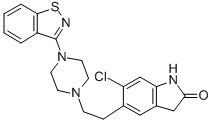
Ziprasidone Hydrochloride
- CAS NO.:122883-93-6
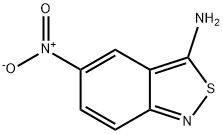
- Empirical Formula: C21H21ClN4OS
- Molecular Weight: 412.943
- MDL number: MFCD06795476
- EINECS: 602-903-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-11 08:41:34
What is Ziprasidone Hydrochloride?
Description
Both p.o. and i.m. formulations of ziprasidone were launched in Sweden for the treatment of schizophrenia and agitated psychoses. It is the sixth marketed atypical antipsychotic after clozapine, risperidone, olanzapine, sertindole and quetiapine. The synthesis of ziprasidone involves a novel one-step process for the preparation of 3-(1- piperazinyl)-1,2-benzisothiazole followed by coupling with a chlorooxindole fragment. Ziprasidone is a very potent 5-HT2A/D2 antagonist with a ratio of about 11 in favor of the serotonin receptor. It also shows very high 5-HT2c antagonistic activity, high 5-HT1A agonistic and 5-HT1D antagonistic activity, as well as moderate antagonism of α1 and H1 receptors and moderate norepinephrine and serotonin reuptake inhibition. Its complex binding profile for serotonin and dopamine receptors resulted during clinical trials in high antipsychotic efficacy with low extrapyramidal side effects and also in antidepressive action with low propensity for weight gain in opposition to other atypical and typical neuroleptics. An intramuscular formulation of ziprasidone was demonstrated to be superior to haloperidol, a conventional neuroleptic, for the short-term treatment of agitation in acutely psychotic patients. When administered orally in the fed state, this well-tolerated agent which strongly binds to plasma proteins shows a bioavailability of about 60% which is almost 2 fold greater than in the fasted state. It is transformed into 4 circulating major metabolites by different enzyme systems. The small QTc prolongation observed with ziprasidone was found to be comparable to other antipsychotic drugs and it is considered to be without significant risk.
Originator
Pfizer (US)
The Uses of Ziprasidone Hydrochloride
Ziprasidone (Geodon, Zeldox) was the fifth atypical antipsychotic to gain FDA approval. In the United States, Ziprasidone is approved for the treatment of schizophrenia, and the intramuscular injection form of ziprasidone is approved for acute agitation i
Manufacturing Process
Preparation of 5-[2-[4-(1,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)-1-piperazinyl]ethyl]-6-chloro-
1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one
A 20-gallon glass lined tank, under a nitrogen atmosphere, was charged with
33.5 liters of water and 9.4 kilograms (kg) of sodium carbonate (dense, 89.1
moles, 3.4 eq.). The resulting mixture was stirred to give a solution. To the
solution 6.4 kg of 2-chloroethyl-6-chloro-oxindole (27.8 moles, 1.06 eq.) was
charged, followed by 6.7 kg of 3-piperazinyl-1,2-benzisothiazole hydrochloride
(26.2 moles, 1.0 eq.). This was stirred and heated to reflux (100°C). After 11
hours the reaction was sampled for high pressure liquid chromatography
(HPLC) assay. The reflux was continued for another 2 hours then the reaction
was cooled to 25°C and the slurry stirred for 1 hour. The product was
observed and found to be essentially free from lumps and gummy matter. The
product was collected by filtration. A 14 liter water was added to the tank and
cooled to 12°C and then used to wash the product. The cake was pulled as
dry as possible, and the product was returned to the tank along with 40 liters
of isopropyl alcohol (IPO). This was cooled and then stirred for 2 hours and
the product was collected by filtration. The cake was washed with 13.4 liters
of fresh IPO, then dried under vacuum at 30° to 40°C. After drying, 17.3 kg
of the title compound was obtained. This was in excess of the theoretical
weight yield due to some residual carbonate in the crude product.
Recrystallization of 5-[2-[4-(1,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)-1-piperazinyl]ethyl]-6-
chloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one
To a clean and dry 100-gallon glass lined tank was charged 9.0 kg of the
material obtained above and 86 gallons of tetrahydrofuran (THF). The slurry
was heated to reflux and held for 1 hour. The hazy solution was then filtered
through a 14" sparkler precoated with filter aid and backed with a Fulflo filter
to a clean, dry, and "spec free" glass-lined tank on a lower level. The batch
was concentrated by vacuum distillation. Another 8.3 kg of the material
obtained in above was dissolved in 83 gallons of THF in the upper tank. This
was filtered to the lower tank. The tank lines and sparkler were rinsed with 10
gallons of THF. The batch was concentrated to about 22 gallons, then cooled
to 5°C and stirred for 1 hour. The product was collected by filtration. Then 20
gallons of fresh IPO were cooled in the tank and used to rinse the product
cake. The product was collected and dried under vacuum at 45°C; yielding
9.05 kg of product (83.8% yield for the coupling and recrystallization. The
product matched the spectra of a standard NMR and showed the correct
retention time by HPLC with 99.7% assay. Another way for preparation of 5-(2-(4-(1,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)-piperazinyl)ethyl)-6-chloro-1,3-dihydro-2-H-
indol-2-one.
A clean and dry 20-gallon glass lined tank was charged with 19 L of water and
4.44 kg of sodium carbonate, after the carbonate had dissolved 4.29 kg (17.5
moles) of 5-(2-chloroethyl)-6-chloro-oxindole and 3.62 kg (16.5 moles) of 1-
(1,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)piperazine were added. The aqueous slurry was
heated to reflux and the temperature maintained for 14 hours. When the
reaction was complete the solution was cooled to 20°C and filtered. The wet
product was reslurried in 23 L of isopropyl alcohol at room temperature for 2
hours. The product was collected by filtration on 2 large Buchner funnels, each
was washed with 3.4 L of fresh isopropyl alcohol. The product was vacuum
dried at 30° to 40°C. until no isopropyl alcohol remained, giving 5.89 kg
(86.4% yield) of the desired free base which matched a standard sample by
high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
A clean and dry 20-gallon reactor was charged with 17.4 gallons of deionized
water and 4.44 L of concentrated hydrochloric acid, to give a 0.77 M solution.
To the solution was added 4.44 kg of the anhydrous 5-(2-(4-(1,2-
benzisothiazol-yl)-1-piperazinyl)-ethyl)-6-chloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one
free base. The slurry was warmed to 65°C and held for 18 hours. The slurry
was cooled to room temperature. The product was filtered and washed with
2x5-gallon portions of deionized water, and then air dried at 50°C for 30
hours. The dried product contained 4.4% water and the x-ray diffraction
method confirmed that the desired product was obtained.
brand name
Zeldox
Therapeutic Function
H-Indol-2-one, 5-(2-(4-(1,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)-1- piperazinyl)ethyl)-6-chloro-1,3-dihydro-, monohydrochloride monohydrate
General Description
A Certified Spiking Solution?; applicable to use in forensic drug analysis or calibrator preparation by LC/MS or GC/MS. Ziprasidone is sold under the trade names Geodon? and Zeldox for treatment of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Recent studies have suggested that Ziprasidone may increase the risk of Type II diabetes and hyperglycemia.
Properties of Ziprasidone Hydrochloride
| Melting point: | >300 °C |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO > 10 mM |
| form | Powder |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
Safety information for Ziprasidone Hydrochloride
Computed Descriptors for Ziprasidone Hydrochloride
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 122883-93-6 Ziprasidone hydrochloride 99%View Details
122883-93-6 Ziprasidone hydrochloride 99%View Details
122883-93-6 -
 122883-93-6 98%View Details
122883-93-6 98%View Details
122883-93-6 -
 Ziprasidone hydrochloride 99%View Details
Ziprasidone hydrochloride 99%View Details
122883-93-6 -
 Ziprasidone hydrochloride 122883-93-6 98%View Details
Ziprasidone hydrochloride 122883-93-6 98%View Details
122883-93-6 -
 122883-93-6 Ziprasidone hydrochloride 98%View Details
122883-93-6 Ziprasidone hydrochloride 98%View Details
122883-93-6 -
 Ziprasidone hydrochloride 98.00% CAS 122883-93-6View Details
Ziprasidone hydrochloride 98.00% CAS 122883-93-6View Details
122883-93-6 -
 Ziprasidone CAS 122883-93-6View Details
Ziprasidone CAS 122883-93-6View Details
122883-93-6 -
 Ziprasidone Hydrochloride APIView Details
Ziprasidone Hydrochloride APIView Details
138982-67-9
