Xipamide
Synonym(s):5-(Aminosulfonyl)-4-chloro-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-hydroxy-benzamide;BE 1293;BEI 1293;MJF 10938
- CAS NO.:14293-44-8
- Empirical Formula: C15H15ClN2O4S
- Molecular Weight: 354.81
- MDL number: MFCD00865927
- EINECS: 238-216-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
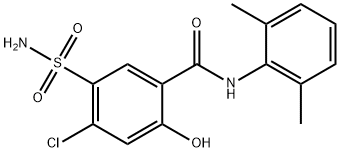
What is Xipamide?
Chemical properties
Off-White Solid
Originator
Aquaphor,Beiersdorf,W. Germany ,1971
The Uses of Xipamide
Xipamide is a diuretic and antihypertensive agent.
Definition
ChEBI: Xipamide is a member of benzamides.
Manufacturing Process
The 4-chloro-5-sulfamyl salicylic acid used as starting point was prepared in
the following way:
(a) 4-Chloro-5-Chlorosulfonyl Salicylic Acid: 100 grams 4-chloro salicylic acid
was added portionwise with stirring at about -5°C to 275 ml chlorosulfonic
acid. The temperature was not allowed to rise above +3°C. At the end of the
addition, the solution formed was stirred for 1 hour in an ice bath, then for 1 hour at 20°C and finally for 2 1/2 hours at 80°C oil bath temperature. Then
the dark brown solution, after ensuing slow cooling with vigorous stirring, was
poured onto ice; the precipitate was vacuum filtered, washed with water and
dried. After recrystallization from toluene the compound formed had a melting
point of 181° to 183°C.
(b) 4-Chloro-5-Sulfamyl Salicylic Acid: 40 grams 4-chloro-5-chlorosulfonyl
salicylic acid obtained from (a) was added portionwise with stirring to 250 ml
liquid ammonia. This was allowed to stand for 2 hours, then the precipitate
was vacuum filtered and dissolved in 500 ml water. The solution was filtered
and the filtrate was treated with 2 N hydrochloric acid until no more
precipitation occurred. The 4-chloro-5-sulfamyl salicylic acid obtained as the
precipitate was filtered off and finally recrystallized from water, MP 258° to
260°C.
5.0 grams 4-chloro-5-sulfamyl salicylic acid was suspended in 100 ml water-
free chlorobenzene and then 2.44 grams of 2,6-dimethylaniline and 0.9 ml
phosphorus trichloride were added to the suspension in turn. The reaction
mixture was heated under reflux for 5 hours. After cooling, the chlorobenzene
was separated from the precipitate by decantation. The latter was finally
collected on a filter and washed, first with chlorobenzene and, after drying,
with 2 N hydrochloric acid and water. The compound obtained by
recrystallization from methanol had a melting point of 256°C.
Therapeutic Function
Diuretic, Antihypertensive
Clinical Use
Thiazide diuretic:
Hypertension
Oedema
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Analgesics: increased risk of nephrotoxicity with
NSAIDs; antagonism of diuretic effect.
Anti-arrhythmics: hypokalaemia leads to increased
cardiac toxicity; effects of lidocaine and mexiletine
antagonised.
Antibacterials: avoid administration with
lymecycline.
Antidepressants: increased risk of hypokalaemia
with reboxetine; enhanced hypotensive effect with
MAOIs; increased risk of postural hypotension with
tricyclics.
Antiepileptics: increased risk of hyponatraemia with
carbamazepine.
Antifungals: increased risk of hypokalaemia with
amphotericin.
Antihypertensives: enhanced hypotensive effect;
increased risk of first dose hypotension with postsynaptic alpha-blockers like prazosin; hypokalaemia
increases risk of ventricular arrhythmias with sotalol.
Antipsychotics: hypokalaemia increases risk
of ventricular arrhythmias with amisulpride;
enhanced hypotensive effect with phenothiazines;
hypokalaemia increases risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with pimozide - avoid concomitant use.
Atomoxetine: hypokalaemia increases risk of
ventricular arrhythmias.
Cardiac glycosides: increased toxicity if hypokalaemia
occurs.
Ciclosporin: increased risk of nephrotoxicity and
possibly hypomagnesaemia.
Cytotoxics: increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
due to hypokalaemia with arsenic trioxide; increased
risk of nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity with platinum
compounds.
Lithium excretion reduced (increased toxicity).
Metabolism
Xipamide is excreted in the urine, partly unchanged
and partly in the form of the glucuronide metabolite.
In patients with renal impairment excretion in the bile
becomes more prominent.
Properties of Xipamide
| Melting point: | 255-256 °C |
| Density | 1.2743 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6100 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO: soluble20mg/mL, clear |
| form | powder |
| pka | pKa 4.75±0.04(0.4% MeOH
in H2O) (Uncertain) |
| color | white to beige |
| Water Solubility | 58mg/L(25 ºC) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 14293-44-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Xipamide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Xipamide
Xipamide manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 14293-44-8 Xipamide 98%View Details
14293-44-8 Xipamide 98%View Details
14293-44-8 -
 14293-44-8 98%View Details
14293-44-8 98%View Details
14293-44-8 -
 Xipamide CAS 14293-44-8View Details
Xipamide CAS 14293-44-8View Details
14293-44-8 -
 Xipamide 95% CAS 14293-44-8View Details
Xipamide 95% CAS 14293-44-8View Details
14293-44-8 -
 Xipamide CAS 14293-44-8View Details
Xipamide CAS 14293-44-8View Details
14293-44-8 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1