Ziprasidone
- CAS NO.:146939-27-7
- Empirical Formula: C21H21ClN4OS
- Molecular Weight: 412.94
- MDL number: MFCD00866661
- EINECS: 203-794-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 15:53:33
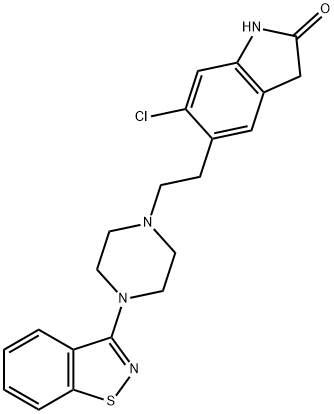
What is Ziprasidone?
Absorption
In the absence of food, ziprasidone's oral bioavailability is 60%, and absorption may reach 100% if ziprasidone is taken with a meal containing at least 500 kcal. The difference in bioavailability has little to do with the fat content of the food and appears to be related to the bulk of the meal since more absorption occurs the longer ziprasidone remains in the stomach.
Toxicity
The most common adverse reactions reported with ziprasidone include somnolence, respiratory tract infections, extrapyramidal symptoms, dizziness, akathisia, abnormal vision, asthenia, vomiting, headache and nausea.
Chemical properties
Tan Solid
Originator
Geodon,Pfizer,USA
The Uses of Ziprasidone
Labelled Ziprasidone, which is used as an antipsychotic. Combined serotonin (5HT2) and dopamine (D2) receptor antagonist.
The Uses of Ziprasidone
Ziprasidone (Geodon, Zeldox) was the fifth atypical antipsychotic to gain FDA approval. In the United States, Ziprasidone is approved for the treatment of schizophrenia, and the intramuscular injection form of ziprasidone is approved for acute agitation i
The Uses of Ziprasidone
Labeled Ziprasidone, intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of Ziprasidone by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry.
Definition
ChEBI: A piperazine compound having 1,2-benzothiazol-3-yl- and 2-(6-chloro-1,3-dihydro-2-oxindol-5-yl)ethyl substituents attached to the nitrogen atoms.
Background
Disorders such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder can significantly impair mood, cognition, and behavior. These mental illnesses can often be accompanied by comorbidities such as depression and substance abuse, and can significantly impact the quality of life of patients and caregivers. Luckily, several treatment options for psychotic disorders have been introduced to market since the realization of chlorpromazine's antipsychotic properties in 1952.
Second generation antipsychotics (commonly referred to as atypical antipsychotics) include clozapine, quetiapine, olanzapine, aripiprazole and ziprasidone among others, and are generally thought to be as efficacious as first generation antipsychotics but differ in their adverse effect profiles. First generation antipsychotics are associated with extrapyramidal adverse effects while atypical antipsychotics are linked to weight gain, impaired glucose tolerance and metabolic syndrome.
Ziprasidone is used to treat schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. It can effectively reduce the rate and time of relapses in schizophrenia, and can be used to treat manic episodes in bipolar disorder although the mechanism of action is unknown. Although ziprasidone is classified as an atypical antipsychotic, it appears to have a lower incidence of metabolic adverse effects compared to other medications in the same class.
Indications
In its oral form, ziprasidone is approved for the treatment of schizophrenia, as monotherapy for acute treatment of manic or mixed episodes related to bipolar I disorder, and as adjunctive therapy to lithium or valproate for maintenance treatment of bipolar I disorder. The injectable formulation is approved only for treatment of acute agitation in schizophrenia.
Manufacturing Process
Preparation of 5-[2-[4-(1,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)-1-piperazinyl]ethyl]-6-chloro-
1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one
A 20-gallon glass lined tank, under a nitrogen atmosphere, was charged with
33.5 liters of water and 9.4 kilograms (kg) of sodium carbonate (dense, 89.1
moles, 3.4 eq.). The resulting mixture was stirred to give a solution. To the
solution 6.4 kg of 2-chloroethyl-6-chloro-oxindole (27.8 moles, 1.06 eq.) was
charged, followed by 6.7 kg of 3-piperazinyl-1,2-benzisothiazole hydrochloride
(26.2 moles, 1.0 eq.). This was stirred and heated to reflux (100°C). After 11
hours the reaction was sampled for high pressure liquid chromatography
(HPLC) assay. The reflux was continued for another 2 hours then the reaction
was cooled to 25°C and the slurry stirred for 1 hour. The product was
observed and found to be essentially free from lumps and gummy matter. The
product was collected by filtration. A 14 liter water was added to the tank and
cooled to 12°C and then used to wash the product. The cake was pulled as
dry as possible, and the product was returned to the tank along with 40 liters
of isopropyl alcohol (IPO). This was cooled and then stirred for 2 hours and
the product was collected by filtration. The cake was washed with 13.4 liters
of fresh IPO, then dried under vacuum at 30° to 40°C. After drying, 17.3 kg
of the title compound was obtained. This was in excess of the theoretical
weight yield due to some residual carbonate in the crude product.
Recrystallization of 5-[2-[4-(1,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)-1-piperazinyl]ethyl]-6-
chloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one
To a clean and dry 100-gallon glass lined tank was charged 9.0 kg of the
material obtained above and 86 gallons of tetrahydrofuran (THF). The slurry
was heated to reflux and held for 1 hour. The hazy solution was then filtered
through a 14" sparkler precoated with filter aid and backed with a Fulflo filter
to a clean, dry, and "spec free" glass-lined tank on a lower level. The batch
was concentrated by vacuum distillation. Another 8.3 kg of the material
obtained in above was dissolved in 83 gallons of THF in the upper tank. This
was filtered to the lower tank. The tank lines and sparkler were rinsed with 10
gallons of THF. The batch was concentrated to about 22 gallons, then cooled
to 5°C and stirred for 1 hour. The product was collected by filtration. Then 20
gallons of fresh IPO were cooled in the tank and used to rinse the product
cake. The product was collected and dried under vacuum at 45°C; yielding
9.05 kg of product (83.8% yield for the coupling and recrystallization. The
product matched the spectra of a standard NMR and showed the correct
retention time by HPLC with 99.7% assay. Another way for preparation of 5-(2-(4-(1,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)-piperazinyl)ethyl)-6-chloro-1,3-dihydro-2-H-
indol-2-one.
A clean and dry 20-gallon glass lined tank was charged with 19 L of water and
4.44 kg of sodium carbonate, after the carbonate had dissolved 4.29 kg (17.5
moles) of 5-(2-chloroethyl)-6-chloro-oxindole and 3.62 kg (16.5 moles) of 1-
(1,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)piperazine were added. The aqueous slurry was
heated to reflux and the temperature maintained for 14 hours. When the
reaction was complete the solution was cooled to 20°C and filtered. The wet
product was reslurried in 23 L of isopropyl alcohol at room temperature for 2
hours. The product was collected by filtration on 2 large Buchner funnels, each
was washed with 3.4 L of fresh isopropyl alcohol. The product was vacuum
dried at 30° to 40°C. until no isopropyl alcohol remained, giving 5.89 kg
(86.4% yield) of the desired free base which matched a standard sample by
high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
A clean and dry 20-gallon reactor was charged with 17.4 gallons of deionized
water and 4.44 L of concentrated hydrochloric acid, to give a 0.77 M solution.
To the solution was added 4.44 kg of the anhydrous 5-(2-(4-(1,2-
benzisothiazol-yl)-1-piperazinyl)-ethyl)-6-chloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one
free base. The slurry was warmed to 65°C and held for 18 hours. The slurry
was cooled to room temperature. The product was filtered and washed with
2x5-gallon portions of deionized water, and then air dried at 50°C for 30
hours. The dried product contained 4.4% water and the x-ray diffraction
method confirmed that the desired product was obtained.
brand name
Geodon (Pfizer).
Therapeutic Function
H-Indol-2-one, 5-(2-(4-(1,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)-1- piperazinyl)ethyl)-6-chloro-1,3-dihydro-, monohydrochloride monohydrate
Biological Functions
"Ziprasidone is chemically similar to risperidone but with a substitution of piperzinyl and benzisothiazole for piperidinyl and benzisoxazole and with minor aromatic modification. Like risperidone, ziprasidone is a high-affinity antagonist at 5-HT2A/C and D2 receptors as well as at adrenergic α1/α2 and histamine H1 receptors. Moreover, ziprasidone can activate 5-HT1A receptors that regulate dopaminergic neurotransmission in brain regions involved in critical cognitive functions. Thus, in addition to D2 partial agonism, 5-HT1A agonism is now thought to be an important pharmacological property for atypical antipsychotic drug efficacy.
General Description
Ziprasidone (Geodon, a benzisothiazolpiprazinylindolonederivative) also has the structuralfeatures of a hybrid molecule between a butyrophenone antipsychoticand a trazodone-like antidepressant. It is highlymetabolized to four major metabolites, only one of which, Smethyldihydroziprasidone,likely contributes to its clinical activity. In humans, less than 5% of the dose isexcreted unchanged. Reduction by aldehyde oxidase accountsfor about 66% of ziprasidone metabolism; two oxidative pathwaysinvolving hepatic CYP3A4 account for the remainder.
General Description
Ziprasidone, 5-[2-[4-(1,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)-1-piperazinyl]ethyl]-6-chloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one, is available as the hydrochloride monohydrate for oral administration (Geodon) and as the mesylate trihydrate saltfor intramuscular (IM) injection. The compound is well absorbedwith peak plasma levels occurring at 6 to 8 hours afteroral administration. The oral absorption is enhanced approximatelytwofold in the presence of food. Ziprasidone isbound about 99% to plasma proteins, primarily to albuminand α1-acid glycoprotein. Ziprasidone is not displaced in thepresence of two highly protein bound drugs, warfarin andpropranolol. Ziprasidone is extensively metabolized withonly about 5 % of the drug excreted unchanged.23 In humans,two major pathways are responsible for the metabolism ofziprasidone: (a) oxidation by CYP3A4 (one third) and (b) reductionby aldehyde oxidase (two thirds).The combinedaction of these metabolic pathways leads to four majorcirculating metabolites: benzisothiazole piperazine sulfoxide(BITP-sulfoxide), benzisothiazole piperazine sulfone (BITPsulfone),ziprasidone sulfoxide, and S-methyldihydroziprasidone.
Mechanism of action
Ziprasidone (half-life, 6 hours) has an oral bioavailability of approximately 60%, which can be enhanced in the presence of fatty foods. It is extensively metabolized (<5% excreted unchanged) by aldehyde oxidase, which results in reductive cleavage of the S–N bond, and then by S-methylation. Ziprasidone also can undergo CYP3A4-catalyzed N-dealkylation and S-oxidation.
Pharmacokinetics
Ziprasidone is classified as a "second generation" or "atypical" antipsychotic and is a dopamine and 5HT2A receptor antagonist with a unique receptor binding profile. As previously mentioned, ziprasidone has a very high 5-HT2A/D2 affinity ratio, binds to multiple serotonin receptors in addition to 5-HT2A, and blocks monoamine transporters which prevents 5HT and NE reuptake. On the other hand, ziprasidone has a low affinity for muscarinic cholinergic M1, histamine H1, and alpha1-adrenergic receptors.
Metabolism
Ziprasidone is heavily metabolized in the liver with less than 5% of the drug excreted unchanged in the urine. The primary reductive pathway is catalyzed by aldehyde oxidase, while 2 other less prominent oxidative pathways are catalyzed by CYP3A4. Ziprasidone is unlikely to interact with other medications metabolized by CYP3A4 since only 1/3 of the antipsychotic is metabolized by the CYP3A4 system.
There are 12 identified ziprasidone metabolites (abbreviations italicized): Ziprasidone sulfoxide, ziprasidone sulfone, (6-chloro-2-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-5-yl)acetic acid (OX-COOH), OX-COOH glucuronide, 3-(piperazine-1-yl)-1,2-benzisothiazole (BITP), BITP sulfoxide, BITP sulfone, BITP sulfone lactam, S-Methyl-dihydro-ziprasidone, S-Methyl-dihydro-ziprasidone-sulfoxide, 6-chloro-5-(2-piperazin-1-yl-ethyl)-1,3-dihydro-indol-2-one (OX-P), and dihydro-ziprasidone-sulfone.
As suggested by the quantity of metabolites, ziprasidone is metabolized through several different pathways. Ziprasidone is sequentially oxidized to ziprasidone sulfoxide and ziprasidone sulfone, and oxidative N-dealkylation of ziprasidone produces OX-COOH and BITP. OX-COOH undergoes phase II metabolism to yield a glucuronidated metabolite while BITP is sequentially oxidized into BITP sulfoxide, BITP sulfone, then BITP sulfone lactam. Ziprasidone can also undergo reductive cleavage and methylation to produce S-Methyl-dihydro-ziprasidone and then further oxidation to produce S-Methyl-dihydro-ziprasidone-sulfoxide. Finally dearylation of ziprasidone produces OX-P, and the process of hydration and oxidation transforms the parent drug into dihydro-ziprasidone-sulfone.
Although CYP3A4 and aldehyde oxidase are the primary enzymes involved in ziprasidone metabolism, the pathways associated with each enzyme have not been specified.
Properties of Ziprasidone
| Melting point: | 213-215°C |
| Boiling point: | 554.8±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.369±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 13.34±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | Brown to Dark Brown |
| Merck | 14,10171 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 146939-27-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Ziprasidone
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H317:Sensitisation, Skin H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P272:Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P333+P313:IF SKIN irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Ziprasidone
Ziprasidone manufacturer
Svak Life Sciences
VIVAN Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Ramdev Chemicals Pvt Ltd
Ralington Pharma
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 146939-27-7 Ziprasidone 98%View Details
146939-27-7 Ziprasidone 98%View Details
146939-27-7 -
 Ziprasidone 98%View Details
Ziprasidone 98%View Details -
 Ziprasidone 99%View Details
Ziprasidone 99%View Details
146939-27-7 -
 Ziprasidone 146939-27-7 98%View Details
Ziprasidone 146939-27-7 98%View Details
146939-27-7 -
 146939-27-7 Ziprasidone 98%View Details
146939-27-7 Ziprasidone 98%View Details
146939-27-7 -
 Ziprasidone 95% CAS 146939-27-7View Details
Ziprasidone 95% CAS 146939-27-7View Details
146939-27-7 -
 Ziprasidone hydrochloride hydrate CAS 146939-27-7View Details
Ziprasidone hydrochloride hydrate CAS 146939-27-7View Details
146939-27-7 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1