel. Care must be exercised to assure complete combustion to prevent the formation of phosgene. An acid scrubber is necessary to remove the halo acids produced. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal
Properties of 1,3-Dichlorobenzene
| Melting point: | -25--22 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 172-173 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.288 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 5 mm Hg ( 38.8 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 146 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Difficult to mix. |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Clear colorless to slightly yellow |
| Odor | Pleasant odor |
| Water Solubility | 0.0123 g/100 mL (25 ºC) |
| FreezingPoint | -24℃ |
| Merck | 14,3055 |
| BRN | 956618 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 2.14 at 20.00 °C (inert gas stripping, Hovorka and Dohnal, 1997) |
| Dielectric constant | 5.0 |
| Stability: | Stability Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, aluminium, aluminium alloys. Moisture-sensitive. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 541-73-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzene, 1,3-dichloro-(541-73-1) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 73) 1999 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | m-Dichlorobenzene (541-73-1) |
Safety information for 1,3-Dichlorobenzene
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. |
Computed Descriptors for 1,3-Dichlorobenzene
| InChIKey | ZPQOPVIELGIULI-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
1,3-Dichlorobenzene manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Aarti Industries Limited (AIL)
LANXESS India Pvt. Ltd.
Chirag Organics Pvt Ltd
ARRAKIS INDUSTRIES LLP
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 1,3-Dichlorobenzene 98%View Details
1,3-Dichlorobenzene 98%View Details -
 541-73-1 99%View Details
541-73-1 99%View Details
541-73-1 -
 1, 3-Dichlorobenzene, 98% CAS 541-73-1View Details
1, 3-Dichlorobenzene, 98% CAS 541-73-1View Details
541-73-1 -
 1,3-Dichlorobenzene extrapure CAS 541-73-1View Details
1,3-Dichlorobenzene extrapure CAS 541-73-1View Details
541-73-1 -
 m-Dichlorobenzene CAS 541-73-1View Details
m-Dichlorobenzene CAS 541-73-1View Details
541-73-1 -
 1,3-Dichlorobenzene CAS 541-73-1View Details
1,3-Dichlorobenzene CAS 541-73-1View Details
541-73-1 -
 Meta Di Chloro Banzene CAS 541-73-1View Details
Meta Di Chloro Banzene CAS 541-73-1View Details
541-73-1 -
 1,3-DICHLOROBENZENE For Synthesis CAS 541-73-1View Details
1,3-DICHLOROBENZENE For Synthesis CAS 541-73-1View Details
541-73-1