Xanthinol
- CAS NO.:2530-97-4
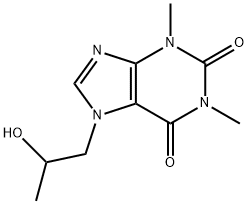
- Empirical Formula: C13H21N5O4
- Molecular Weight: 311.34
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-28 08:28:43
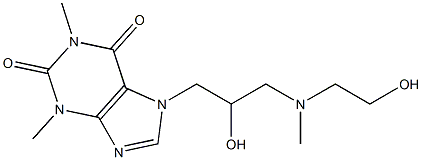
What is Xanthinol?
Absorption
Xanthinol is readily absorbed in the body with an absorption half life of 0.4 h. After absorption, xanthinol nicotinate rapidly degardes into the negatively charged nicotinic acid and the positively charged xanthinol ion.
Toxicity
It is thought to cause flushing, hypotension and abdominal pain.
Indications
Xanthinol is primarily used in diet supplements to increase the brain metabolism of glucose and obtain ATP. Xanthinol is also used as an agent to reduced cholesterol as it is a vasodilator. Its action allows having an elevated rate of blood flow in the brain which helps improve memory function, concentration and awareness. Thus, due to his actions, xanthinol is indicated to improve cerebrovascular and peripheral vascular disorders as well as hyperlipidaemias.
Background
Xanthinol is a very potent water-soluble derivative of niacin that can be found in diet supplements. It is also known as xanthinol nicotinate. Xaninthol is known to be a potent vasodilator that can easily pass through the cell membrane and once inside the cell it causes an increase in glucose metabolism resulting in an increased energy. It was approved as a drug in 1998 in Canada and nowadays its status is cancelled post marketing.
Definition
ChEBI: 7-[2-hydroxy-3-[2-hydroxyethyl(methyl)amino]propyl]-1,3-dimethylpurine-2,6-dione is an oxopurine.
Pharmacokinetics
Reports indicate that xanthinol increases blood flow in the vascular beds. The use of xanthinol in clinical trials have reported improvements in the performance of healthy elderly individuals in short- and long-term memory tests. The later effect is explained by the enhancing on the cell metabolism and oxygen supply in the brain by the rise of ATP in erythrocytes which allows penetration into capillaries easier and a higher oxygen pressure in the capillary blood which improves oxygenation of surrounding tissue.
Metabolism
As part of the metabolism of xanthinol, there is a formation of two metabolites that correspond to stereoisomeric forms of 2-coffeinyl-N-methyl-6-hydroxy-morpholines. These metabolites can be described structurally as semiacetals of a terminal aldehyde formed from xanthinol.
Safety information for Xanthinol
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1