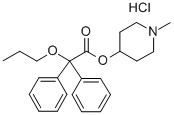
(1-Methyl-4-piperidyl) 2,2-diphenyl-2-propoxy-acetate
- CAS NO.:60569-19-9
- Empirical Formula: C23H29NO3
- Molecular Weight: 367.48
- MDL number: MFCD00865259
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-28 23:16:16

What is (1-Methyl-4-piperidyl) 2,2-diphenyl-2-propoxy-acetate?
Absorption
Propiverine is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract with maximum plasma concentrations attained after 2.3 hours. the mean absolute bioavailability of mictonorm 15 mg tablets (propiverine) is 40.5 %. It undergoes heavy first-pass metabolism in the liver .
Toxicity
The most common adverse reactions reported in patients treated with propiverine include dry mouth, headache, accommodation disorder, constipation, abdominal pain, dyspepsia and fatigue .
Propiverine may cause drowsiness and blurred vision. This may impair the ability to exert activities that require mental alertness such as operating a motor vehicle or other machinery, or to perform hazardous work while taking this drug .
There have been reports of QT interval prolongation with antimuscarinic medications in the same class of drugs of propiverine hydrochloride. Some drugs that may cause QT/QTc interval prolongation may increase the risk of a rare, but serious ventricular arrhythmia called torsades de pointes. Patients at risk for QT/QTc interval prolongation, such as those with diagnosed heart failure, long QT syndrome, recent significant hypokalemia episodes or receiving other drugs known to prolong QT/QTc, should be closely monitored while treated with propiverine. Patients who experience prolonged QT/QTc or symptoms of possible arrhythmias including dizziness, palpitations or fainting should be electrocardiographically evaluated and monitored for electrolyte disturbances .
Propiverine, like other anticholinergics, induces mydriasis. Therefore, the risk to induce acute angle-closure glaucoma in individuals predisposed with narrow angles of the anterior chamber may be increased. Drugs of this class, including propiverine, have been reported to induce or precipitate acute angle-closure glaucoma .
No clinical data are available on the use of propiverine in pregnant women. Studies in animals have shown reproductive toxicity .
Background
Propiverine is a widely used antimuscarinic drug with a mixed mode of action in the treatment of symptoms associated with overactive bladder (OAB) .
Overactive bladder (OAB) is a chronic condition of the lower urinary tract characterized by urinary urgency, increased frequency of urination, and nocturia (frequent waking during the night to urinate). OAB has a negative impact on quality of life and may lead to leakage and inconvenient urinary accidents , . Overactive bladder syndrome affects millions of elderly individuals in the United States and shows equal prevalence in men and women. The impact of OAB on quality of life is sometimes devastating, especially to elderly patients with other medical conditions .
Propiverine hydrochloride is a bladder detrusor muscle relaxant drug with dual antimuscarinic and calcium-modulating properties for the treatment of OAB .
Indications
Indicated for symptomatic treatment of urinary incontinence and/or increased urinary frequency and urgency in patients with overactive bladder (OAB) . Propiverine may also be used in patients with neurogenic bladder as a result of spinal cord injury .
Definition
ChEBI: Propiverine is a diarylmethane.
Pharmacokinetics
Propiverine hydrochloride inhibits abnormal contractions of bladder smooth muscle in vivo through not only its anticholinergic activity but also its concurrent calcium antagonistic activity . Through the above-mentioned mechanism, propiverine is able to relieve the symptoms of overactive bladder.
In animal models, this administration of this drug leads to a dose-dependent decrease in intravesical pressure of the bladder and an increase in bladder capacity . In patients with symptoms of OAB resulting from idiopathic detrusor muscle overactivity (IDO) or neurogenic detrusor overactivity (NDO), propiverine showed dose-dependent efficacy and tolerability .
Metabolism
The major metabolites were found to be as follows; 4-piperidyl diphenylpropoxyacetate (DM-P-4), 1-methyl-4-piperidyl benzilate (Dpr-P-4) and 1-methyl-4-piperidyl diphenyl-(2 carboxy) ethoxyacetate (ω-COOH-P-4) in the liver, Dpt-p-4, DM-P-4 in the kidney, and DM-P-4, DPr-P-4 in the lung . In the same pharmacokinetic study, All pharmacologically active compounds such as the unchanged compound, 1-methyl-4-piperidyl benzilate N-oxide (DPr-P-4 (N→O)), Dpt-p-4 and 1-methyl-4-piperidyl diphenylpropoxyacetate N-oxide (P-4 (N→O)) were present in the urinary bladder, a target organ for P-4, at higher concentrations than in the plasma .
Propiverine is metabolized by both intestinal and hepatic enzymes. The main metabolic pathway involves the oxidation of the piperidyl-N _and is mediated by _CYP 3A4 and _flavin-containing monooxygenases (FMO) _1 and 3 and results in the formation of the second main metabolite M-5, the plasma concentration of which is greater in concentration that of the parent substance propiverine. Four metabolites have been identified in the urine following propiverine ingestion; 3 them are pharmacologically active metabolites that may contribute to its therapeutic effect (M-5, M-6, M-23) .
The mean absolute bioavailability of propiverine IR 15 mg is 40.5% .
Properties of (1-Methyl-4-piperidyl) 2,2-diphenyl-2-propoxy-acetate
| Boiling point: | 484.2±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.12±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| pka | 7.76±0.10(Predicted) |
Safety information for (1-Methyl-4-piperidyl) 2,2-diphenyl-2-propoxy-acetate
Computed Descriptors for (1-Methyl-4-piperidyl) 2,2-diphenyl-2-propoxy-acetate
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 873-83-6 6-Aminouracil (or) 4-Amino-2,6- dihydroxypyrimidine, (or) 6-Amino2,4-pyrimidinediol 99%View Details
873-83-6 6-Aminouracil (or) 4-Amino-2,6- dihydroxypyrimidine, (or) 6-Amino2,4-pyrimidinediol 99%View Details
873-83-6 -
 55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 -
 N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
13162-05-5 -
 Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 207557-35-5 99%View Details
207557-35-5 99%View Details
207557-35-5 -
 2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0 -
 181228-33-1 (S)-Methyl 3-amino-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)propanote Hydrochloride (DAP-OMe. HCl) 99%View Details
181228-33-1 (S)-Methyl 3-amino-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)propanote Hydrochloride (DAP-OMe. HCl) 99%View Details
181228-33-1