Xanthophyll
Synonym(s):Lutein;Xanthophyll solution;α-Carotene-3,3′-diol;β, ε-carotene;β, ε-carotene-3,3′-diol
- CAS NO.:127-40-2
- Empirical Formula: C40H56O2
- Molecular Weight: 568.87
- MDL number: MFCD08435941
- EINECS: 204-840-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:50:41
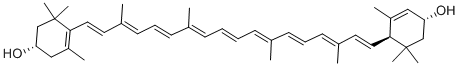
What is Xanthophyll?
Description
Lutein is a dietary carotenoid that has been found in eggs and yellow-colored fruits and vegetables and has diverse biological activities. It reduces hyperglycemia-induced mitochondrial DNA damage and production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and promotes mitochondrial biogenesis in ARPE-19 cells when used at a concentration of 10 μM. Lutein (20 mg/kg) increases nitric oxide (NO) production and decreases serum levels of endothelin-1 in a rat model of hyperhomocysteinemia. Dietary administration of lutein (0.2%) decreases monocyte migration and lesion size in an ApoE-/- and Ldlr-/- mouse models of atherosclerosis. Lutein reduces infarct size and cardiac malondialdehyde (MDA), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and troponin T levels, and increases cardiac levels of catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), and Nrf2 in a rat model of heart failure induced by isoproterenol . It forms a retinal pigment in human eyes, and high dietary intake of lutein is positively correlated with reduced risk of age-related macular degeneration and cataracts in humans.
Characteristics
While it is one of the most widespread naturally occurring carotenoid alcohols, it does not possess any vitamin A activity. Xanthophyll is a yellow pigment, which can be isolated from certain natural products, and produced synthetically.
Xanthophyll is the major substance causing yolks to have a deeper yellow color. It has no nutritive value. Years ago when chickens ran freely on the farm they ate grass which contains xanthophyll. Modern production units put enough xanthophyll in the ration of chickens to produce a medium-yellow yolk.
Feeds that contain large amounts of xanthophylls produce a deep yellow color in the beak, skin, and shank of yellowskinned breeds of chickens. The consumer associates this pigmentation with quality and, in many cases, is willing to pay a premium price for a bird of this type. Also, processors of egg yolks are frequently interested in producing dark-colored yolks to maximize coloration of egg noodles and other food products. The latter can be accomplished by adding about 60 mg of xanthophyll per kilogram of diet. In recognition of these consumer preferences, many producers add ingredients that contain xanthophylls to poultry rations.
The Uses of Xanthophyll
Xanthophyll is one of the most widespread carotenoid alcohols in nature. Originally isolated from egg yolk, also isolated by chromatography from nettles, algae, and petals of many yellow flowers.
The Uses of Xanthophyll
Xanthophyll has been used:
- to quantify circulating lutein in birds
- to study its effect on the synthesis of factor D (FD) by adipocytes
- for the quantification of carotenoids from the leaves of Brassica oleracea
Background
Lutein is an xanthophyll and one of 600 known naturally occurring carotenoids. Lutein is synthesized only by plants and like other xanthophylls is found in high quantities in green leafy vegetables such as spinach, kale and yellow carrots. In green plants, xanthophylls act to modulate light energy and serve as non-photochemical quenching agents to deal with triplet chlorophyll (an excited form of chlorophyll), which is overproduced at very high light levels, during photosynthesis.
Indications
Xanthophylls are taken for nutritional supplementation, and also for treating dietary shortage or imbalance.
What are the applications of Application
Xanthophyll is one of the most widespread carotenoid alcohols
Definition
ChEBI: Lutein is a carotenol. It has a role as a food colouring and a plant metabolite. It derives from a hydride of a (6'R)-beta,epsilon-carotene.
Biotechnological Production
Petals of marigold flowers (Tagetes erecta and Tagetes patula) currently represent the main source of commercial Xanthophyll. More than 95 % of the Xanthophyll is esterified, and about half of this fraction is esterified with fatty acid. Therefore, saponification is a part of the downstream processing. Xanthophyll is supplemented to food and feed for aquaculture and poultry farming. Furthermore, Xanthophyll is suggested to be beneficial for health, for example, to prevent age-related macular degeneration [97] and progression of early atherosclerosis. In algae, Xanthophyll is accumulated in the nonesterified form. The alga Muriellopsis sp. is able to accumulate Xanthophyll up to high levels and is easy to cultivate photoautotrophically. The effects of critical growth and production parameters in outdoor continuous cultures have been investigated. Under optimized conditions, 40 g dry cell mass/m2 and 180 mg/m2 Xanthophyll were produced per day, respectively. Further optimization was performed by introduction of agitation with a paddlewheel in a semicontinuous cultivation system and by CO2 addition. Thus, the Xanthophyll content was increased to 0.4–0.6 % of the dry mass at a productivity level comparable to that in a closed tubular photobioreactor. Beneficial for Xanthophyll synthesis were high temperatures, high irradiance, an optimum pH value for biomass formation, and the addition of inducers such as H2O2 or NaClO in the presence of Fe2+ (for the generation of stress-inducing chemical species), especially under heterotrophic growth conditions where spontaneous oxidative stress is absent.
General Description
Lutein is a yellow dihydroxylated carotenoid which is found to be a common constituent in many dietary supplements.
Agricultural Uses
Xanthophyll is the yellow pigment in leaves containing oxygen and is derived from carotens, which is sometimes absorbed by insects. It is present, for instance, in the skin of caterpillar of cabbage and of white butterfly and in the cocoons of silkworms.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Dietary carotenoid with no vitamin A potency. Increases macular pigment concentration in the eye and may improve visual function.
Pharmacokinetics
Lutein was found to be present in a concentrated area of the macula, a small area of the retina responsible for central vision. The hypothesis for the natural concentration is that lutein helps protect from oxidative stress and high-energy light. Several studies show that an increase in macula pigmentation decreases the risk for eye diseases such as Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD).
Metabolism
Not Available
Properties of Xanthophyll
| Melting point: | 195 °C |
| Boiling point: | 572.66°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | 18Cd +165° (c = 0.7 in benzene) |
| Density | 0.9944 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | n20/D1.361-1.363 |
| Flash point: | 269.1±27.5 °C |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Dichloromethane (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly, Heated, S |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 14.61±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | Red to Very Dark Red |
| λmax | λ: 441-451 nm Amax |
| Merck | 13,10120 |
| BRN | 2068547 |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive, Temperature Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 127-40-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | .beta.,.epsilon.-Carotene-3,3'-diol, (3R,3'R,6'R)- (127-40-2) |
Safety information for Xanthophyll
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. P403+P235:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep cool. |
Computed Descriptors for Xanthophyll
| InChIKey | KBPHJBAIARWVSC-RGZFRNHPSA-N |
Xanthophyll manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 127-40-2 Xanthophyll 98%View Details
127-40-2 Xanthophyll 98%View Details
127-40-2 -
 127-40-2 98%View Details
127-40-2 98%View Details
127-40-2 -
 Xanthophyll 127-40-2 98%View Details
Xanthophyll 127-40-2 98%View Details
127-40-2 -
 127-40-2 Xanthophyll 98%View Details
127-40-2 Xanthophyll 98%View Details
127-40-2 -
 127-40-2 99%View Details
127-40-2 99%View Details
127-40-2 -
 Marigold Extract (Lutein) 99%View Details
Marigold Extract (Lutein) 99%View Details -
 Xanthophyll CAS 127-40-2View Details
Xanthophyll CAS 127-40-2View Details
127-40-2 -
 Lutein CAS 127-40-2View Details
Lutein CAS 127-40-2View Details
127-40-2
