1-Chloro-1,1-difluoroethane
- CAS NO.:75-68-3
- Empirical Formula: C2H3ClF2
- Molecular Weight: 100.5
- MDL number: MFCD00000779
- EINECS: 200-891-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-06 13:21:43
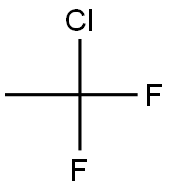
What is 1-Chloro-1,1-difluoroethane?
Description
Chlorodifluoroethane is a flammable, colorless, nearly odorless gas. Molecular weight=100.50;Specific gravity (H2O:1)=1.1; Boiling point=2 9.5℃;Freezing/Melting point=2 131℃; Flash point=flammable gas; Autoignition temperature=632℃. The explosive limits are: LEL=6.2%; UEL=17.9%. HazardIdentification (based on NFPA 704 M Rating System):Health 2, Flammability 2, Reactivity 1. Practically insolublein water; solubility=0.2% at 5℃.
Chemical properties
colourless gas
Chemical properties
Chlorodifluoroethane is a flammable, colorless gas. Nearly odorless.
Chemical properties
Chlorodifluoroethane is a liquefied gas and exists as a liquid at room temperature when contained under its own vapor pressure, or as a gas when exposed to room temperature and atmospheric pressure. The liquid is practically odorless and colorless. Chlorodifluoroethane is noncorrosive and nonirritating.
The Uses of 1-Chloro-1,1-difluoroethane
Please view www.aldrich.com/epaods regarding the EPA′s request for application information of Ozone Depleting Substances
Production Methods
Chlorodifluoroethane is prepared by the chlorination of difluoroethane in the presence of a suitable catalyst; hydrochloric acid is also formed. The chlorodifluoroethane is purified to remove all traces of water and hydrochloric acid, as well as traces of the starting and intermediate materials.
General Description
A colorless, odorless gas shipped as a liquid under own vapor pressure. Contact with the unconfined liquid may cause frostbite by evaporative cooling. Easily ignited. Vapors heavier than air. A leak may be either liquid or vapor. May asphyxiate by the displacement of air. Prolonged exposure to fire or intense heat may cause the containers to violently rupture and rocket.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable.
Reactivity Profile
1-Chloro-1,1-difluoroethane is chemically inert in many situations, but can react violently with strong reducing agents such as the very active metals and the active metals. Can react with strong oxidizing agents or weaker oxidizing agents under extremes of temperature.
Hazard
Flammable gas. Explosive limits in air 9.0– 14.8%.
Health Hazard
Vapors may cause dizziness or asphyxiation without warning. Some may be irritating if inhaled at high concentrations. Contact with gas or liquefied gas may cause burns, severe injury and/or frostbite. Fire may produce irritating and/or toxic gases.
Fire Hazard
EXTREMELY FLAMMABLE. Will be easily ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Will form explosive mixtures with air. Vapors from liquefied gas are initially heavier than air and spread along ground. CAUTION: Hydrogen (UN1049), Deuterium (UN1957), Hydrogen, refrigerated liquid (UN1966) and Methane (UN1971) are lighter than air and will rise. Hydrogen and Deuterium fires are difficult to detect since they burn with an invisible flame. Use an alternate method of detection (thermal camera, broom handle, etc.) Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Cylinders exposed to fire may vent and release flammable gas through pressure relief devices. Containers may explode when heated. Ruptured cylinders may rocket.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Chlorodifluoroethane is a hydrochlorofluorocarbon (HCFC) aerosol propellant previously used in topical pharmaceutical formula- tions. However, it is no longer permitted for use in pharmaceutical formulations because of its harmful effects on the environment. It was also generally used in conjunction with difluoroethane to form a propellant blend with a specific gravity of 1. Chlorodifluoroethane was also used in combination with chlorodifluoromethane and hydrocarbon propellants. Chlorodifluoroethane may be used as a vehicle for dispersions and emulsions.
Safety Profile
Very ddly toxic by inhalation. Mutation data reported. A very dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat, flame, or oxidzing materials. To fight fire, stop flow of gas. Can react vigorously with oxidizing materials. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Fand Cl-.
Safety
Chlorodifluoroethane is no longer permitted for use as an aerosol propellant in topical pharmaceutical formulations. It is generally regarded as an essentially nontoxic and nonirritant material.
Deliberate inhalation of excessive quantities of chlorofluorocarbon propellant may result in death, and the following ‘warning’ statements must appear on the label of all aerosols:
WARNING: Avoid inhalation. Keep away from eyes or other mucous membranes.
(Aerosols designed specifically for oral and nasal inhalation need not contain this statement.)
WARNING: Do not inhale directly; deliberate inhalation of contents can cause death.
or
WARNING: Use only as directed; intentional misuse by deliberately concentrating and inhaling the contents can be harmful or fatal.
Additionally, the label should contain the following information:
WARNING: Contents under pressure. Do not puncture or incinerate container. Do not expose to heat or store at room temperature above 120°F (498℃). Keep out of the reach of children.
In the USA, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) additionally requires the following information on all aerosols containing chlorofluorocarbons as the propellant:
WARNING: Contains a chlorofluorocarbon that may harm the public health and environment by reducing ozone in the upper atmosphere.
Potential Exposure
Chlorodifluoroethane is used in refrigerants; solvents; as a propellant in aerosol sprays; and as an intermediate in the production of highly specialized fluoropolymers.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash affected partsin warm water. Seek medical attention immediately. If thischemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure, beginrescue breathing (using universal precautions, includingresuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
If frostbite has occurred, seek medical attention immediately; do NOT rub the affected areas or flush them withwater. In order to prevent further tissue damage, do NOTattempt to remove frozen clothing from frostbitten areas. Iffrostbite has NOT occurred, immediately and thoroughlywash contaminated skin with soap and water.
storage
Chlorodifluoroethane is a nonreactive and stable material. The liquefied gas is stable when used as a propellant and should be stored in a metal cylinder in a cool, dry place.
Shipping
UN25171-Chloro-1,1-difluoroethane or Refrigerant gas R-142b, Hazard Class: 2.1; Labels: 2.1- Flammable gas. Cylinders must be transported in a secure upright position, in a well-ventilated truck. Protect cylinder and labels from physical damage. The owner of the compressed gas cylinder is the only entity allowed by federal law (49CFR) to transport and refill them. It is a violation of transportation regulations to refill compressed gas cylinders without the express written permission of the owner.
Incompatibilities
The liquefied gas poured into water may be violently explosive. This is due to the phase transition from superheated liquid to vapor. Chlorodifluoroethane is generally chemically inert; however, it can react violently with strong reducing agents such as hydrides and highly active metals. It will react with strong oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides strong oxidizing agents. It can also react with weak oxidizers under extreme temperatures. Decomposes in heat to form phosgene; HF and hydrogen chloride
Incompatibilities
Compatible with the usual ingredients used in the formulation of pharmaceutical aerosols. Chlorodifluoroethane can react vigorously with oxidizing materials.
Waste Disposal
Return refillable compressed gas cylinders to supplier
Properties of 1-Chloro-1,1-difluoroethane
| Melting point: | −131 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | −10 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.108 |
| vapor density | 3.49 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 2196 mm Hg ( 21 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.3672 (estimate) |
| explosive limit | 18% |
| Stability: | Stable. Highly flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, metals - use brass regulators, steel cylinders for storage. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 75-68-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Ethane, 1-chloro-1,1-difluoro-(75-68-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | HCFC-142b (75-68-3) |
Safety information for 1-Chloro-1,1-difluoroethane
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H220:Flammable gases H280:Gases under pressure H420:Hazardous to the ozone layer |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P410+P403:Protect from sunlight. Store in a well-ventilated place. |
Computed Descriptors for 1-Chloro-1,1-difluoroethane
New Products
2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Strontium Carbonate, 98% Wang resin Sodium hydrogenphosphate, anhydrous 2-Bromo-3-methoxyaniline hydrochloride, 95% (Custom work) 1-Bromo-4-chlorobenzene, 99% Benzocaine, 98% (R)-2-Methylpyrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (De Mepro) Ramipril Sacubitril- Valsartan Boc-his(trt)-OH Fmoc-L-Glu-OtBu Boc-L-Tyr(tBu)-OH Semi carbazide Hydrochloride 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 2-Chloromethyl-4-methyl-quinazoline Trans-4-Aminocyclohexanol [4tac] 2-[1-(Mercaptomethyl)Cyclopropyl]Acetic AcidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 15761-38-3 N-Boc-L-Alanine >98%View Details
15761-38-3 N-Boc-L-Alanine >98%View Details
15761-38-3 -
 2,4-Diamino 6-Chloro Pyrimidine 156-83-2 >98%View Details
2,4-Diamino 6-Chloro Pyrimidine 156-83-2 >98%View Details
156-83-2 -
 6485-34-3 Saccharin Calcium >98%View Details
6485-34-3 Saccharin Calcium >98%View Details
6485-34-3 -
 Boc-Gly-Gly-Phe-Gly-OH 187764-46-6 >98%View Details
Boc-Gly-Gly-Phe-Gly-OH 187764-46-6 >98%View Details
187764-46-6 -
 (S)-2-Methylpyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid HCl (MePro) 1508261-86-6 >98%View Details
(S)-2-Methylpyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid HCl (MePro) 1508261-86-6 >98%View Details
1508261-86-6 -
 Fmoc-Gly-Pro-OH >98%View Details
Fmoc-Gly-Pro-OH >98%View Details
212651-48-4 -
 18568-74-8 >98%View Details
18568-74-8 >98%View Details
18568-74-8 -
 138-41-0 P-Carboxy benzene sulfonamide >98%View Details
138-41-0 P-Carboxy benzene sulfonamide >98%View Details
138-41-0
